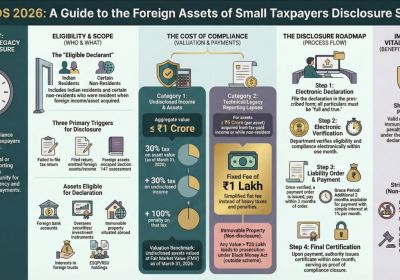
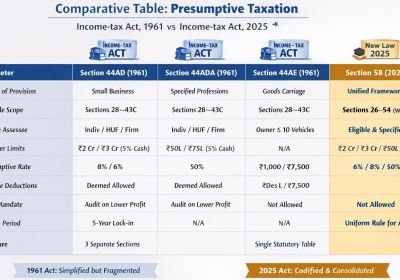
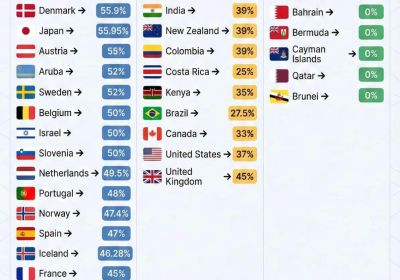
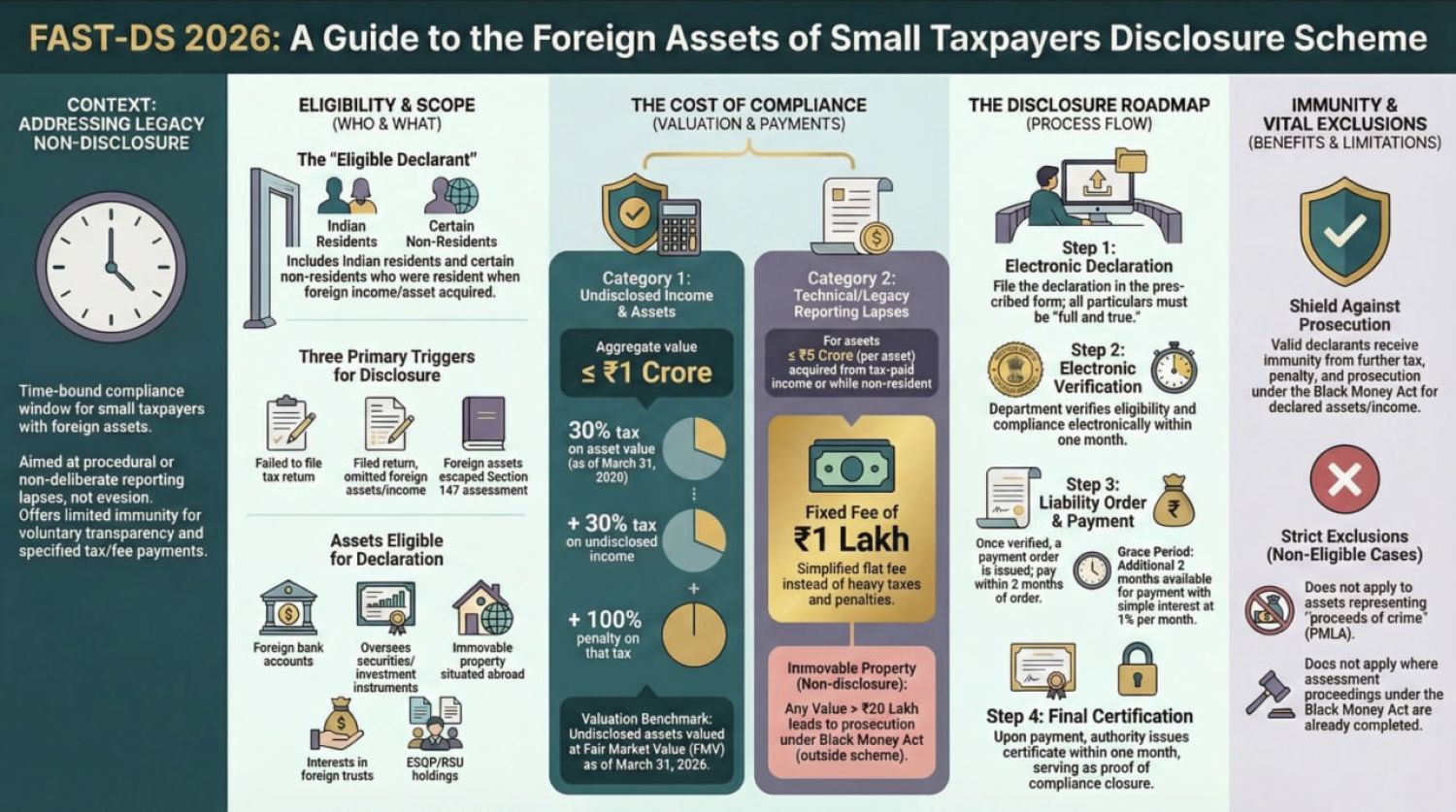
Table of Contents

Budget Finance Bill, 2025 (Union Budget 2025-26) Proposals on Indirect & Direct Taxes By FM
-
The Finance Bill 2025, presented by Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman on February 1, 2025, is available for download on the official Union Budget website. You can access the PDF directly using the following link: Finance Bill 2025 PDF For additional budget documents and information, please visit the Union Budget portal: Union Budget Portal
- Once the Finance Bill, 2025 is approved by both Houses of Parliament—Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha—and receives the President of India's assent, it becomes the Finance Act, 2025. The Government of India will then notify the final Act, which will include the applicable tax provisions and amendments for the financial year.
- The provisions of the Finance Act typically take effect from April 1 of the respective financial year unless specified otherwise. Let me know if you need updates or analysis on the final Finance Act, 2025, once it's notified. for details about Budget Finance Bill, 2025 (Union Budget 2025-26) and proposals on indirect and direct taxes, you may visit link These resources provide comprehensive details on the budget proposals for the financial year 2025-26.
- The Union Budget 2025 introduces key reforms across multiple sectors, focusing on taxation, infrastructure, social welfare, healthcare, education, and investment policies. This budget emphasizes tax simplification, increased exemptions, investment in AI, healthcare, and infrastructure, and provides a significant boost for farmers, startups, and urban development. In the Union Budget 2025, Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced significant changes to the personal income tax structure to enhance the spending power of the middle class and stimulate economic growth.
Key Highlights of Union Budget 2025
General Announcements under Union Budget 2025-26
Kisan Credit Card limit raised to INR 5 lakh from INR 3 lakh.
Infrastructure boost for 5 IITs established post-2014; IIT Patna to expand.
Medical Education: 10,000 new medical seats in one year; 75,000 in five years.
AI Research: INR 500 crore allocated for Centre for Excellence in AI.
GIG Workers: New Social Welfare Scheme introduced.
Jal Jeevan Mission extended till 2028.
Urban Challenge Fund of ₹1 lakh crore to boost urban development.
Greenfield Airports planned for Bihar, in addition to Patna expansion.
Private Sector R&D gets INR 20,000 crore push.
Tourism Development: Top 50 destinations to be developed, focusing on Buddhist sites.
‘Heal in India’ initiative to promote medical tourism.
Insurance Sector: 100% FDI allowed if premiums are fully invested in India.
KYC Registry to be revamped for better compliance.
Customs Duty Rationalization with a focus on simplified tariff structure.
Life-saving drugs: 36 exempted from duty; 5% duty on 6 essential drugs.
Direct & Indirect Tax Reforms under Union Budget 2025-26
New Income Tax tax bill is to be introduced next week.
Personal Income Tax Reforms are targeted at the middle class.
Income tax exemption up to INR 12 lakh.
Revised Income Tax Slabs (Details awaited).
TDS & TCS Rationalization for easier compliance.
TDS on Rent: Limit increased from INR 2.4 lakh to INR 6 lakh.
TDS Exemption for Senior Citizens: Limit raised from INR 50,000 to INR 1,00,000.
TCS on Education Remittances: Removed for overseas education expenses.
Updated Return Filing Window extended from 2 years to 4 years.
Revised Income Tax Slabs:
The new income tax slabs are as follows:
Income up to INR 4,00,000: No tax
INR 4,00,001 to INR 8,00,000: 5%
INR 8,00,001 to INR 12,00,000: 10%
INR 12,00,001 to INR 16,00,000: 15%
INR 16,00,001 to INR 20,00,000: 20%
INR 20,00,001 to INR 24,00,000: 25%
Above INR 24,00,000: 30%
These adjustments aim to provide substantial relief to taxpayers across various income brackets.
Standard Deduction: For salaried individuals, the standard deduction has been increased to ₹70,000. This means that individuals earning up to INR 12,70,000 can effectively reduce their taxable income by ₹70,000, thereby lowering their tax liability.
Tax Exemption Threshold: The Finance Minister also proposed that individuals with an annual income of up to ₹12,00,000 will not be required to pay any income tax. This move is expected to benefit a significant portion of the salaried class, increasing their disposable income and encouraging spending.
Support for Charitable Trusts and Institutions: To reduce the compliance burden on small charitable trusts and institutions, the government has proposed measures to simplify their regulatory requirements. While specific details were not provided in the announcement, this initiative aims to facilitate the operations of these organizations, allowing them to focus more on their philanthropic activities.
Key Documents for your Full Read, the Budget 2025
The Union Budget 2025-2026, presented by Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman on February 1, 2025, encompasses several key documents that provide comprehensive insights into the government's financial plans and policies. Here are the primary documents for your reference:
-
Finance Bill 2025: This bill outlines the legal amendments required to implement the budget's financial proposals. Finance Bill 2025
-
Finance Minister's Speech: The speech delivered by the Finance Minister during the budget presentation, detailing the government's economic agenda and key initiatives. Finance Minister's Speech
-
Memorandum Explaining the Provisions in the Finance Bill: This document provides detailed explanations of the provisions included in the Finance Bill. Memorandum Explaining the Provisions in the Financial Bill
-
Key to Budget Document, 2025: A guide that explains the structure and components of the budget documents, aiding in their understanding.Key to Budget Document, 2025
-
Budget Highlights (Key Features): A summary of the main features and initiatives proposed in the budget. Budget Highlights (Key Features)
-
Expenditure Budget (Full): A comprehensive account of the government's expenditure across various ministries and departments. Expenditure Budget (Full)