Table of Contents
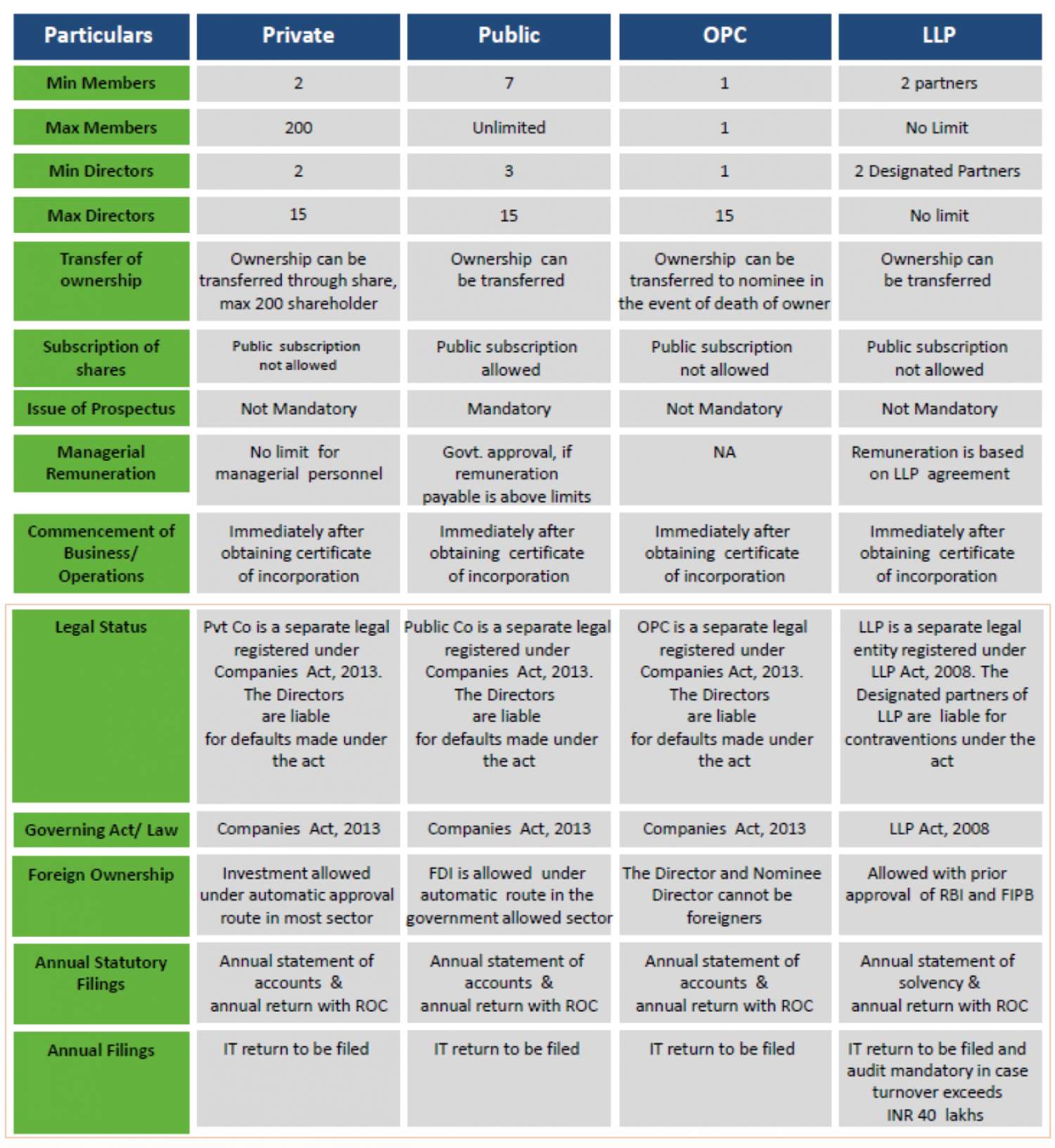
Comparative features of different type of business entity in India can be formed
In India, we have three major types of business frameworks, respectively sole proprietorship, partnership, and company (Pvt or public), but several years ago a new hybrid form of partnership and company are known as Limited Liability (LLP) emerged. Each mechanism seems to have its own pros and cons and relies on the particular circumstances of each business owner as to which structure is better suited to its business. It includes the level of personal responsibility you are willing to pay for your business obligations, your personal tax status, the level of administration you want to conduct, and how you want your business to be perceived.
Below, the factors listed are important and can help you in deciding on the best line of business structure.
Features |
Limited Liability Partnership) |
Private Limited Company |
Sole Proprietorship |
Partnership |
|
Starting up |
Mandatory registration |
Mandatory Registration |
No registration required |
Registration is optional |
|
Business Name |
Approval required prior to incorporation |
Approval required prior to incorporation |
No approval required. Should not infringe trademark or copyright |
No approval required. Should not infringe trademark or copyright |
|
Legal Status |
Separate legal entity |
Separate legal entity |
Not a legal entity |
Not a separate legal entity |
|
Foreign Nationals |
Allowed. Min 1 resident Designated partner needed |
Allowed |
Not allowed |
Not allowed |
|
Repatriation |
Not allowed |
Allowed |
Not allowed |
Not allowed |
|
Persons |
Min : 2, Max: No Limit |
Min: 2, Max: 50 |
Min: 1, Max : 1 |
Min: 2, Max: 20 |
|
Charter Document |
LLP Agreement |
Memorandum of Association (MoA) and Articles of Association (AOA) |
None |
Partnership Deed |
|
Business Licenses |
Applicable as per business requirements |
Applicable as per business requirements |
Applicable as per business requirements |
Applicable as per business requirements |
|
Validity |
Perpetual succession |
Perpetual succession |
Till death of Owner |
Dissolved on death of a partner. Can be dissolved at the will of all partners or even one partner can give notice for dissolving. |
|
Registering Authority |
Registrar of Limited Liability Partnerships, MCA |
Registrar of Companies, MCA |
None |
Registrar of Firms |
|
Governing Act |
The LLP Act, 2008 |
The Companies Act, 1956 |
None |
The Indian Partnership Act, 1932 |
|
Compliance Requirements |
Moderate |
High |
Low |
Low |
|
Income Tax Rates |
30% |
30% |
Individual rates |
30% |
|
Profit-Sharing |
Exempt from tax |
Taxable |
Taxable |
Exempt from tax |
|
Liability |
Limited up to contribution in LLP (except in case of Fraud) |
Limited up to the extent of shares hold (except in case of Fraud) |
Unlimited. Personal property is also covered |
Unlimited. Personal property is also covered |
|
Capacity to Sue |
As a Firm |
As a Company |
Individual-level |
As a Firm (in the case of registered firms). Individually/ Collectively (in case of not registered firms) |
|
Market Reputation |
Moderate |
High |
Low |
Low |
|
Winding up/ Dissolution |
The prescribed process to be followed |
The prescribed process to be followed |
Easy |
Easy |
Types of Companies:
1. Classification on the Basis of Incorporation
a. Chartered Companies:
The chartered company, a kind of corporation that emerged in the early modern era in Europe. It possessed certain rights and privileges and was governed by certain obligations under a special charter given to it by the sovereign authority of the State, such a charter defining and restricting certain rights, privileges, and obligations and the areas in which they were to be enforced. The charter generally provides a trading monopoly on a company in a particular geographic region or on a specific form of trade item.
b. Statutory Companies:
Companies are established by a special act Act by the Parliament or State Assembly. The constitution of the organization is set out in the Memorandum of Association (MOA). Rules related to the day-to-day management of statutory corporations are set down in the Articles of Association (AOA). Audit of the statutory company shall be performed by the Comptroller and Auditor General of India (CAGI)
c. Association Not for Profit:
According to Section 25, the Central Government can, by license, grant that an association may be registered as a company with limited liability, without using the terms 'limited' or 'private limited' as part of its name. The license would be issued only in the case of 'non-profit organization.' In other terms, the Central Government can only issue the license if it is confident that:
(i) The purpose of the association to be established as a limited company is to promote sport, trade, literature, science, religion, charity or any other useful object.
(ii) It intends to apply its income, if any, to the promotion of its objects.
(iii) Prohibits the payment of dividends to its members.
2. Classification on the Basis of Membership
a. public Company
It can be said that a public corporation is an organisation which are as follows:
i). It consists of at least 7 members.
ii). has a minimum paid-up capital of Rs. 5 lakh or more paid-up capital as may be prescribed.
iii). It is a subsidiary of a corporation and is not a private company.
iv). It does not limit the right to transfer its shares.
v). does not prohibit any invitation to subscribe to any of the company's shares or debentures.
vi). No invitation or acceptance of deposits shall be prohibited. (The name of the public company should be given to ltd. ex. National Aluminum Company Limited, Chennai)
b. Private Company
A private limited company is a type of company formed with a minimum of 2 shareholders and 2 directors. The minimum requirement for approved or paid-up capital of Rs. 1 lakh has been omitted by the Companies (Amendment) Act 2015 w.e.f. 29 May 2015. Another essential element of a private limited company is that, by virtue of its articles of association, it, restricts the right to sell its shares and also forbids any invitations to the market to subscribe to the company's securities. A maximum of 200 persons can become shareholders in a private company.
3. Classification on the Basis of Liability
a. Company Limited by Shares
A company limited by shares is a company in which the liability of its shareholders is limited by its Memorandum to the sum (if any) not charged on the shares owned by them. Companies limited by stock can be either public or private companies. If the member has paid the full sum of the shares, his liability shall be zero.
Thus, the two main features of a company limited in shares are as follows:
i). the liability of its members shall be limited to the amount (if any) remaining unpaid on the shares owned by them.
ii). Such liability can be carried out either during the lifetime of the business or during the winding-up of the business.
b. Company Limited by Guarantee
A company in which the member’s liability is limited to a fixed amount as defined out from the Memorandum of Association of the Company. This implies that the liability of the members is restricted by the MoA to the defined standards, since they have guaranteed to contribute to the assets of the company, in the case of the winding-up of the company.
c. Unlimited Company
An unlimited company are companies whose liability is not restricted. the liability of the member shall remove when he/she stops being a member of that company.
4. Classification on the Basis of controls
a. Government Companies
Government companies are companies authorized under the Indian Companies Act,1956 in which not less than 51% including its paid-up share capital is owned by the central government or any state government, or partially by the central government, in part by one or more state governments. Private interest in capital and management in this type of organisation is not permitted. It enjoys financial control and an autonomous staffing structure. The company does not have to concern about auditing, accounting, and budgetary control measures.
b. Holding Companies
A Holding Company is a parent company that owns a dominant position in a variety of companies. For example, if the shares of a limited company or a private company are owned by another company, that company is called the 'Holding Company.' The partnership formed is that of a subsidiary and a holding company. In most cases, the branches work separately, except in the case of ownership.
c. Subsidiary Companies
A company with more than 51percent of its overall share capital held by another company, i.e. a holding company, either by itself or in collaboration with its subsidiaries, as well as a holding company, shall also be called a subsidiary company.
5. Classification on the Basis of Nationality
a. Domestic Companies
A domestic company refers to a company organised in and engaged in commercial affairs in its own country.
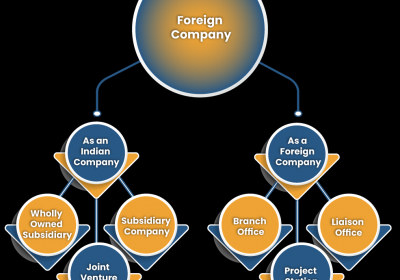
b. Foreign Companies
A foreign company means a company incorporated in a country outside India under the law of that country. The following documents must be registered with the Registrar of Companies within 30 days from the date of establishment of the company in India.
(i) A certified copy of the contract or legislation under which the corporation is incorporated, or a memorandum and articles of the company written in English.
(ii) The complete address of the company's office address.
(iii) A database of directors and secretaries of the company.
(iv) The contact details of any person resident in India who is licensed to do so;
(v) The complete address of the principal place of business of the company in India.
c. Multi-National Companies
The Multi-National Company (MNC) is large industrial company which are as follows:
i. Operations in more than one nation
ii. Conducts development, marketing and research activities on an international scale in those countries.
iii. Looks to boost profits all over the world.
An MNC can be a domestic company or a foreign company.
Rajput Jain and Associates has a Satisfaction guarantee for its clients, whereby money is refunded if the client is unhappy with the services. The Company Profile enclosed will help you make the most of what we can offer. If you have any questions, please contact us. Profile: https://carajput.com/assets/RJA.pdf
Doing Business in India https://carajput.com/publications/1__DD744811-L.pdf
I take great pleasure to introduce and offer Our Services.