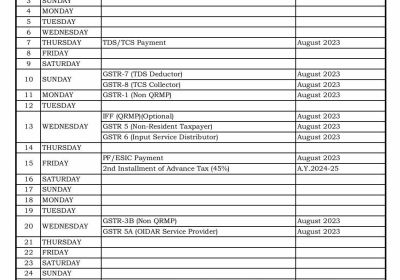
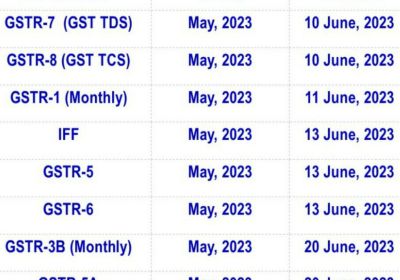
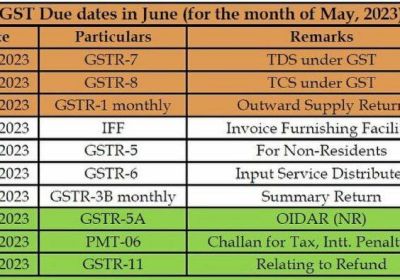
The financial elements of a financial statement are broadly classified into five categories. These are grouped according to the monetary characteristics they possess. Let’s have a brief understanding of all five.
Assets
An asset is a resource (either tangible or intangible) that is in control of the enterprise to derive monetary benefits from its use. Some of the points to be remembered are:
- An asset should not necessarily have a physical existence.
- An asset need not necessarily be owned. It should only be in control of the enterprise. An asset taken on lease from its owner will not be mentioned in the books of the owner but to whom it is in control of or leased.
- In order for an asset to be recognized, there should be sufficient control over it. For example copyrights, patents, trademarks, etc.
- An asset in order to be called an asset should be able to reap future financial benefits. An asset that ceases to have any value in a current accounting period cannot be termed as an asset.
- An asset’s value or cost should be easily calculable or measurable.
Liabilities
Liability is defined as an obligation of an enterprise that arose as a result of past events. Some of the important points to be remembered in its context are:
- A liability is recognized with the evidence shown in the balance sheet date.
- Certain provisions like provision for depreciation, provision for bad and doubtful debts, and other provisions are not considered a liability but rather as a reduction in the value of the asset.
Equity
Equity can be defined as the remaining interest of an enterprise over its assets after the deduction of liabilities from it. In short, equity is the excess of aggregate assets over aggregate liabilities.
Income
Income can be:
- any increase in the economic benefit as a result of inflow or encashment of asset
- Increase in equity with the decrease in liability.
Income also includes revenues and gains. Revenue is an income that arises during the ordinary course of business whereas, again is an income that may or may not arise during the normal course of business.
Expense
The expense is an antonym of income. The following are considered as an expense:
- Any decrease in the economic benefit as a result of outflow
- Deterioration of assets
The expense is defined as the charges incurred in the ordinary course of business like wages paid, rent paid, etc., whereas losses may or may not incur in the ordinary course of business. For example loss on the sale of fixed assets. Expenses are shown on the debit side of profit and loss A/C.
Regards
Rajput Jain & Associates