Table of Contents
- Officially Valid Documents For Address Verification Of Individuals Under Ifsca (aml/cft And Kyc) Guidelines, 2022
- Officially Valid Documents (ovd) – Address Verification
- Compliance Responsibility Of International Financial Services Centres Authority Regulated Entities
- Financial Intelligence Unit - India (fiu-ind): Strengthening The Kyc Process By Avoiding 12 Common Mistakes
- About Rajput Jain And Associates
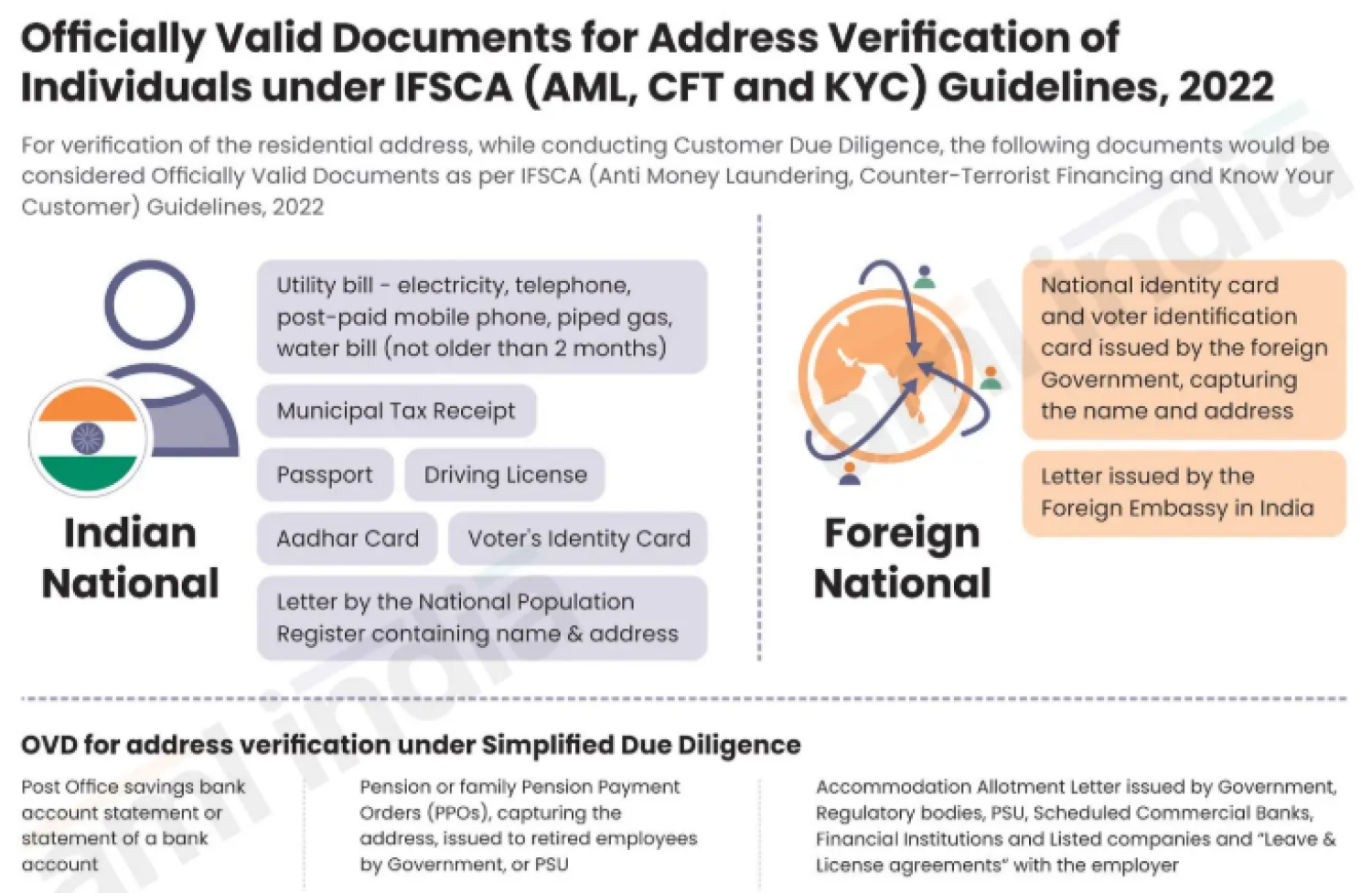
Officially Valid Documents for Address Verification of Individuals under IFSCA (AML/CFT and KYC) Guidelines, 2022
The International Financial Services Centres Authority has issued the IFSCA (AML, CFT, and KYC) Guidelines, 2022, prescribing detailed anti-money laundering and combating the financing of terrorism requirements for regulated entities operating in International Financial Services Centres Authorities. A key component of these guidelines is the Know Your Customer (KYC) process, which requires regulated entities to obtain customer identification details, verify address using reliable and independent documents, and ensure consistency between the KYC form and the address proof submitted. The guidelines specify a list of officially valid documents acceptable for address verification.
Officially Valid Documents (OVD) – Address Verification
For Resident Individuals : The following documents are generally accepted as officially valid documents for address verification: passport, driving license, Aadhaar card, voter's identity card, NREGA job card (duly signed by a state government officer), and any other document notified by the Government of India as an officially valid document. The address mentioned in the KYC form must match the address mentioned in the officially valid documents submitted.
For Foreign Natural Persons : For foreign individuals, acceptable address verification documents typically include a valid passport, a government-issued identity card containing an address, a driving license (if accepted under applicable jurisdiction), a recent utility bill/bank statement (as permitted under the guidelines), and Any other reliable and independent document as allowed by IFSCA
Regulated entities must ensure Documents are valid and not expired, Translations are obtained (if required) and Enhanced due diligence is applied where risk is higher
Compliance Responsibility of International Financial Services Centres Authority Regulated Entities
Entities regulated by the International Financial Services Centres Authority must verify the authenticity of OVDs, maintain proper documentation records, conduct Customer Due Diligence (CDD), apply enhanced due diligence (EDD) in high-risk cases, and ensure enterprise-wide AML risk assessment. Failure to comply may attract regulatory action.
Financial Intelligence Unit - India (FIU-IND): Strengthening the KYC Process by Avoiding 12 Common Mistakes
FIU-IND plays a central role in safeguarding India’s financial system from money laundering and terrorist financing. A strong Know Your Customer (KYC) framework is the first line of defense. Steps to Strengthen KYC : FIU-IND Implement automated screening and validation systems. FIU-IND also conducts periodic KYC audits and remediation and updates internal AML/CFT policies regularly, maintains detailed audit trails, and ensures continuous staff training. Below are 12 common KYC mistakes that reporting entities should avoid to strengthen compliance under AML/CFT requirements.
- Incomplete Customer Identification: Failing to collect full legal name, PAN/Aadhaar (where applicable), date of birth, and other mandatory identifiers.
- Accepting Invalid or Expired OVDs : Not verifying validity of Officially Valid Documents (OVDs) or accepting expired documents without proper justification.
- Address Mismatch Not Reviewed : Ignoring discrepancies between the KYC form and address proof submitted.
- Poor Beneficial Ownership (BO) Identification : Not identifying ultimate beneficial owners in companies, LLPs, trusts, or layered structures.
- Inadequate Risk Profiling : Applying a uniform approach instead of categorizing customers into low, medium, or high-risk segments.
- Failure to Apply Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) : Not conducting deeper scrutiny for Politically Exposed Persons (PEPs), High-risk jurisdictions, and complex ownership structures.
- Weak Ongoing Monitoring : Treating KYC as a one-time exercise instead of periodically reviewing and updating records.
- Ignoring Suspicious Transaction Indicators : Failure to correlate KYC data with transaction patterns.
- Poor Record Maintenance : Not retaining KYC records and supporting documents for the prescribed statutory period.
- Lack of Screening Against Sanctions Lists : Failure to screen customers against UN Sanctions Lists, domestic watchlists, and other regulatory alerts.
- Over-Reliance on Third Parties : Depending entirely on intermediaries without independent verification.
- Inadequate Staff Training : Employees unaware of AML red flags, documentation standards, or escalation procedures.
About Rajput Jain And Associates
Rajput Jain And Associates is a Rajput Jain And Associates consultancy firm providing comprehensive AML support to entities licensed by the International Financial Services Centres Authority. Services include enterprise-wide risk assessment (EWRA), drafting AML/CFT policies and procedures, customer due diligence (CDD) framework design, KYC review and remediation, and regulatory compliance advisory. Rajput Jain And Associates assists regulated entities in establishing robust AML/CFT controls, including strong customer identification and verification processes aligned with International Financial Services Centres Authority requirements.