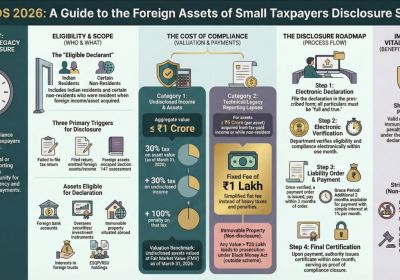
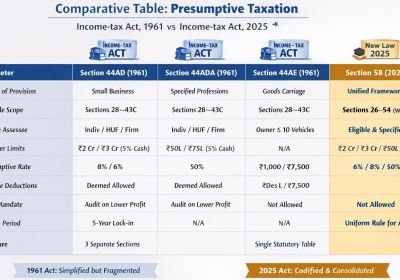
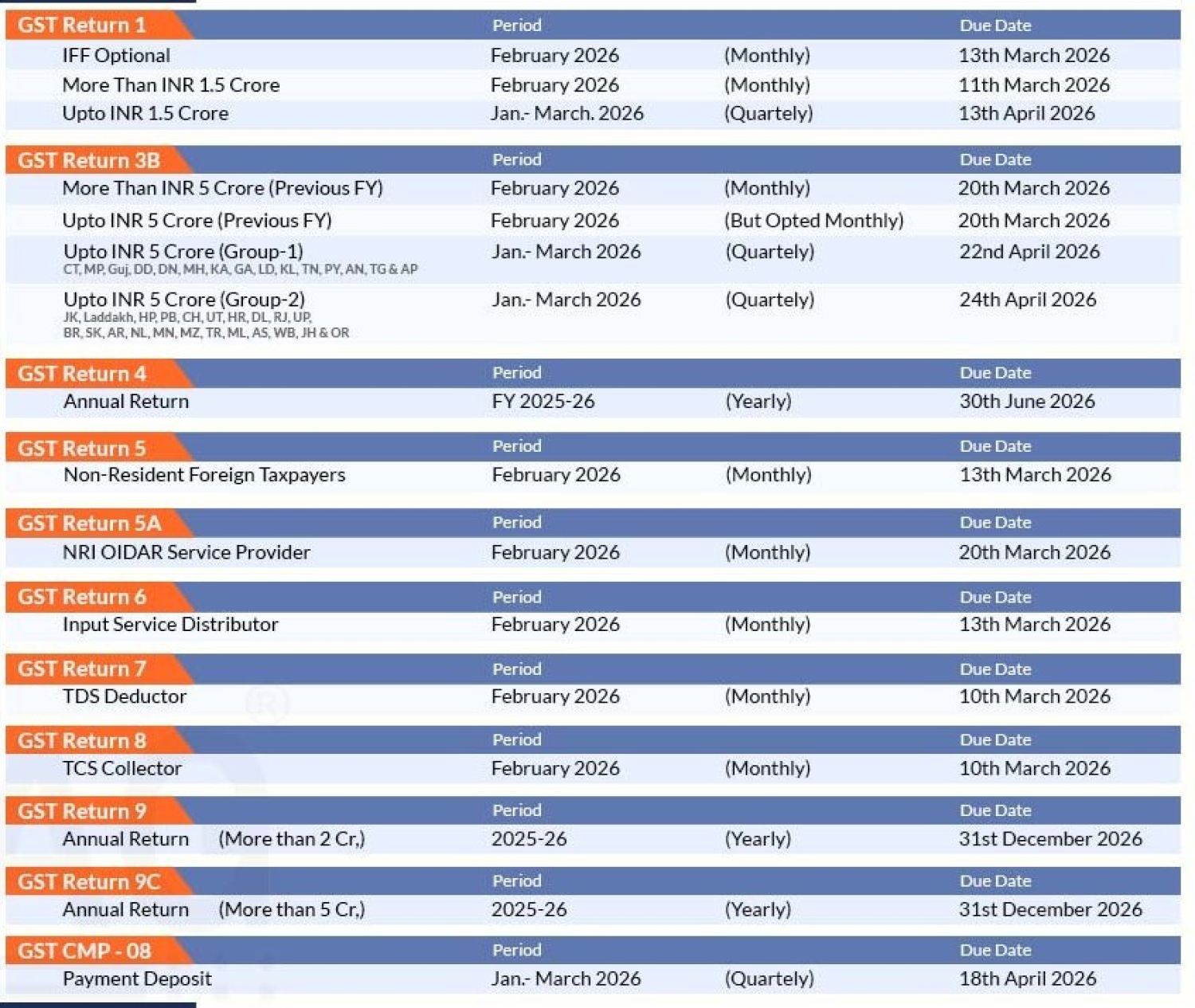
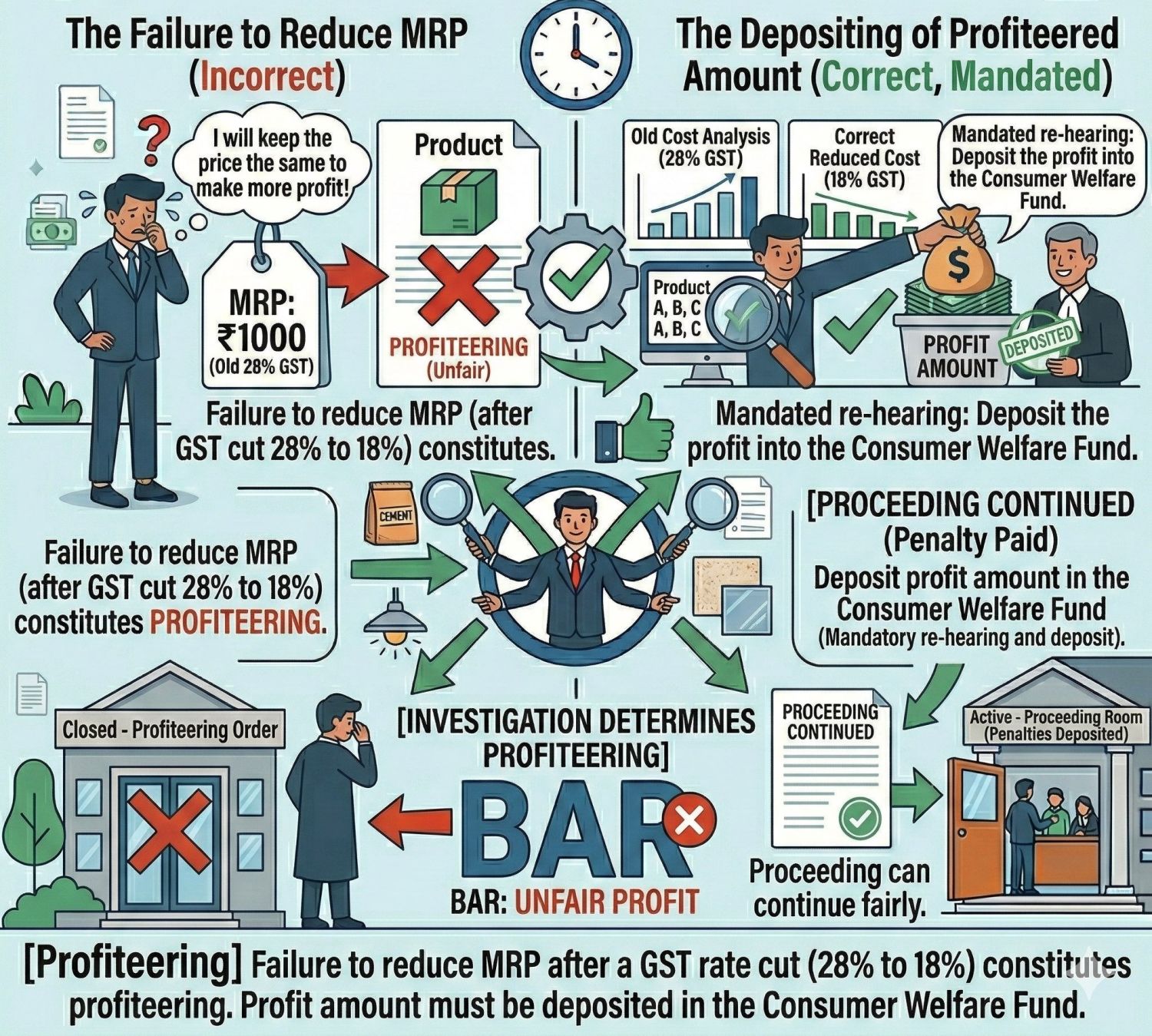
Table of Contents

Frequently Asked Questions related to Tax Audit

Q1.: What is the purpose of section 44AB?
Ans. According to this provision, taxpayers must perform an audit of their company or profession in order to provide an audit report for taxes purposes.
Q2.: Who is in charge of conducting a tax audit?
An audit of a tax return is conducted by a professional chartered accountant or the appropriate authorities.
Q3.: What is the punishment for failing to comply with section 44AB?
Ans. You shall be fined 0.5 percent of total sales, turnover, or gross revenues, or Rs. 1.5 lakh, whichever is less, if you do not comply with section 44AB.
Q4.: Who is exempt from undergoing a tax audit?
The following individuals are exempt from having a tax audit performed:
- Any Assessee who earns money under section 44B.
- An Assessee who earns money under section 44BBA.
- Any Assessee who has their books of accounts audited under other laws is not required to have a tax audit conducted under section 44AB. A tax report, in particular, must be produced in Form 3CA, Form 3CB, or Form 3CD.
Q5.: In a tax audit, what are sales turnover and gross receipt?
Sales Turnover– The term "sales turnover" refers to the total amount of money influenced by a company's sales.
gross revenue- It is not defined in the Income Tax Act. All earnings from the practise of a profession are included in gross receipts.
Basic Tally Manuals For Chartered Accountants Office
- Reference Manual Book Revised Schedule VI of Company Act
- tally manual for tax audit report
- Reference Manual Book statutory Audit under Company Act
Q6.: How do you calculate a stock broker's sales turnover?
When a stock broker purchases stocks on behalf of consumers, the securities are not transferred into his name but are given in the name of the customer. This is also true in the case of sales. On behalf of his customer, the stockbroker holds delivery. Securities do not transfer their ownership to stockbrokers. To assess the value of the turnover, only brokerage must be taken into consideration.
Q7.: In the situation of numerous firms, how do you calculate the sales turnover?
If an assessee owns more than one business, the sale turnover or gross revenues from all of them will be combined, but if the assessee chooses the presumptive tax scheme, the turnover of that firm will be removed from the overall sales turnover or gross receipts calculation.
Q8.: How many tax audit reports can a Chartered Accountant sign?
During an assessment year, a practising CA can perform up to 60 tax audits. The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India clarified that audits performed under a statute that requires an assessee to submit an audit report will not be counted toward the required number of tax audit assignments if the auditee's turnover is less than the limit set out in section 44AB of the IT Act.
Q9.: Is it possible to make changes/revised to a tax audit report?
Normally, the audit report under section 44AB should not be amended, but on rare occasions, a member may do so for the following reasons:
- Change in law;
- Change in interpretation;
- As a result of the aforementioned reasons, the audit report might be changed after it has been filed.
Q10.: Is there a penalty for submitting an on late filing of Audit report ?
If a person fails to have his or her accounts audited or fails to provide the audit report, the assessing officer may order him or her to pay a penalty equivalent to the lesser of 0.5 percent of the total sale, turnover, or gross revenues or 1,50,000 rupees.
However, it should be emphasised that if the failure is due to a justifiable cause, there will be no punishment.
Q11.: What types of documents should taxpayers keep in order to comply with maintenance of books of account?
The following documents must be kept on hand:
- A cash register.
- Journal, if books of accounts are kept according to the commercial accounting method.
- Ledgers.
- Carbon copies of invoices and carbon copies or counterfoils of receipts with a value of more than 25 rupees issued by the assessee.
- Original invoices given to the assessee, as well as receipts for expenses made by him;
- Signed vouchers, if invoices and receipts are not given and the spending amount is less than 50 rupees, and the cash book does not include enough details for these expenditures.
Details required for conduct of Tax audit in India
Documents Required for Tax Audit
- General Information of the Company.
- Related Party and discloser of Associated enterprises Transitions details.
- Information of Disallowed Expenditure
- Balance Sheet and Profit and Loss Account.
- Notes to account as per books finalized Balance sheet discloser.
- Details of Books of Accounts Maintained.
- Address of Branches.
- Details of Payment made to NRI.
- TDS and GST Return Statements.
- Details of Tangible and Intangible Assets.
- In case of Presumptive Taxation, details of income earned under Presumptive Scheme.
- Details of the Inventory and Stock in Trade.
- Special Sought of Business Expenditures Incurred.(Sec 33-35)
- Details of Income tax and GST Paid, along with late fees and penalty.
- Any other details specifically requirement of discloser like Personal Expenses, disallowed expenses, non allowable expenses under the income tax act,
Popular Articles related to Tax Audit :