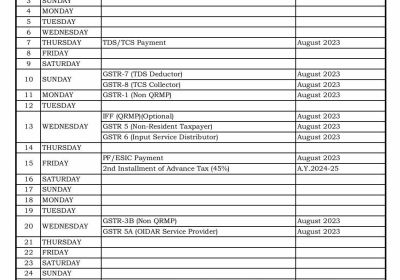
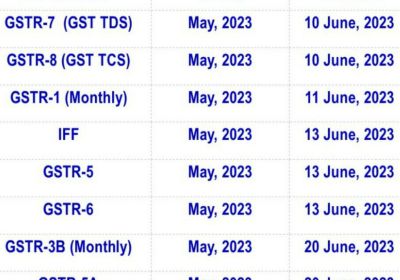
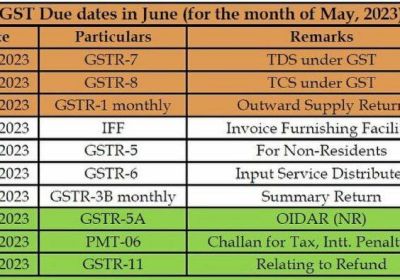
Table of Contents
- Appointment Auditor Or Resignation, Intimation & Related Formalities In Company act 2013
- Failure To Appoint A Auditor
- Documents Needed For Appointment Of New Auditor In The Company?
- Step-by Step Procedure For Auditor’s Resignation And Documents Needed For Appointment Of New Auditors In The Company.
- Appointment Of An Auditor For A Publicly Listed Corporation
- Power And Duties Of Auditor Of The Company
- Resignation Of Auditor
- Procedure Of Filing Form Adt 3 And Auditor Resignation
- Adt 3 Form Statement Shall Contain The Below Details.
- Step-by Step Procedure For Auditor’s Resignation
- Failure By Chartered Accountants To Comply With Sas Per Se Is “gross Negligence” Even If There Is No Ill-motive

Appointment Auditor or Resignation, Intimation & Related Formalities in Company Act 2013
All registered companies, whether they are a one-person corporation, or a limited company or a private limited company are required to keep a proper book of accounts and have them audited. As a result, following the incorporation of a firm, the Board of Directors must appoint an auditor.
First Auditors
- The company's first auditors must be appointed by the directors within 30 days of the company's registration date; otherwise, the shareholders can appoint first auditors within 90 days of incorporation. The requirement and procedure for appointing an auditor are discussed in this article.
Other Auditors
- The appointment of auditors (other than the first auditors) must be made by the company's members in a general meeting. The auditor appointed at the general meeting takes office after the meeting, with the meeting where the appointment was made counting as the first meeting.
- But, if a casual vacancy in the office of auditor arises as a result of registration, the consent of members must be acquired within three months of the Board's recommendation date. The auditor in question may serve until the end of the next annual general meeting. It is required for the Company to file ADT-1 within 15 days of appointing the subsequent auditor.
- Companies are required to appoint an auditor under section 139 of the Companies Act, 2013. If an auditor wishes to resign from his position, he must do so in the proper form and manner to the registrar of companies (ROC). Within 30 days of the date of resignation, the intimation must be given along with a statement.
Failure to appoint a Auditor
- If the Board of Directors fails to appoint an Auditor within 30 days of the company's establishment, the Board should notify the company's members of the failure to appoint an Auditor. Members can then appoint an auditor at an extraordinary general meeting within 90 days, and the auditor will serve until the end of the first annual general meeting.
- If no auditor is selected or re-appointed at any annual general meeting, the current auditor of the company will continue to be the auditor of the company.
Documents Needed for Appointment of New Auditor in the company?
When a firm appoints a new auditor, the company shall submit the Below mention documents.
- ROC E- Form MGT-14 with a copy of the resolution passed in the board meeting.
- ROC E- Form ADT -1 to be filed with the MCA.
In addition to the above ROC forms, the below details must be given to the ROC.
- New auditor firm Name.
- New auditor firm Address.
- PAN number & Email address
- No of years for which the CA firm is appointed.
- Resigning auditor firm Information
- New auditor firm Date of appointment
- DSC Signed Form ADT 1 (with the DSC signature of Company director).
The ADT-1 form shall be filed within 30 days from the date of the appointment of the new auditing firm. Every company has to follow the prescribed rules as per the Companies Act for the resignation and appointment of an auditor firm.
Step-By Step Procedure for Auditor’s Resignation and Documents needed For Appointment of new Auditors in the company.
- The Companies Act of 2013 stipulates a specific procedure for the resignation of auditors. Companies are required to appoint an auditor under section 139 of the Companies Act, 2013. If an auditor wishes to resign from his position, he must do so in the proper form and manner to the registrar of companies (ROC). the intimation must be given along with a statement. In this post, you'll learn more about filing this statement (Form ADT-3) Within 30 days of the date of resignation,.
- The formalities for an auditor's resignation are discussed in this article. The ROC must also be informed of the grounds for the resignation. The auditor must carry out a procedure when the resignation is submitted to the company. We've included the entire procedure as well as other connected formalities.
Appointment of an Auditor for a Publicly Listed Corporation
- The provisions governing the appointment of an auditor for a public business are more strict than those governing the appointment of an auditor for a private firm. A listed business, for example, cannot select an individual as auditor for more than five years in a row. In addition, an audit firm cannot serve as the auditor of a publicly listed company for more than two terms of five consecutive years.
Power and Duties of Auditor of the Company
- An auditor is an impartial individual hired by the company to offer an opinion on whether the company's financial statements are free of major misstatements, fraud, or errors and are compliant with accounting standards. It is vital to understand that the Company is responsible for maintaining a book of accounts and preparing financial statements. The Auditor cannot keep the Company's Book of Accounts or create financial statements since it would jeopardize his or her independence.
Resignation of Auditor
To beginning, the auditor must inform the company of his or her resignation and file a statement in the form of an ADT-3 form. Within 30 days of the resignation date, this statement would be sent to the RoC.
Procedure of Filing Form ADT 3 and Auditor Resignation
- An auditor must file a statement in the form of ADT-3 form after giving notice of resignation to the company. Within 30 days of the resignation date, this statement must be provided to the RoC.
- The Auditor's Resignation Act, Section 140(2), allows an auditor to resignation. It stipulates that an auditor must file a declaration of resignation with the Registrar within 30 days after his resignation date, as specified in the Rules.
ADT 3 Form statement shall contain the below details.
- Name of the auditor’s firm.
- Address of the resigning auditor firm.
- Reasons of resignation
- Email address of the auditor firm
- Resigning auditor firm’s contact numbers.
- Permanent account number of the auditor firm.
- Form ADT3 must be DSC signed by any one member of the auditor firm.
If a resigning auditor fails to file with the ROC of his resignation within the required 30 days, Then He faces a penalty of INR 50,000 to INR 5,00,000/-.
Step-by Step Procedure for Auditor’s Resignation
The procedure for resigning as an auditor must be followed in the order listed below. Any errors in the procedure can be avoided if the following steps are followed carefully:
- Step 1: Auditor Firm has to submit the resignation letter and Form ADT3 to the company.
- Step 2: Board of Director of meetings shall be organized with all the directors to effect the resignation.
- Step 3: Company shall obtain a consent letter from the new auditor firm under sections 139 and 141, Co. Act 2013.
- Step 4 : Board of Director of meetings shall be called. All the members of the company shall be called to the meeting for filling the vacancy of the auditor.
- Step 5: New Proposed Auditors’ Firm is to be appointed in such meeting held.
- Step 6: Intimate the Appointed auditor/ Auditors’ firm regarding the date of appointment in the Company.
- Step 7: File the ROC form ADT-1 for the appointment of the new auditor in the Company.
A company must follow the specified formalities/procedures for appointing a new auditor following an auditor's resignation.
Failure by Chartered Accountants to comply with SAs per se is “gross negligence” even if there is no ill-motive
- National Financial Reporting Authority in 1 of the case law decided that Failure by Chartered Accountants to compliance with Standards of Auditing’s in an audit is per se "gross negligence" even if there is no ill-motive on his part. Failure by Chartered Accountants to comply with Standards of Auditing (SAs) in an audit is per se gross negligence and amounts to professional misconduct according to the 2nd Schedule to CA Act, 1949, even if there is no ill-motive on Chartered Accountants part.