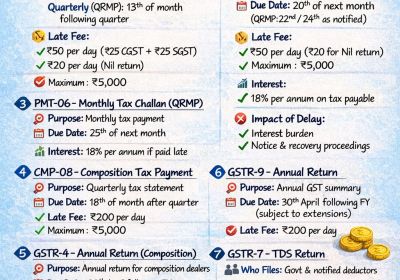
Table of Contents

A person cannot be imposed penalty under GST without giving him the opportunity of being heard
What is issue:
- Whether or not the Petitioner is GST liable to pay GST tax along with penalty equal to 100% of tax? An e-way bill was created with a validity date of September 28, 2020. By the time the goods arrived at their final destination on September 29, 2020, the e-way bill already had expired.
-
According to Section 129(3) of the CGST Act, 2017, the Assessing Authority issued the SCN to the Petitioner with the justification "goods not covered by legal papers." The petitioner paid the requested sum for tax and penalty because he wanted the products to arrive at their destination as soon as possible and did not take advantage of the chance to be heard. The Respondent then issued an Order dated December 31, 2021 in which tax and a penalty equivalent to 100% of the tax due were levied. The petitioner filed the writ petition after feeling wronged by the contested order.
Delhi High Court Order Held:
- The Hon’ble Delhi High Court in dated April 23, 2022 - W.P. No (C) 8585 of 2022 held as under:
- According to a Honorable Delhi High Court Order, it is undisputed that the tax has been paid on the subject goods and the challenged demand has only been made since, at the time of interception,
- In the unlikely event that any E-way bills were invalid, the petitioner did not seek to dodge taxes in this case. However, the challenged GST Demand also demands payment of a penalty in addition to the GST tax.
- Furthermore, that the petitioner paid the requested tax and penalty amount because he wanted the goods to show up at the intended destination as soon as possible, but that he did not take advantage of the opportunity to demonstrate that the goods could not be supplied before the e-way bill's validity period ran out.
- In order to give the Petitioner the appropriate opportunity to provide relevant data or evidence to support its case that the delay in transporting the goods to their destination was due to legitimate reasons, the Honorable Delhi High Court Order Held set aside the impugned order and remanded the matter to the AO to take a fresh decision in the matter.
- Furthermore, it was said that the designated person should keep in mind Section 126 of the Central Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017, which, among other things, refers to an omission or mistake in documentation that is easily rectifiable.
Relevant Provisions:
Section 126 – General disciplines related to penalty
- Section 126(2) of under CGST Act: GST Penalty imposed under CGST Act shall depend on the facts & circumstances of each case and shall be commensurate with the degree & severity of breach.
- Section 126(3) of under CGST Act: No penalty shall be imposed on any person without giving him an opportunity of being heard under the GST law.
Section 129(3) of the CGST Act: Seizure Detention & release of goods & Conveyances in transit
(3) The proper officer detaining or seizing goods or conveyance shall issue a notice within seven days of such detention or seizure, specifying the penalty payable, and thereafter, pass an order within a period of seven days from the date of service of such notice, for payment of penalty under clause (a) or clause (b) of sub-section (1).”
Minor negligence or Just expiration of e- way bill will not amount to tax evasion
- Madhya Pradesh High Court in the matter of Daya Shanker Singh v. State of Madhya Pradesh directed AO to refund back the penalty imposed from the assessee because of the mere expiration of E-way bill just by few hours as it did not amount to tax evasion, gross negligence or fraudulent intent.
- In other decision of The Hon’ble Madras High Court in the Commissioner of CGST & Central Excise Vs India Yamaha Motor Private Limited has held that in a case where GST Liability has not been remitted, interest U/s 50 of the CGST Act is leviable even if the GST Taxpayer has adequate credit balance in his credit ledger or cash ledger,