Table of Contents

Understanding FIU IND Reporting Requirements for Regulated Entities
All Regulated Entities (REs) in India are mandated under the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA) to file specific reports with the Financial Intelligence Unit–India (FIU IND) for designated transactions. These reports play a crucial role in helping FIU‑IND detect, track, record, and prevent financial crime.
Mandatory Reports Under PMLA
Regulated Entities must file the following reports depending on the nature of transactions: Cash Transaction Report (CTR), Property Transaction Report (PTR), Cross Border Wire Transfer Report (CBWTR), Counterfeit Currency Report (CCR), Non‑Profit Organization Transaction Report (NTR) and Suspicious Transaction Report (STR). Timely and accurate filing of these reports strengthens India’s financial monitoring framework and ensures compliance with AML/CFT obligations.
Who are “Regulated Entities (REs)”? ”?
Regulated entities include (illustrative list): banks (public, private, and cooperative), NBFCs, payment system operators, stockbrokers, mutual funds, portfolio managers, insurance companies, authorized dealers & forex entities, designated professionals (where notified), certain NGOs/NPOs, and Virtual Asset Service Providers (VASPs), where applicable. Each RE must Register on the FIU-IND reporting portal and Appoint a principal officer and also File reports electronically in prescribed formats
What is FIU-IND, and why does reporting matter?
FIU-IND (Financial Intelligence Unit – India) is the central national agency responsible for receiving, processing, and analyzing. financial transaction reports to combat money laundering, terror financing, and financial crime. Under the Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002 (PMLA), certain entities are classified as Regulated Entities (REs) and are legally required to report specified transactions to FIU-IND. These reports act as early-warning signals for suspicious or illegal financial activity.
Why timely & accurate reporting is critical
Failure or delay can lead to monetary penalties, regulatory action by RBI/SEBI/IRDAI, adverse audit findings, and PMLA prosecution in extreme cases. Accurate reporting helps strengthen India’s AML/CFT ecosystem, improve FATF compliance ratings, and protect REs from reputational and legal risk.
Mandatory Reports under PMLA—Explained One by One
Cash Transaction Report (CTR)
Cash Transaction Report covers the cash transactions exceeding INR 10 lakh in a single day and includes cash deposits, cash withdrawals, and a series of linked cash transactions. In this CTR reporting, the main point is threshold-based, not suspicion-based, and Even genuine transactions must be reported and purpose of CTR reporting is to Track large cash movements that could indicate tax evasion or laundering
Property Transaction Report (PTR)
The Property Transaction Report covers the purchase or sale of immovable property and where the transaction value exceeds prescribed limits or shows risk indicators. Typically reported by banks/financial institutions financing property, and reporting obligations arise where RE is involved in the transaction flow. FIU-related Property Transaction Report The purpose is to prevent laundering through real estate a high-risk sector.
Cross Border Wire Transfer Report (CBWTR)
Cross Border Wire Transfer Report covers : reporting of Cross-border wire transfers above ₹5 lakh (or equivalent) Includes Inward remittances, Outward remittances and SWIFT transfers. Purpose of Cross Border Wire Transfer Report is Monitor international fund flows and Detect terror financing, shell entities, hawala-type layering
Counterfeit Currency Report (CCR)
What it covers is the detection of fake notes, suspected counterfeit currency, and impugned banknotes. Counterfeit Currency Report Reporting trigger Whenever counterfeit currency is detected, there is no threshold. The purpose of Counterfeit Currency Report is Track circulation of fake currency and organised crime networks
Non-Profit Organisation Transaction Report (NTR)
Non-Profit Organisation Transaction Report covers transactions of non-profit organizations (NPOs) exceeding prescribed limits. Why special focus on NPOs? To tease International AML frameworks (FATF) treat NPOs as potential misuse channels for terror financing. The purpose of the nonprofit organization transaction report is to ensure funds are used for legitimate charitable objectives.
Suspicious Transaction Report (STR)
Suspicious Transaction Report is most critical in this FIU compliance reporting. What the Suspicious Transaction Report covers: Any transaction that appears unusual, illogical, inconsistent with the customer profile, and without apparent economic purpose. Important features of the Suspicious Transaction Report is No monetary threshold, the customer must not be informed (tipping-off is prohibited), and it must be filed as soon as suspicion arises. We can see the examples like sudden high-value transfers, frequent round-tripping, complex layering, and mismatches between income and transactions. The purpose of the Suspicious Transaction Report is to provide core intelligence input for FIU-IND investigations.
Expert Compliance Support :
Aligning with FIU‑IND reporting obligations can be complex, but you don’t have to navigate it alone. Rajput Jain & Associates provides expert guidance on FIU‑IND reporting compliance, PMLA and AML/CFT obligations, risk assessment and internal control frameworks, and end‑to‑end regulatory support for regulated entities. FIU-IND compliance is not just filing reports. It involves risk-based customer due diligence, internal AML policies, monitoring systems, staff training, periodic reviews & audits. Rajput Jain & Associates is positioned here as providing:
- FIU-IND registration & reporting support
- STR analysis and documentation
- AML/CFT risk assessment
- End-to-end PMLA compliance handholding
- This is especially relevant because non-compliance often happens due to lack of process, not intent.
If Company are a Regulated Entity, you are legally required to report certain transactions to FIU-IND. These reports help the government detect financial crime. Understanding what to report, when to report, and how to report is critical — and expert support can make compliance smoother and safer.
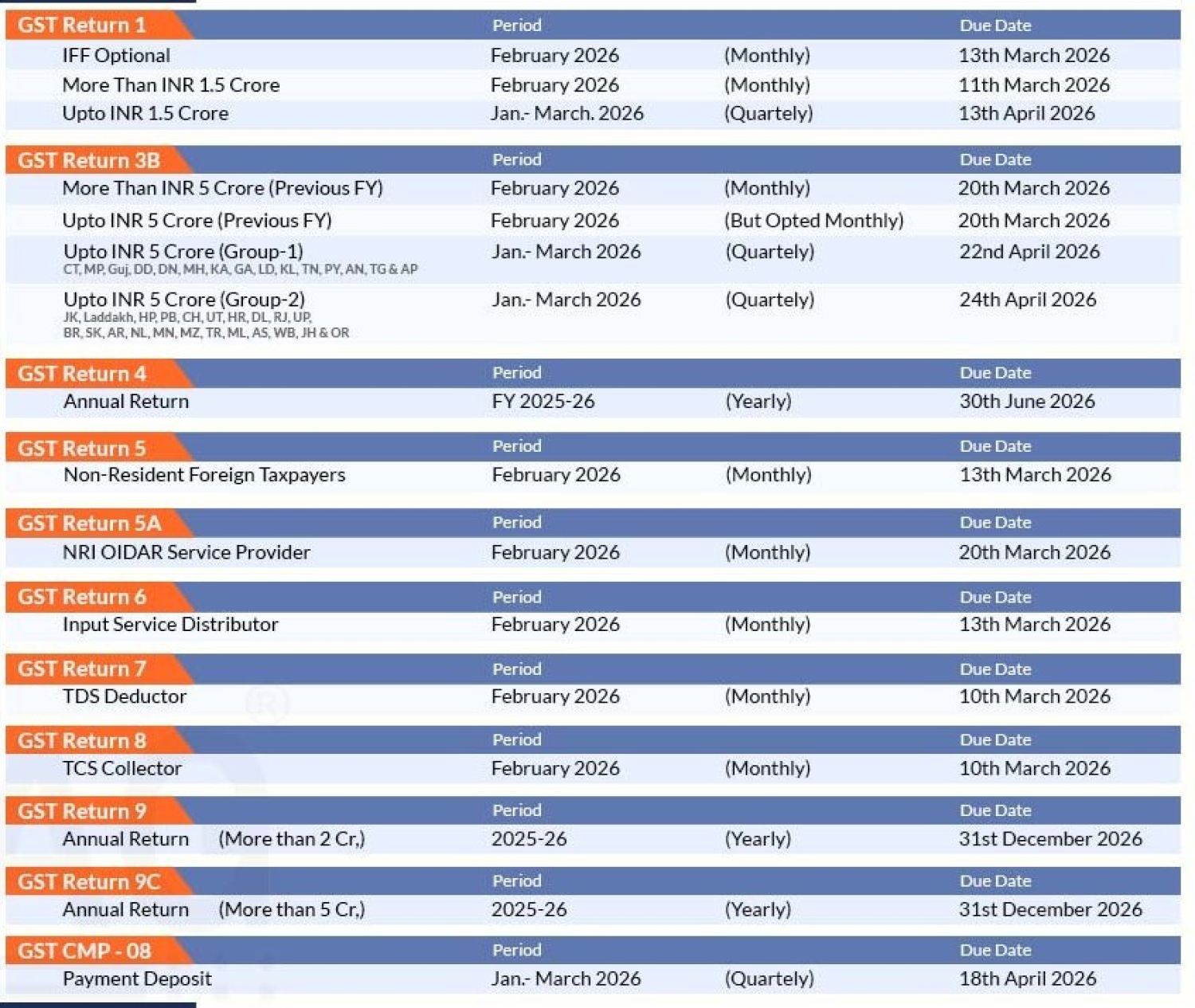
Due Dates for Filing Financial Intelligence Unit Reports via FINnet Gateway
All reports must be filed electronically through the FINnet Gateway as required by the Financial Intelligence Unit (FIU‑IND). Reporting Schedule
| Report Type | Description | Due Date |
|---|---|---|
| CTR – Cash Transaction Report | Cash transactions INR 10 lakh or more | 15th day of the succeeding month |
| CCR – Counterfeit Currency Report | Report of forged or counterfeit currency detected | 15th day of the succeeding month |
| NTR – Non-Profit Transaction Report | Any transaction > INR 10 lakh involving NPO receipts | 15th day of the succeeding month |
| CBWTR – Cross‑Border Wire Transfer Report | Cross‑border transfer INR 5 lakh or more | 15th day of the succeeding month |
| IPR—Immovable Property Report | Purchase/sale of immovable property exceeding INR 50 lakh | 15th day of the month following the quarter end |
| STR – Suspicious Transaction Report | Any suspicious transaction (cash or non‑cash) | Within 7 working days of determining the transaction as suspicious |
FIU‑IND & RBI Signed a MoU
The Financial Intelligence Unit–India (FIU‑IND) and the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) have signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) in New Delhi on April 17, 2025 to enhance coordination and ensure stronger compliance with the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA). Key Objectives & Areas of Collaboration
- Strengthened Coordination Mechanism : Appointment of a Nodal Officer and Alternate Nodal Officer by both FIU‑IND and RBI to facilitate seamless coordination.
- Enhanced Intelligence Sharing : Exchange of essential intelligence, data, and insights from respective systems to support risk identification and compliance monitoring.
- Streamlining Reporting Processes : Joint development of process guidelines for how regulated/reporting entities must file PMLA‑related reports to FIU‑IND.
- Capacity Building & Training : Conducting training sessions, workshops, and awareness programs for regulated entities to enhance understanding of AML/CFT requirements.
- Strengthening AML/CFT Supervision : Improving the skills of RBI‑regulated entities in managing money laundering and terrorism financing risks. and ensuring alignment of practices with global financial crime compliance standards.
- Risk Analysis & Identification: Joint analysis of risks, vulnerabilities, and weak areas across financial sectors. and Identifying red flags and warning indicators related to suspicious transactions.
- Compliance Enforcement : Ensuring RBI‑regulated entities comply with PMLA Provisions, PML Rules and RBI AML/CFT Guidelines
- Governance & Review Mechanism : Quarterly review meetings to exchange updates, share insights, and address emerging risk areas.
-
This FIU and RBI - MoU significantly strengthens India’s AML/CFT ecosystem by Enhancing regulatory coordination, Improving reporting , efficiency, Boosting sector‑wide compliance capabilities, Aligning practices with global FATF‑style standards & Building a proactive, intelligence‑driven approach to combating financial crime