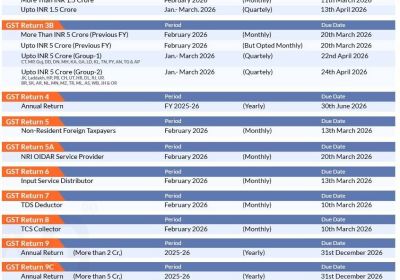
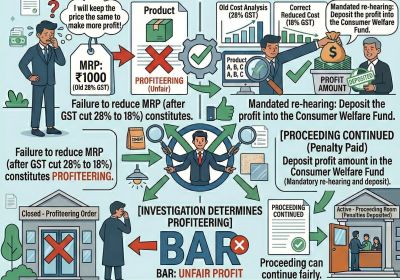
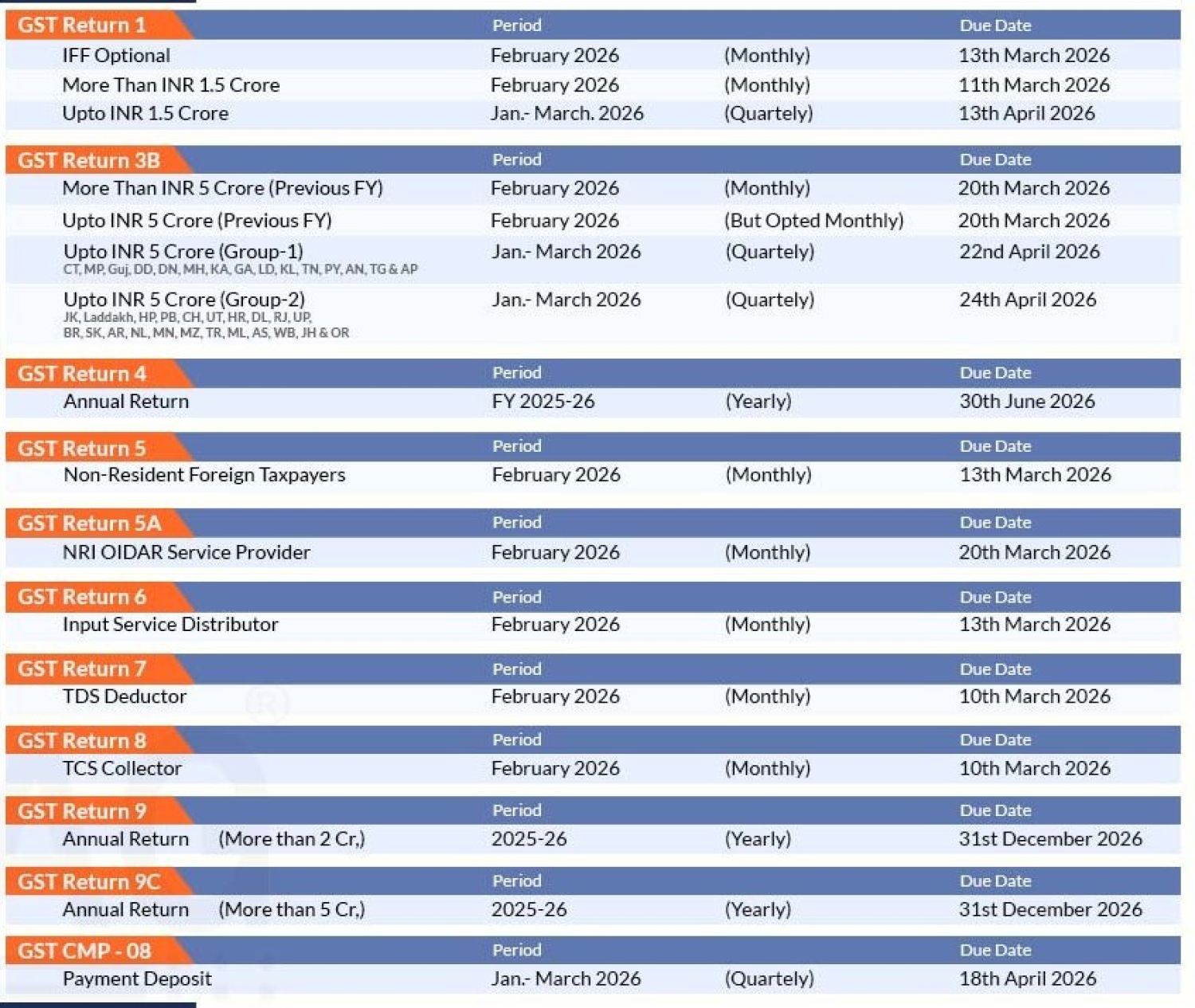
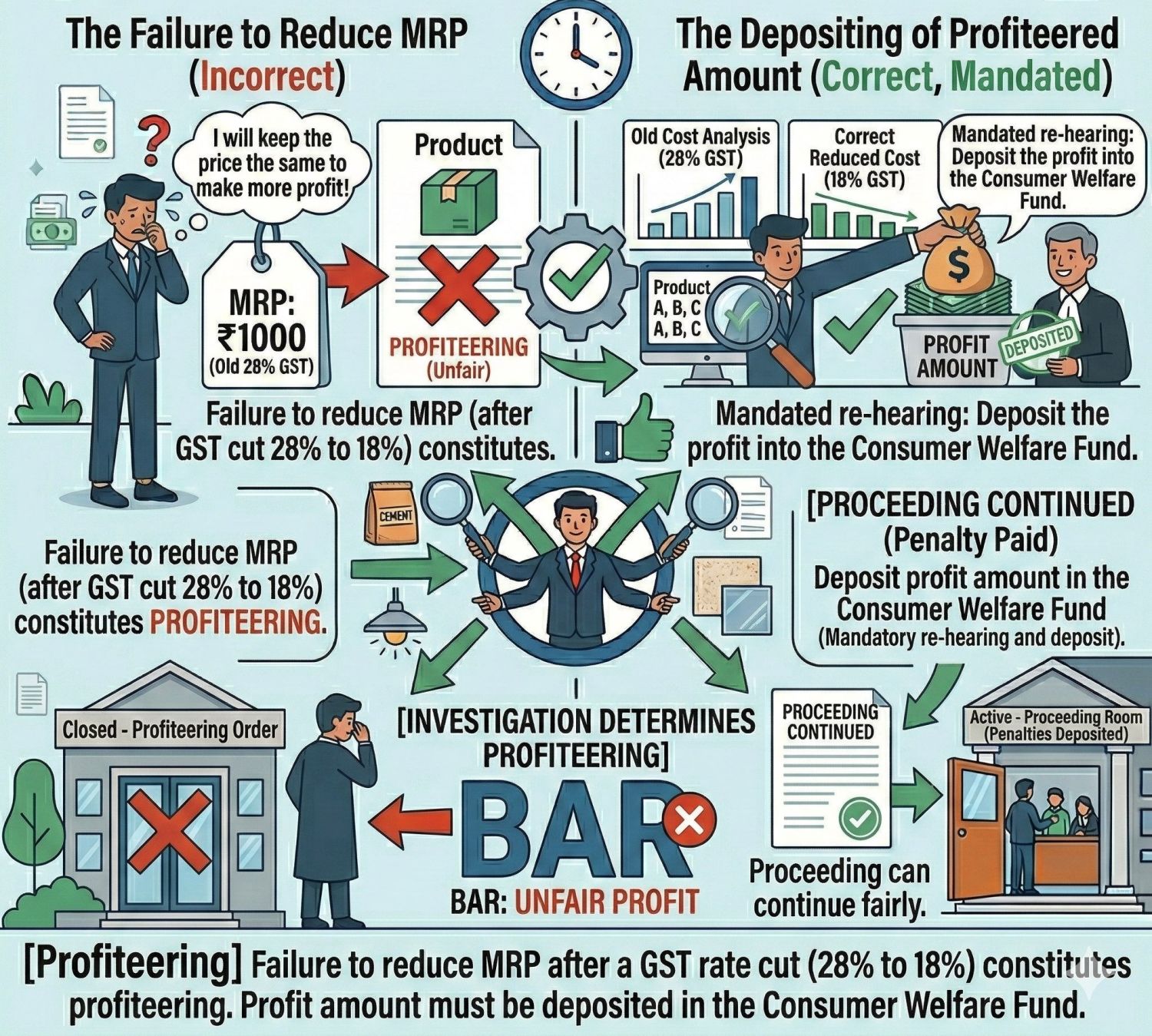
Table of Contents

GST Impact on Importers and Exporters
The implementation of the General Sales tax bill has been delayed by our Finance Minister. Due to this, there is a constant amount of anxiety that is prevailing among the people running the export-import business in India. With the help of this article we can get a clear picture of how the GST bill will affect the export and import business in the country.
IMPORT
Only after some Amendments are made in the constitution can the GST be levied on the imports as presently there are no acts present in the Constitution of India for the GST to be levied.
Irrespective of the fact that if imported goods are produced domestically or not, CGST and SGST will be levied on international imports at the time of importation. Incidence of tax as per convention will take its destination principle and the revenue from the tax from the SGST will be earned by the state in which the imported products are consumed.
Having entered into various free-trade activities, it is a difficult task for India to utilize customs duty as an exercise to ensure a balanced playing field. Now there are various endeavours to consider foreign goods on the same level as domestic goods.
Previously importers would be using custom duties to get benefits. They will have to pay a small amount for the manufactured products that they used to produce the export goods. The new GST act would not offer such special treatment to the import goods. GST would be imposed on goods that are imported regardless of whether or not they are being used for re-export. This would be ensured by the General Sales tax act, by imposing CGST and SGST on imports. Therefore a balance in terms of imports should be generated for the domestic industry and the manufacturing sector.
GST legislature would be drafted on destination based principle thereby:
1. On imports in between different businesses, SGST is to be levied and remitted to the state where the imports are located irrespective of where the products have entered the country. But the destination needs to be mentioned on the import invoice to mean the address of the importer.
2. You should collect the SCST on business to consumer goods and they should be remitted to the state. Here the place of residence of the person is to import the goods regardless of the fact from where the goods have been bought. They are not interested in the original location of production of the goods.
Import Taxes That Would Carry On
There are certain definite duties that cannot be subsumed 7under the GST regime even having after the introduction of the duties. These duties are as under:
1: Basic Custom Duty
2: Anti-Dumping Duty
3: Safeguard Duties
There have been rising industries even after the production of the GST. They are the gaining sectors of leather products, furniture and fixtures, coal and lignite, agricultural machinery, industrial machinery and other machinery which iron and steel as for example the coal and steel and railway transport equipment, printing and publishing equipment and tobacco products. There are several moderate gainers which include metal products and nonferrous metals. It also includes transport equipment and other railways.
Imports are expected to decline in the market. These include textile and readymade garments, mineral and beverages, coal, crude oil and petroleum and gas and iron ore.
EXPORT
The GST can be organized according to the concept of destination. Thus exports by zero-rating avoid the GST burden. The products that are exported without VAT charging are referred to as the products with a Zero rating. You can also refund the VAT that is paid. Thus the goods are exported on tax shorns. Countries have VAT resorting to zero export ratings.
There are several export taxes that are bound to carry on. They include:
- Export Duty : This might not be subsumed under the GST regime
- SEZ : With the help of GST, you can make sure that all the producers and distributors are treated as complete pass-through and the exports are guaranteed to be zero-rated. In this way, one cannot possibly be exempt directly. There is a definite purpose for setting up SEZ. It was to motivate and encourage the production of goods that are to be exported out of India. In this way, even after one withdraws, this would directly benefit the units which are set up in SEZ and would still continue to enjoy exemption in respect of goods and services exported by it. You would be taxed if you sale anything by SEZ to the Domestic Tariff Area. There is a similar law which deals with the exemption of SEZ.
- Foreign Trade Policy : There are certain exemption schemes that are available under the Foreign Trade Policy 2009-2014. There are also certain central excise and custom legislation that might be available. Although there is a discussion about some government duties and documents prepared, there are exemptions that are currently available under custom legislation.