Table of Contents

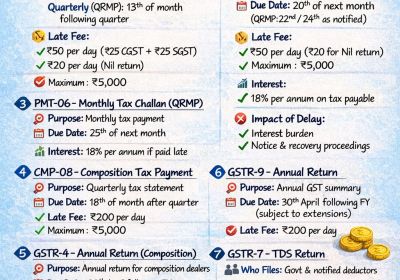
Summary of the key Recommendations in 54th GST Council Meeting
The 54th GST Council met under the Chairpersonship of Union Minister for Finance &Corporate Affairs Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman in New Delhi. The 54th GST Council Meeting made key recommendations regarding cover a wide range of items and services, including the introduction of Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM), changes to GST rates on certain products, and clarifications on various tax treatments. These recommendations aim to provide clarity, improve compliance, and streamline GST processes for taxpayers across various sectors. The formal implementation will occur through relevant notifications, circulars, and amendments. Here’s a summary of the key decisions:
Goods:
- Metal Scra-Supply of Metal Scrap Covered under RCM & TDS :
- Reverse Charge Mechanism will also apply to the supply of metal scrap from an unregistered person to a registered person. RCM will apply to metal scrap supplied by an unregistered person to a registered person. The registered recipient will be responsible for paying the tax, even if the supplier is under the threshold limit. The RCM, Objective at addressing revenue leakages and ensuring better tax compliance.
- Additionally, a TDS of 2% will be applicable on B2B supplies of metal scrap by a registered person. This measure is aimed at strengthening tax collection on transactions involving metal scrap, a sector prone to tax evasion. TDS of 2% will be applicable on B2B supplies of metal scrap by registered persons.
- Roof Mounted Package Unit (RMPU) Air Conditioning Machines for Railways:
- These machines will be classified under HSN 8415, attracting 28% GST.
- Car and Motorcycle Seats:
- Car seats are reclassified under HSN 9401, increasing the GST rate from 18% to 28% to align with motorcycle seats.
Services:
- Life and Health Insurance:
- A Group of Ministers (GoM) will be formed to holistically review GST on life and health insurance. The report is expected by October 2024.
- Transport of Passengers by Helicopters:
- GST at 5% will apply to the transport of passengers on a seat-share basis. 18% GST will continue for helicopter charters.
- Flying Training Courses:
- Approved courses by DGCA-approved Flying Training Organizations (FTOs) are exempt from GST.
- Research and Development Services:
- Exemption on the supply of research and development services by government entities, universities, or institutions using government or private grants. Past demands to be regularized on an “as is where is” basis.
- Preferential Location Charges (PLC):
- PLC for real estate services will be considered part of the composite supply of construction services, attracting the same GST as the main supply.
- Affiliation Services:
- Affiliation services provided by State/Central educational boards will be exempt prospectively. However, GST of 18% applies to universities providing affiliation services to their constituent colleges.
- Import of Services by Branch Offices:
- Import of services by foreign airline branch offices from related establishments abroad, without consideration, will be exempt from GST. The GST Council has recommended an exemption on the import of services by a branch office of a foreign airline company from a related person or its establishment located outside India when the services are provided without consideration.
- This decision is particularly relevant for foreign airline companies operating in India through branch offices. It addresses situations where the Indian branch receives services from its head office or another related foreign entity, but no payment or consideration is exchanged for these services.
- Exemption on Import of Services: The services provided to the Indian branch office by a related entity abroad will not be subject to GST, provided they are offered without any monetary consideration.
- Regularisation of Past Period: The Council has also proposed to regularise past transactions under this provision on an "as is where is" basis. This means that any such service transactions from the past will be retrospectively aligned with the new exemption, ensuring that businesses are not penalized for earlier imports of services without consideration.
- Renting of Commercial Property Covered under RCM:
- RCM will apply when an unregistered person rents commercial property to a registered person, preventing revenue leakage.
- When an unregistered person rents out commercial property to a registered person, the transaction will now fall under Reverse Charge Mechanism.
- This ensures that the tax liability shifts to the registered recipient of the service, reducing the risk of revenue leakage, as the unregistered supplier is not directly liable to pay GST.
-
ITC shall be available on Demo vehicles if bought from Vehicle Manufacturer.
-
Place of supply has been clarified for -
a.RCM on Advertisement by Indian Co. to Foreign Company
b.Data hosting services
c.Cloud Computing Services -
Ancillary/Intermediate Services by GTA:
- The GST Council has issued a clarification on the taxation of ancillary services provided by Goods Transport Agencies (GTA).
- Services like loading/unloading provided in the course of transportation by road will form part of composite supply if accompanied by a consignment note. If invoiced separately, they will not be treated as composite supply.
- Composite Supply of Ancillary Services: Ancillary or intermediate services provided by a GTA, such as loading, unloading, packing, unpacking, transshipment, or temporary warehousing, will be treated as part of a composite supply of goods transportation, when issued under a single consignment note.
- This means that these services are bundled with the main service of transporting goods and will be taxed together under the GST rate applicable to the main transportation service.
- Separate Invoicing: If these ancillary services are invoiced independently (i.e., issued separately from the transportation of goods), they will not be considered as part of a composite supply. In such cases, each ancillary service will attract GST separately at the applicable rate.
-
Changes/Clarifications in GST Tax Rates under 54th GST Council Meeting:
- Namkeens and Extruded/Expanded Savory Food Products:
- The GST rate for extruded or expanded savory or salted products (other than un-fried or un-cooked snack pellets) under HS Code 1905 90 30 has been reduced from 18% to 12%.
- This brings it in line with namkeens, bhujia, mixture, chabena, and similar edible preparations (pre-packaged and labeled) under HS Code 2106 90, which are already taxed at 12%.
- The 5% GST rate will continue to apply to un-fried or un-cooked snack pellets, manufactured through the process of extrusion.
- Clarification: The reduced GST rate of 12% on extruded or expanded products (other than un-fried or un-cooked snack pellets) under HS 1905 90 30 will be applicable prospectively.
- Cancer Drugs:
- The GST rate on specific cancer drugs, including Trastuzumab Deruxtecan, Osimertinib, and Durvalumab, has been reduced from 12% to 5%.
- This reduction is aimed at making critical cancer treatments more affordable.
Facilitation of Trade in 54th GST Council Meeting :
- Waiver of Interest or Penalty:
- GST Council Approves Amnesty Scheme for Tax Demands u/s 73 for 2017-18, 2018-19 and 2019-20
- A new procedure for waiving interest or penalties for tax demands under Section 73 of CGST Act for FYs 2017-18, 2018-19, and 2019-20 will be introduced.
- Mechanism for Implementing Section 16 Amendments:
- Special procedures for rectification of orders related to wrong input tax credit claims will be notified, simplifying compliance for affected taxpayers.
- Clarifications on IGST Refunds:
- Clarifications on IGST refunds where inputs were imported without IGST under specific exemptions but later paid with interest, simplifying refund processes.
Other Measures in 54th GST Council Meeting :
The recent 54th GST Council Meeting recommendations by the GST Council include significant improvements to the existing GST return architecture, particularly in terms of ledger management and invoice processing.
B2C E-Invoicing:
- A pilot for B2C e-invoicing will be rolled out in selected sectors and states, improving business efficiency and enabling customers to verify invoices reported in GST returns.
- The GST Council has proposed the introduction of a pilot for B2C e-Invoicing, following the successful implementation of e-invoicing in the B2B sector. This move is designed to extend the benefits of digital invoicing to the retail sector and bring about the following key advantages:
- Improved Business Efficiency: B2C e-invoicing is expected to streamline retail operations by automating and digitizing the invoicing process, reducing manual errors, and enhancing overall efficiency.
- Cost-Efficiency: Businesses will benefit from reduced operational costs through decreased paper usage, manual data entry, and storage expenses, making the process more environmentally sustainable.
- Customer Transparency: Retail customers will have the option to verify their invoices directly in the GST system, ensuring the accurate reporting of transactions and improving overall transparency.
- Voluntary Pilot Rollout: The pilot will be implemented on a voluntary basis in selected sectors and states. This phased approach will allow for adjustments based on feedback before considering broader implementation.
Invoice Management System:
- Enhancements will include a Reverse Charge Mechanism ledger and Input Tax Credit Reclaim ledger, allowing taxpayers to manage invoices and Input tax credit claims better.
- The IMS will enable taxpayers to manage invoices effectively by providing options to accept, reject, or keep invoices pending. This will help in determining the availment of Input tax credit.
- The IMS is an optional tool designed to reduce errors in Input tax credit claims and improve reconciliation. The system is expected to reduce notices issued for Input tax credit mismatches in returns.
New Ledgers:
- Reverse Charge Mechanism Ledger: A new ledger will be introduced to track transactions under the Reverse Charge Mechanism. This is aimed at better management and clarity over reverse charge liabilities.
- Input Tax Credit Reclaim Ledger: This ledger will facilitate the tracking of reclaimed ITC, allowing taxpayers to manage reclaimed credits more efficiently.
Opening Balance Declaration:
Taxpayers will be required to declare their opening balances for these new ledgers by 31st October 2024.
Latest GST Update: Clarifications on Waiver of Interest & Penalty
What’s This Circular About?
GST Circular 248 Explained in Simple Terms : The CBIC issued this circular to clarify doubts related to the waiver of interest and penalty under Section 128A of the CGST Act, 2017. This is a golden opportunity for businesses with old GST demands (non-fraud) to settle dues without extra cost of interest and penalties. (Circular No. 248/05/2025-GST, Dated 27th March 2025)
Background: Section 128A of CGST Act : Section 128A was inserted recently to give relief to taxpayers by waiving interest and penalty in certain cases. Here’s the core benefit Waiver of Interest & Penalty on demands under Section 73 (non-fraud GST demands)
For period: 1st July 2017 to 31st March 2020 Condition: Full tax amount must be paid on or before 31st March 2025 Key Clarifications from Circular 248
Who Can Get the Waiver?
Taxpayers who have GST demands raised under Section 73 (non-fraud cases) for the specified period.
Even if the taxpayer has already paid the tax, they can get a waiver of interest and penalty.
What If You Paid Interest or Penalty Already?
No refund will be given for any interest or penalty already paid.
What If Only Tax Is Paid?
If tax is paid but interest and penalty are pending, and tax was paid on or before 31st March 2025, then interest and penalty will be waived.
Applicable to Which Notices?
Only Section 73 cases (non-fraud, no suppression of facts).
Section 74 cases (fraud or suppression) are not covered.
Is Any Application Required?
No separate application is needed. If conditions are met, the proper officer will automatically drop interest and penalty.
Deadline to Avail This Benefit: 31st March 2025 - GST Taxpayer must pay full tax dues under Section 73 for the period 1st July 2017 – 31st March 2020 before this date.