Table of Contents
Taxation Aspect of a Hindu Undivided Family (HUF)
A.Introduction:
- Hindu Undivided Family stands for Hindu Undivided Family. It is a legal entity created by a Hindu family, which can also be formed by Buddhists, Jains, and Sikhs. HUF is recognized as a separate tax entity, allowing families to pool assets and save on taxes.
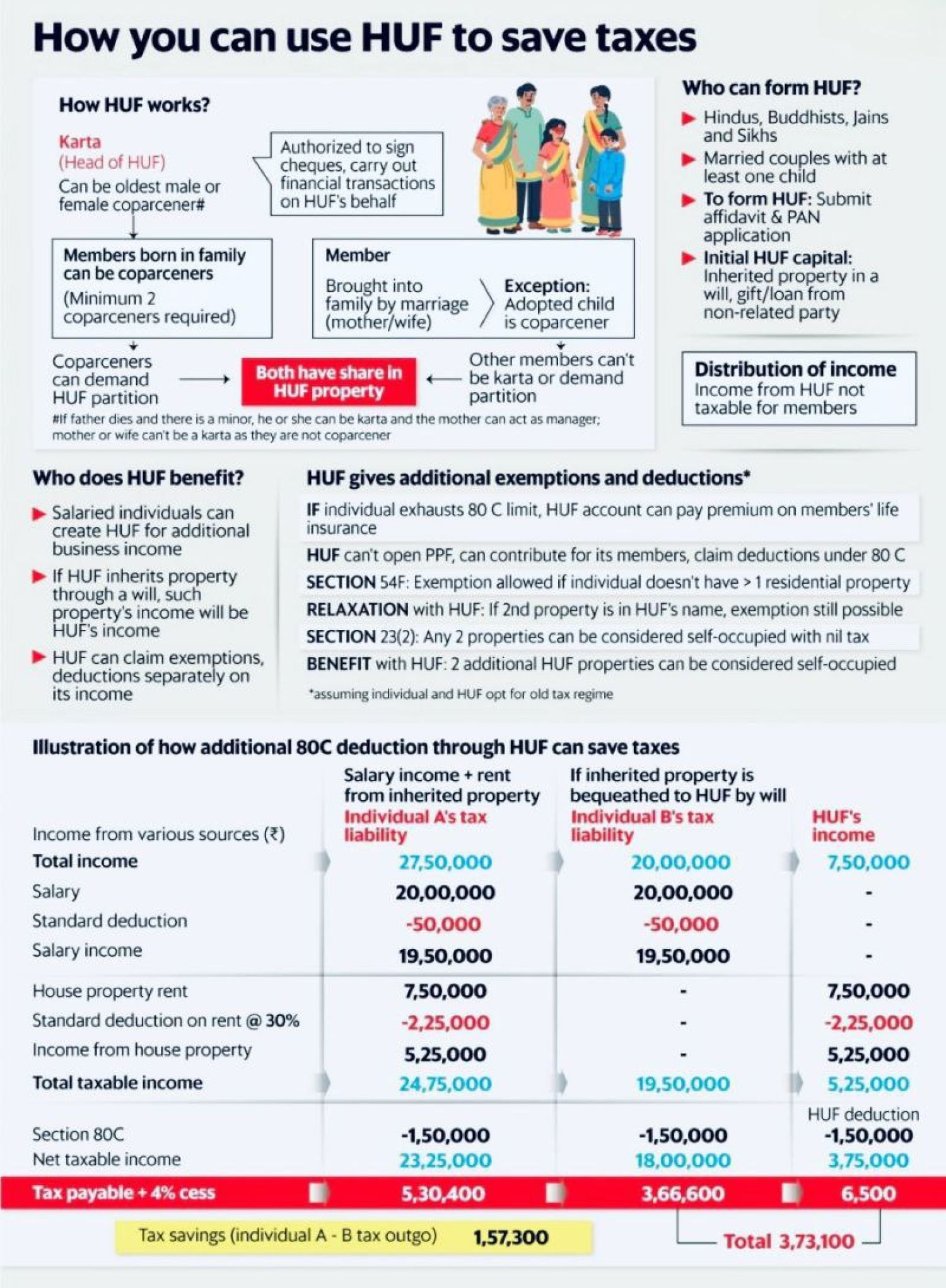
- A Hindu Undivided Family (HUF) is a distinct tax entity created by a Hindu family, which can include Buddhists, Jains, and Sikhs. It allows for pooling of family assets and provides significant tax benefits by being taxed separately from its members. The HUF is headed by a Karta and includes coparceners, who are family members within four generations that have an interest in the family property by birth, including both sons and daughters.
Formation and Structure of Hindu Undivided Family (HUF)
- A Hindu Undivided Family is created when a Hindu family comes together to form a single unit. The family pools its assets, which are then managed by the HUF.
- The Karta, typically the senior-most male member, heads the HUF. The Karta manages the HUF's affairs and makes decisions on behalf of the family.
- Coparceners are the members of the HUF who have an interest in the family property by birth. This includes both sons and daughters (since 6th September 2005) up to four generations from the common ancestor.
- Coparceners are the main members with the right to demand partition of the HUF property. They include:
- The Karta (head of the family)
- Sons and daughters
- Grandchildren
- Great-grandchildren
- Members who join the family by marriage (spouses of coparceners) are not considered coparceners but are members of the HUF.
Understanding a Hindu Undivided Family (HUF)
- The Income Tax Act offers various provisions for taxpayers to legally reduce their tax liabilities, one of which is through the creation of a Hindu Undivided Family (HUF).
- The head of an Hindu Undivided Family is called the Karta, typically the senior-most male member. In the event of the Karta's death, the eldest male member of the family becomes the new Karta.
- Under Hindu law, any male or female born into a joint family up to four levels of lineal descent from a common male ancestor is considered a coparcener. Members joining through marriage are not coparceners but are considered members.
- An Hindu Undivided Family has its own Permanent Account Number (PAN) and files a separate income tax return from its members.
B. HUF Tax Benefits:
- An HUF account is treated similarly to an individual's account for tax purposes, providing several tax benefits.
- The HUF is taxed at the same rates applicable to individual taxpayers.
- Deductions under section 80C of the Income Tax Act are available to HUFs.
- Gifts worth up to Rs 50,000 are tax-free. A father can gift property or money to a son's HUF, specifying it is for the HUF, to enjoy tax benefits under sections 64(2) and 56(2).
- The HUF corpus can be used for investments in tax-free instruments.
- Hindu Undivided Family’s can claim exemptions from capital gains under section 54 and deductions for home loan interest under section 24B.
- HUFs can engage in business activities, provided the funds used belong to the HUF.
- Hindu Undivided Family’s can pay salaries to the Karta and other family members involved in business operations.
- HUFs can own multiple homes without paying taxes on them, unlike individuals who must pay taxes on all but one home they live in.
- Separate Tax Entity: An HUF has its own Permanent Account Number (PAN) and files tax returns independently of its members. This allows the HUF to be taxed separately, potentially leading to significant tax savings.
- Tax Benefits: The HUF enjoys several tax benefits, such as:
- Standard deductions under section 80C of the Income Tax Act.
- Tax exemptions on gifts worth up to Rs 50,000.
- Ability to invest the corpus in tax-free instruments.
- Exemptions on capital gains under section 54.
- Deductions on home loan interest under section 24B.
- Salary payments to Karta and other family members involved in the HUF's business.
- Owning multiple homes without being taxed as "deemed to be let out."
- HUF is a good option for saving taxes. Below is the declaration format for forming an HUF. Link
C. Resident Status:
- An Hindu Undivided Family is considered a resident in India if the control and management of its affairs are wholly or partially situated in India.
D. Partition of Hindu Undivided Family:
- There are total partitions and partial partitions. However, income tax laws in India recognize only total partitions.
- If a member transfers self-acquired property to the HUF without proper sale consideration, the income from such property is taxable in the hands of the member, not the Hindu Undivided Family.
- Rights of Daughters: As of 6th September 2005, daughters of coparceners have the same rights as sons. They are coparceners by birth and have equal rights to partition and share in the family assets.
Understanding these aspects of Hindu Undivided Family taxation can help families manage their tax liabilities effectively and take advantage of the benefits offered by the Income Tax Act.
Tax & Compliance Comparison between HUF vs Individual
|
Particulars |
Individual |
Hindu Undivided Family (HUF) |
|---|---|---|
|
Legal status |
Natural person |
Separate legal & taxable entity |
|
PAN |
One PAN per individual |
Separate PAN for HUF |
|
Bank account |
Personal bank account |
Separate HUF bank account |
|
Head of entity |
Self |
Karta (usually senior-most member) |
|
Tax treatment |
Taxed as individual |
Taxed like an individual, but separately |
|
Basic exemption limit |
Available |
Available separately |
|
Section 87A rebate |
Available (subject to regime) |
Available independently |
|
Deductions (80C, 80D, etc.) |
Available |
Available separately |
|
Choice of tax regime |
Old or New |
Old or New (independent choice) |
|
Income sources |
Salary, business, house property, investments |
Ancestral property, family business, investments from HUF funds |
|
Salary income |
Allowed |
Not allowed (HUF cannot earn salary) |
|
Rental income |
Taxed in individual hands |
Taxed in HUF hands if property belongs to HUF |
|
Business income |
Taxed individually |
Taxed in HUF if business uses HUF capital |
|
Gifts |
Limited exemptions |
Gifts to HUF allowed from members/relatives (conditions apply) |
|
Clubbing provisions |
Applicable |
Strictly applicable if personal assets are transferred |
|
ITR filing |
Mandatory if income exceeds limit |
Separate ITR required |
|
Tax planning scope |
Limited to one entity |
Wider scope due to income splitting |
|
Compliance complexity |
Low |
Moderate (needs discipline & records) |
|
Succession |
As per personal law |
Continues across generations |