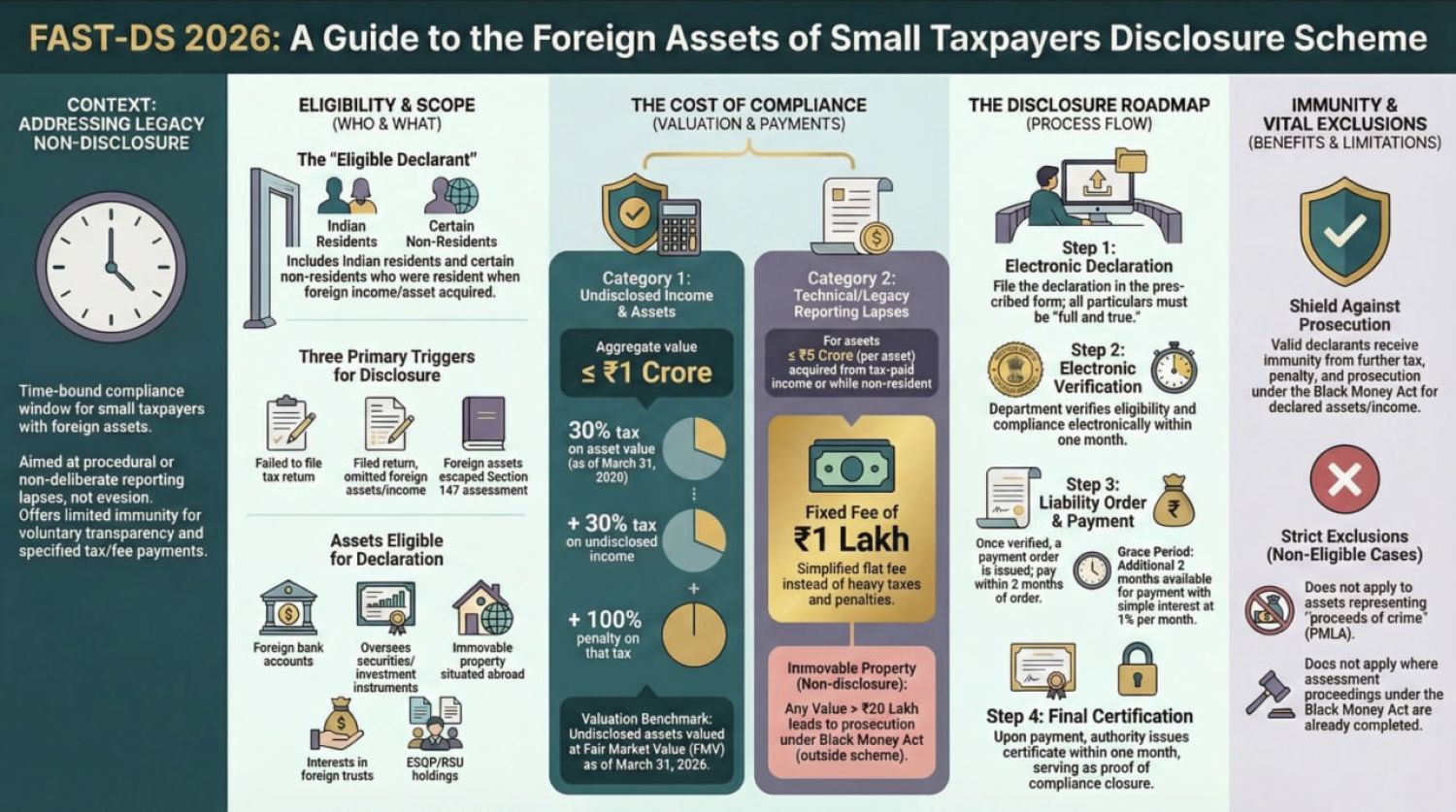
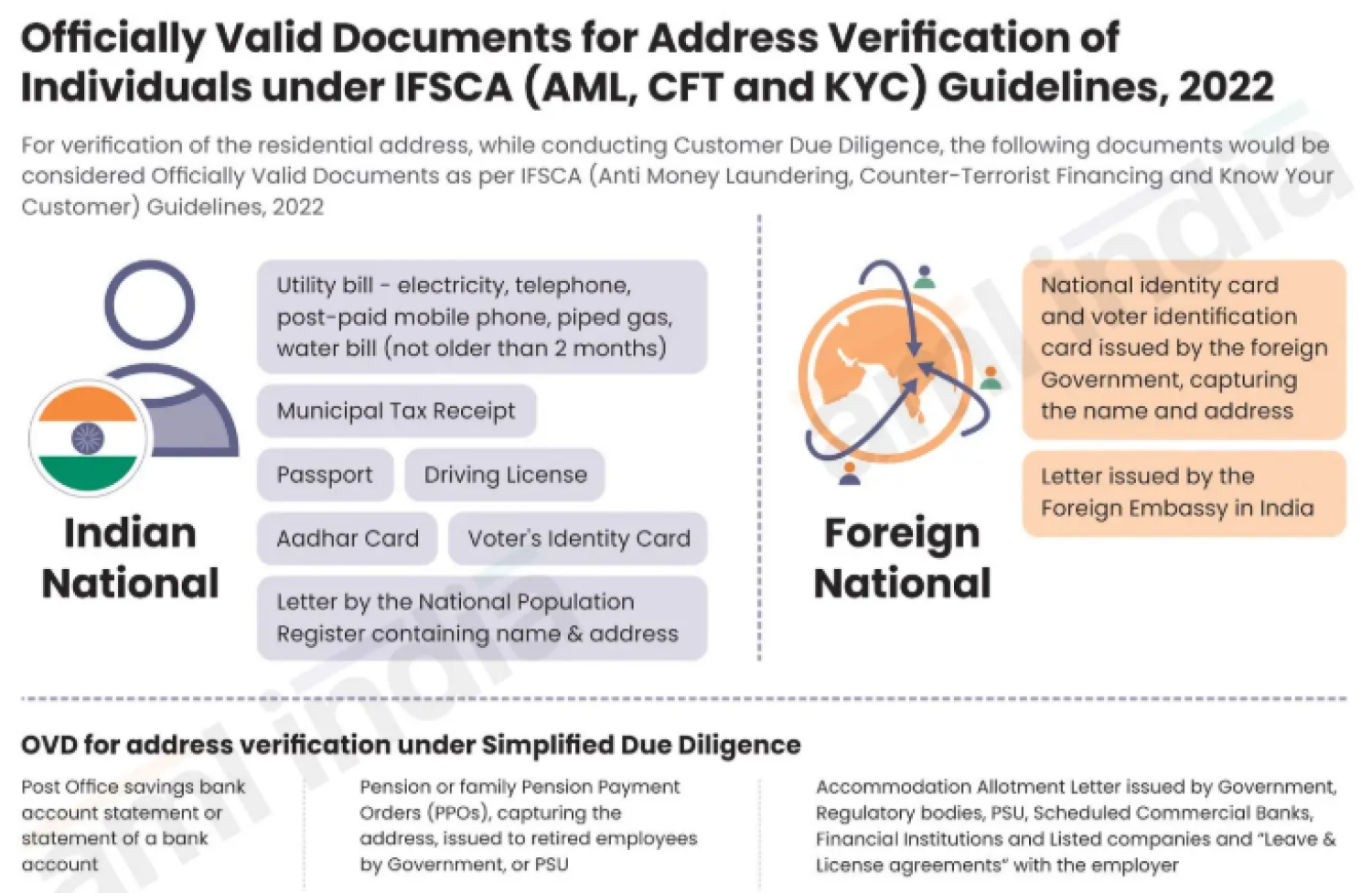
Table of Contents

BASIC FORENSIC AUDIT ASPECTS IN INSOLVENCY AND CODE BANKRUPTCY 2016
PURPOSE OF FORENSIC AUDIT INSOLVENCY AND BANKRUPTCY CODE
1. Events describing, if any,
- Financial Statements with inconsistencies / Red Flags,
- The misuse/diversion of bank funds;
- Overvaluation of current/fixed assets and their non-existence;
- Documentation breach;
- To misinterpret the financial statements sent from time to time to various banks in compliance with the terms of the loan agreements;
- Suppression and/or partial information of facts to the lenders on matters which have implications in lenders’ decision making.
2. Movements of unsecured loans within the defined period.
3. Comprehensive checking of receivables (to verify the validity of debtors/advances and to report on their recoverability and probability of failure, if any, including the age of receivables and the proof of receivables).
4. Examination of bank accounts for both deposits and deposit entries.
5. Outstanding statutory payments
6. Reasons for the DP decline in the account
7. Transactional analysis as per Sections 43, 45, 50, and 66 as per IBC 2016.
IMPORTANCE TRANSACTION TO BE COVERED IN THE FORENSIC AUDIT AND INSOLVENCY RESOLUTION & LIQUIDATION
An essential duty on the part of the RP is to file an application before the NCLT (Adjudicating Authority) to prevent transactions mentioned in the CODE (Section 25(2)(j)).
For this purpose, the RP must press for the Forensic Audit of the Accounts of the Corporate Debtor (CD) of the relevant time period to identify fraudulent activity that is not in the interest of the company and is carried out with a motive other than the interest of the CD. The CODE itself defines purchases in the following sections.
- Preferential transactions (Section 43)
- Avoidance of undervalued transactions (Section 45 & 46).
- Transactions defrauding creditors (Section 49)
- Extortionate Credit transactions (Section 50), and
- Transactions (Section 66) to defraud creditors or for any fraudulent purposes.
Transactions specifically being looked at by the forensic experts
Preferential transactions and relevant time [Section 43]
Avoidance of undervalued transactions [Section 45]
•Liquidator or resolution professional to apply to NCLT to:
1)declare undervalued transactions as void; and
2)reverse the effect of such transaction
3)A transaction shall be considered undervalued where the corporate debtor:
•makes a gift to a person; or;
•enters into a transaction with a person which involves the transfer of one or more assets for a consideration the value of which is significantly less and such transaction has not taken place in the ordinary course of business of the corporate debtor.
Transactions defrauding creditors [Section 49]
•Where NCLT is satisfied that undervalued transaction was deliberately entered into by such corporate debtor:
1)for keeping assets of the corporate debtor beyond the reach of any person who is entitled to make a claim against the corporate debtor; or
2)in order to adversely affect the interests of such a person in relation to the claim the NCLT may, then, make following order(s):
a)restoring the position as it existed before such transaction;
b)protecting the interests of persons who are victims of such transactions
Extortionate credit transactions [Section 50]
•A transaction shall be considered an extortionate credit transaction u/s 50(2) where the terms:
1)require the corporate debtor to make exorbitant payments in respect of the credit provided; or
2)are unconscionable under the principles of law relating to contracts - Regulation 11 of Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board Of India (Liquidation Process) Regulations, 2016.
3)The liquidator or the resolution professional as the case may be, may make an application for avoidance of such transaction to the NCLT if the terms of such transaction required exorbitant payments to be made by the corporate debtor
Fraudulent trading or wrongful trading [Section 66]
•If during the corporate insolvency resolution process or a liquidation process, it is found that any business of the corporate debtor has been carried on with intent:
–to defraud creditors of the corporate debtor or
–for any fraudulent purpose
the NCLT may on the application of the resolution professional pass an order that any persons who were knowingly parties to the carrying on of the business in such manner shall be liable to make such contributions to the assets of the corporate debtor as it may deem fit.
Persons not eligible to be resolution applicant [Section 29A]
a)un-discharged insolvent;
b)wilful defaulter;
c)classified as NPA as per guidelines of the RBI;
d)convicted for any offence punishable with imprisonment for 2 years or more;
e)is disqualified to act as a director under Co. Act;
f)is prohibited by SEBI from trading in securities or accessing the securities markets;
g)has been a promoter or in the management or control of a corporate debtor in which a preferential transaction, undervalued transaction, extortionate credit transaction or fraudulent transaction has taken place and in respect of which an order has been made by NCLT;
h)has executed an enforceable guarantee in favour of a creditor in respect of a corporate debtor under CIRP