INTRODUCTION
With the introduction of IBC 2016, there has been a transformative turnaround in the corporate distress resolution framework of India. The act provided a new lease of life to a Company whose future was earlier based on debt restructuring and sale. In India, most organizations are driven by their promoters. With the introduction of Section 29A under IBC 2016, the Company’s management and its related parties, being responsible for the insolvency of the Company, are restricted from regaining the control over the business. This results in an imbalance situation for MSMEs and was best addressed through Pre-Pack schemes.
Under a Pre-pack scheme, the debtor negotiates with the creditors to remain in the existing business and keep its operations as a going concern. It is best suited where the Company is going into insolvency due to any macroeconomic disturbances and not because of fault in the management. Pre-Packaged scheme aims at blending various corporate restructuring tools involving sale of assets of the debtor to another company, refinancing and interim financing, change in management etc., before the debtor goes into insolvency proceedings under IBC.
In the situation of pandemic, it was believed that there could be a possible rise in corporate and individual insolvencies, and the economies are presented with a big challenge to keep themselves afloat. The World Bank and the International Monetary Fund provided various measures and the same were implemented in a three-phased approach. In the first phase, some interim measures need to be taken to halt any sought of insolvency and debt enforcement activities. In the second phase, where a huge wave of insolvencies is expected, it may be feasible to address them by transitional measures, like providing a pre-pack scheme for out-of-court workouts, to lower the insolvency application. And the last phase would be for regular debt resolution tools to address the remaining debt application and maintenance of economic growth in the medium term.
Considering the reports of World Bank, the Indian Government came up with certain measures like extension of moratorium on loan repayments, providing infusion of liquidity into the banking system to provide credit to financially distressed entities, relief in asset classification banking norms. The Government also increased the threshold of default for filing of an insolvency application by the creditor from Rs. 1 lakh to Rs. 1 crore, to protect the interest of the MSMEs who were the most affected sector.
ORDINANCE FOR PRE-PACK SCHEME
The Government of India, Vide the Ordinance dated 04.04.2021, inserted a Chapter IIIA has been inserted in the IBC to deal with the pre-packaged insolvency resolution process. Under this, various conditions have been prescribed Section 54A for making an application for initiating pre-packed insolvency resolution.
PRE-PACK INSOLVENCY RESOLUTION PROCESS
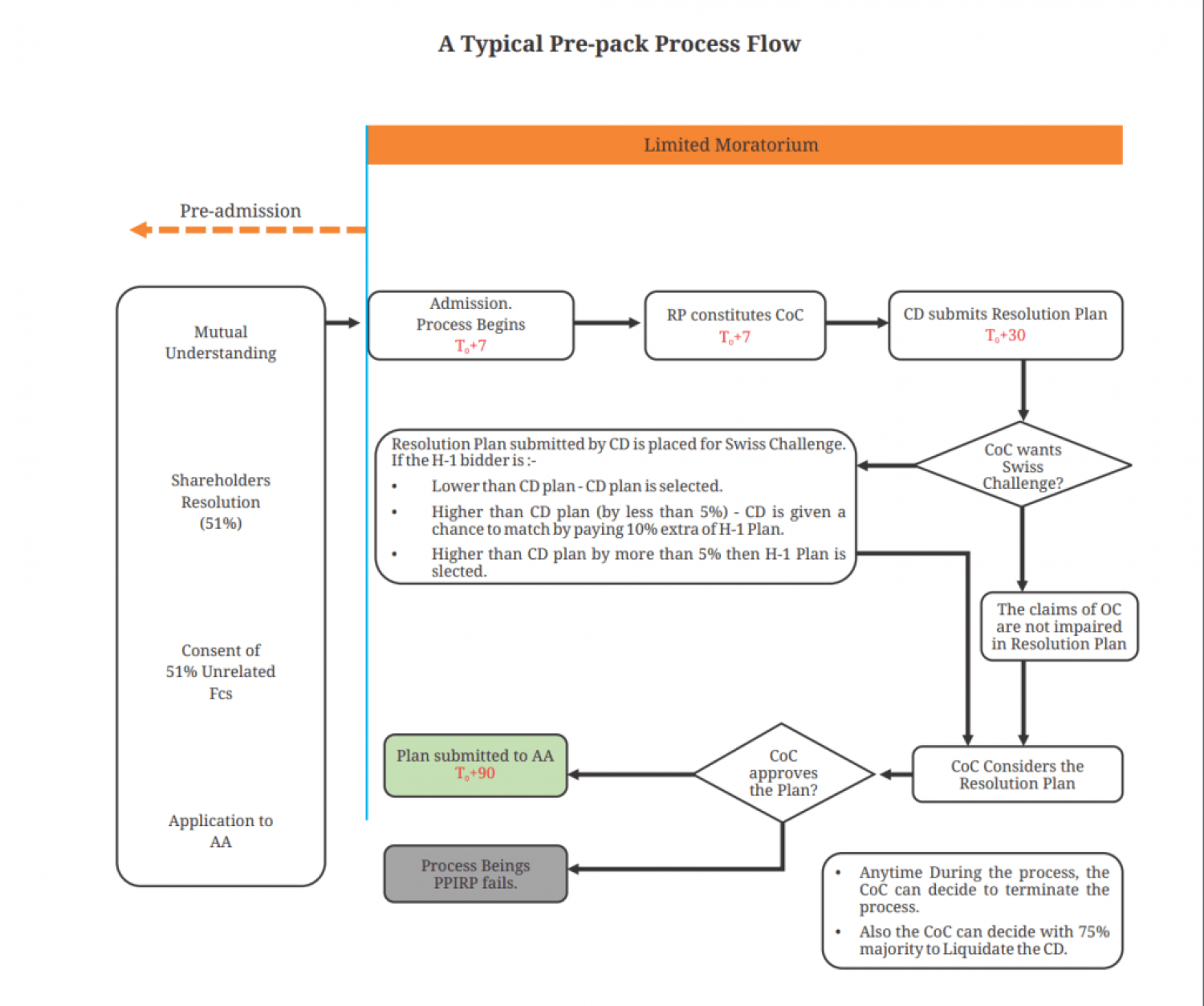
Once the pre-application conditions have been fulfilled, and the application has been made for initiation of Pre-pack Insolvency Resolution Process for a Corporate Debtor with the Adjudicating Authority, it takes only 4 more steps for the process to be completed. The steps are follows –
1. The Resolution Professional shall place the resolution plan in the meeting of COC and get it approved by them. And once their approval is received, the same be submitted to the Adjudicating Authority for their approval.
2. The Adjudicating Authority passes an order of termination of the process, in the following events –
- The COC, after discussing the plan, passed a resolution seeking termination.
- No resolution plan has been submitted to the Adjudicating Authority within 90 days, from the beginning of CIRP.
- The resolution plan has been rejected by the COC in their meeting.
- The approved plan by COC, has been rejected by the Adjudicating Authority.
3. The Adjudicating Authority after considering the plan, passes an order to initiate CIRP.
4. After the approval, if the COC approves a plan that does provide for change in the management to a third person, or the pre-pack process is required to be terminated, the Adjudicating Authority shall pass an order of liquidation.
SUMMARY OF PRE-PACK PROCESS
MECHANISM FOR MSME
Under the Pre-Packaged Insolvency Resolution Process, when a MSME unit defaults in payment of a debt, the existing promoter and its group, is allowed to propose a Base Resolution Plan to the creditors, to resolve their financial stress. The existing management is also allowed to continue to manage the unit during the period of insolvency resolution. This provision is in contrast with the CIRP, where the existing management (including the promoters) is totally kept out of the management of the company. In the CIRP, a Resolution Professional (RP) is appointed to manage the affairs of the company and the approvals of various aspects are made by the committee of creditors. And where any resolution plan is proposed and passed, the ongoing business is transferred to a new promoter. In the opposite case, the company goes into liquidation.
In the new PIRP, there is a new strategy called the ‘creditor-in-control’ model, which is the least disruptive model and will ensure the continuity of the business and preserve jobs.
The provisions of Pre-pack Insolvency for MSME shall not apply to cases that are pending in the court. They are applicable only on fresh cases, filed after the passing of the Ordinance
An Approval by 66% votes in favour, has to be obtained by the Corporate Debtor from its Financial Creditors, and the same shall not involve any vote by its related parties. The timeline for competition of Pre-Pack insolvency process for MSME is provided to be 120 days from the date of commencement.
The Adjudicating Authority will then make an order to admit or reject the Application, within 14 days of receipt of such application. However, in case the application is rejected, the Adjudicating Authority is required to provide a notice to the applicant to rectify the defect in the Application within 7 days.
Order for Moratorium shall also apply to the Pre-Pack insolvency Process for MSME. The Moratorium order shall be valid from the commencement of the pre-pack process and will cease to exist, when the process is either completed or terminated. Under the PIRP, the control and management of the business, lies with the current promoters and management of the Corporate Debtor. The Base Resolution Plan is also submitted by them and in case the same is not accepted, the Resolution Professional shall invite prospective Resolution Applicants to submit a Resolution Plan.
The proposed plans are placed in the meeting of the Committee of Creditors and the same be approved by 66% votes in favour of the plan. The COC is free to initiate the liquidation of the business, any time before the approval of the resolution plan, by passing a resolution with 66% votes in favour of it. The Adjudicating Authority having any information related to fraudulent conduct of the Company and/or gross mismanagement, may pass an order of liquidation.
CREDITOR’s PERSPECTIVE
The main focus of the amendments was on how MSMEs can be facilitated more under IBC. The creditor’s perspective is also important on this, because the success of the new mechanism would depend a lot on adoption by the creditors, especially by the banks.
It is important to remember that the plan gets implemented only if creditors with at least 66% of vote share give their consent for filing an application under PIRP. Also, an RP proposed by creditors and approved by creditors having 66% of the vote share can only be appointed, though the costs involved in the PIRP are to be borne by the MSME unit. Many observers believed that PIRPis applicable only to the corporates among MSMEs and not to the sole proprietor and partnerships firms. This had led to reduction in the scope of PIRP as a beneficial mechanism sustains only for MSMEs.
It is generally believed that under CIRPs there is a greater chance of success, where the corporate debtor is a going concern. In respect of PIRP, greater emphasis is given on the continued management of the MSME unit by the existing management and saving jobs of the employees of the unit.
PRE-PACK INSOLVENCY RESOLUTION PROCESS INVOLVES HAIRCUTS
The most important aspect that arises in the PIRP, is that of the haircut in claim settlement. Under CIRP, there are many successful resolutions, but some witnessed handsome haircuts in the claim amount. The creditors, with no other option left, have to accept such haircuts.
But the same cannot be true for the PIRP mechanism. PIRP cases are initiated relating to existing defaults and not to long term NPAs. Further, in the cases of advances provided to the MSMEs, the collateral margin is pretty much higher in comparison to the large corporates going under CIRP. Thus, the value to collateral assets would be higher and enough to completely settle the claim.
OTHER REGULATIONS ON PRE-PACK INSOLVENCY RESOLUTION PROCESS
As discussed above, the main reason for the ordinance was to provide a temporary mitigation between MSMEs, who are under financial distress due to Covid-19. PIRP is seen as an alternative insolvency resolution mechanism for the benefit of MSMEs in the long term.
Considering the other measures taken by the Central Government and the Reserve Bank of India, we can clearly see that the Government is constantly looking for continuation of the MSME sector in India. RBI provided the benefit by providing moratorium on payment of instalments and interest on term loans, relaxations in the drawing power margins for working capital loans, reassessment of working capital cycles. Apart from this, the central government announced a Rs. 3-Lakh Crore Credit guarantee scheme for MSMEs, where they would be provided with some amount of credit, without submitting any security/collateral.
ROLE OF RBI IN PRE-PACK INSOLVENCY RESOLUTION PROCESS
The RBI has taken several steps, for the restructuring of stressed assets and reduction of non-performing assets. But considering the insolvency process, RBI has not provided any sought of path, which the banks and financial institutions shall take for the recovery of their dues. As a result, there is a lack of recognition given to PIRP, and the lenders are left to themselves, for choosing the right path of recovery. And it is most likely that the creditors will focus more on recovery of their dues rather than approving a plan which will revive the business.
Such working will not work in the long run, and will not be in the broader interests of the economy. Thus, in making PIRP realize its potential as a successful resolution mechanism, RBI is required to take measures providing relaxations in asset classification norms for accounts going through PIRP, so that the lenders do not feel that their interests would be not properly served under PIRP.
DISADVANTAGES
- TRANSPARENCY – The major area for the success of PIRP, would be the transparency of working. Transparency is required in the working of the existing management coupled with the role played by the Resolution Professional. This approach is a mix of operating by the creditors and the debtor, thus, in the best interest of the company, they need to be dedicated and transparent in their working for other stakeholders as well.
- APPROVAL FROM ADJUDICATING AUTHORITY – As discussed above, the Resolution plan, placed in the meeting of COC, shall be approved with the consent of 66% of the Financial Creditors. However, the same be implemented only after the approval order received from the Adjudicating Authority/ NCLT. Thus, this stage of PIRP is time consuming, as well as, has an element of uncertainty.
EFFECTIVENESS
As per the ordinance, PIRP is required to be completed within 120 days, from the date of making application to NCLT, including 30 days provided for the Adjudicating Authority to approve the resolution plan. Since the management is under the existing members, the cost involved in hiring a RP for the management of the business is also saved. Also, the resolution plan is submitted to the creditors and their consent is obtained in advance, before initiating the process of PIRP, thus reducing the scope for litigation. The RP appointed will have to focus only on the resolution plan and its approval from the Committee of Creditors and the NCLT. Moratorium is also applicable for PIRP and the NCLT order under PIRP is also binding on all stakeholders such as corporate debtors, its employees, shareholders, creditors, and the government departments.
CONCLUSION
With the introduction of the Pre-Pack insolvency for the MSME, the Indian Insolvency Resolution Framework, has been forfeited. Since the Pre-Pack is limited to Micro, Small and medium enterprise, the Government is planning to accommodate other Corporate as well. However, the success and the failure of MSME Pre-pack should be considered, for every form of business, as they have different features and working conditions.
For the success of PIRP, a steady cooperation is required between different classes of creditors and debtors and unlike in the Insolvency Proceedings under IBC, the promoters, in a PIRP, shall continue to be in control of the business and where they fail to provide necessary information related to the scheme and valuation of the assets to the creditors, the pre-packs scheme would serve no purpose to the creditors, and the same be terminated. The success of Pre-Packs depends directly on the role played by the participants of the process like the Management, Financial Creditor, Resolution Professional and the Adjudicating Authority. Apart from the above benefits, there is a requirement to have adequate checks and balances throughout the process. The important information, related with the management of the Corporate Debtor, requires complete disclosure with strict consequences in cases of any wilful suppression. Also, the related party and/or connected party disclosure, sale/alienation of assets at deeply discounted prices is required.
<table border="1" cellpadding="0" "="">
STAGE OF PROCESS
RELEVANT PARTICULAR
PROVISIONS
DETAILS
SECTION
INITIATION STAGE
APPLICATION FOR PRE-PACK INSOLVENCY PROCESS
APPLICABLE TO MSMES HAVING DEFAULT, NOTIFIED UNDER SECTION 54 OF IBC.
AS PER THE NOTIFICATION DATED 9TH APRIL 2021, THE MINIMUM DEFAULT HAS BEEN NOTIFIED AS INR 10,00,000/-.
SECTION 54A (1), (2)
APPOINTMENT OF RESOLUTION PROFESSIONAL
ANY UNRELATED FINANCIAL CREDITOR’S HOLDING AT LEAST 10% OF VALUE, MAY PROPOSE NAME OF THE INSOLVENCY PROFESSIONAL, AND THE SAME BE APPROVED BY 66% VOTES IN FAVOUR IN MEETING OF COC.
SUCH A PERSON APPOINTED BE ELIGIBLE TO BECOME RP AS PROVIDED UNDER REGULATION 7 OF IBC
SUCH APPROVAL IS REQUIRED TO BE OBTAINED IN THE MEETING OF COC. AND THE NOTICE FOR SUCH MEETING BE SENT TO ALL UNRELATED FINANCIAL CREDITORS, AT LEAST FIVE DAYS PRIOR TO THE MEETING.
SECTION 54A (1) (E)
REGULATION 7
DUTIES OF THE INSOLVENCY PROFESSIONAL
THE INSOLVENCY PROFESSIONAL IS REQUIRED TO FILE AN PREPARE A REPORT CONFIRMING WHETHER THE CORPORATE DEBTOR MEETS THE REQUIREMENTS UNDER SECTION 54A (2), FILE SUCH REPORTS AS MAY BE REQUIRED.
WHERE THE APPLICATION FOR INITIATION OF PRE-PACK PROCESS IS NOT FILED WITHIN 90 DAYS FROM THE APPROVAL OF SCHEME, THE RP SHALL NOT BE LIABLE TO PERFORM ANY FURTHER DUTY.
THE REPORT BE MADE, AS SET IN FORM P8.
THIS REPORT BE FILED WITH THE ADJUDICATING AUTHORITY.THE FORMS AS MAY BE SPECIFIED, SHALL BE FILED ON AN ELECTRONIC PLATFORM.
SECTION 54B READ WITH REGULATION 13
FILING OF APPLICATION
FILING BY THE CORPORATE DEBTOR
THE APPLICATION MUST BE FILED BY THE CORPORATE DEBTOR, NOT LATER THAN NINETY DAYS FROM THE DATE OF APPROVAL BY THE UNRELATED FINANCIAL CREDITOR’S. THE APPLICATION SHALL CONTAIN SEVERAL DECLARATIONS.
THE APPLICATION SHALL SPECIFY THE NAME AND DETAILS OF APPOINTMENT OF THE RESOLUTION PROFESSIONAL APPROVED BY THE COC AND BE FILED IN ACCORDANCE WITH FORM 1 OF THE PRE-PACK RULES
SECTION 54C, READ WITH REGULATION 16 TO 18, AND RULE 4
APPROVAL BY ADJUDICATING AUTHORITY
THE AA SHALL ADMIT OR REJECT THE APPLICATION WITHIN FOURTEEN DAYS FROM THE DATE OF FILING
THE TIME PERIOD PRESCRIBED IS NOT COMPULSORY IN NATURE, IT IS JUST A SUPPORTIVE TIME FRAME.
SECTION 54C (4)
INITIATION OF PIRP
PUBLIC ANNOUNCEMENT
PUBLIC ANNOUNCEMENT BE MADE WITHIN TWO DAYS OF PIRP COMMENCEMENT DATE IN FORM P9, AND BE SENT TO EVERY CREDITOR
IN THIS TYPE OF PUBLIC ANNOUNCEMENT, THE RP IS REQUIRED TO SEND NOTICE TO EACH AND EVERY CREDITOR PERSONALLY, THUS BECOMES A FRUVIROUS TASK.
SECTION 54E (1) (C), READ WITH REGULATION 19
CLAIMS SUBMITTED BY THE CORPORATE DEBTOR
THE RESOLUTION PROFESSIONAL IS REQUIRED TO CONFIRM THE LIST OF CLAIMS SUBMITTED TO IT BY THE CORPORATE DEBTOR, AND INFORM EVERY CREDITOR REGARDING ITS CLAIMS, SEEKING OBJECTIONS IF ANY. SUCH OBJECTIONS BE COMMUNICATED WITHIN 7 DAYS FROM THE RECEIPT OF NOTICE.
THE LIST OF CLAIMS BE MAINTAINED IN FORM P-10, AND SHALL BE UPDATED AND MADE AVAILABLE FOR INSPECTION BY CREDITORS, MEMBERS, PARTNERS, DIRECTORS AND GUARANTORS.
IT IS ALSO PRESCRIBED THAT THE CORPORATE DEBTOR SHALL FILE SUCH CLAIM WITH RP, WITHIN 2 DAYS AFTER THE COMMENCEMENT OF PIRP.
TO AVOID A LENGTHY PROCESS, THE CREDITORS ARE ADVISED THAT THE OBJECTION MAY BE FILED BY THE CREDITORS ON THE BASIS OF THE PUBLIC ANNOUNCEMENT ITSELF, WITHIN SAY, FIFTEEN DAYS FROM THE DATE OF SUCH PUBLIC ANNOUNCEMENT.
SECTION 54F (2) (A) TO (D), READ WITH REGULATION 20
SECTION 54G (1)
FORMATION OF COMMITTEE OF CREDITORS
COMMITTEE OF CREDITORS SHALL COMPRISE OF UNRELATED FINANCIAL CREDITOR’S AND THE SAME BE FORMED WITHIN SEVEN DAYS FROM COMMENCEMENT OF PIRP.
IN CASE THERE ARE NO FINANCIAL CREDITORS, THE TEN LARGEST OPERATIONAL CREDITOR, ALONG WITH ONE REPRESENTATIVE OF EMPLOYEE AND WORKERS EACH, SHALL CONSTITUTE THE COMMITTEE OF CREDITORS.
SUCH COMMITTEE IS REQUIRED TO BE FORMED, FOR APPROVAL OF ALL THE KEY ASPECTS RELATED TO THE BUSINESS. THE SAME INCLUDES THE APPROVAL OF RP, RESOLUTION PLAN ETC.
SECTION 54I (1), (3) READ WITH REG 24-26
MEETING OF COC
THE FIRST MEETING SHALL BE CONDUCTED WITHIN SEVEN DAYS OF ITS CONSTITUTION.
A NOTICE OF THE MEETING SHALL BE SENT TO ALL COMMITTEE OF CREDITORS MEMBERS, AT LEAST THREE DAYS PRIOR TO THE SCHEDULED DATE, AS DECIDED BY THE COMMITTEE OF CREDITORS, AND THE QUORUM SHALL BE THE FINANCIAL CREDITORS, HOLDING HAVING AT LEAST 33% OF VOTING RIGHT IN TOTAL.
THE QUORUM SHALL BE CONSTITUTED ON THE BASIS OF THE VOTING SHARE AND NOT THE NUMBER OF CREDITORS. HOWEVER, THIS MEANS THAT A SINGLE CREDITOR CAN ALSO CONDUCT A MEETING, WHICH SHALL NOT BE FAIR FOR OTHER CREDITORS. THUS, APART FROM THE 33% CRITERIA, AT LEAST 2 FINANCIAL CREDITORS BE ALSO AVAILABLE.
THE CORPORATE DEBTOR IS ALLOWED TO ATTEND THE MEETING OF COC, BUT THEY CANNOT VOTE AND PARTICIPATE IN THE MEETING.
SECTION 54I (2), READ WITH REGULATION 27 TO 34
RESOLUTION PLAN BY THE CORPORATE DEBTOR
THE CORPORATE DEBTOR IS REQUIRED TO SUBMIT A ‘BASE RESOLUTION PLAN’ TO THE RESOLUTION PROFESSIONAL WITHIN TWO DAYS FROM THE COMMENCEMENT OF PIRP.
THE COC MAY INVITE PLANS FROM OUTSIDE ORGANISATION WHERE -
(A) THE BASE PLAN IS REJECTED BY THE COC
(B) THE BASE PLAN IS AGAINST ANY OF THE RIGHT OF THE OPERATIONAL CREDITORS.
IN SUCH A SCENARIO, THE RP IS REQUIRED TO FLOAT AN INVITATION FOR RESOLUTION PLAN FROM ELIGIBLE RESOLUTION APPLICANT, AND THE SAME BE MADE WITHIN 21 DAYS FROM THE COMMENCEMENT DATE
THE COMMITTEE OF CREDITORS SHALL CONSIDER THE BASE RESOLUTION PLAN IN THEIR FIRST MEETING.
ALL THE RESOLUTION PLANS AS PROVIDED BEFORE THE COC, SHALL BE JUDGED ON THE BASIS OF VARIOUS QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE BASIS PROVIDED BY THE ORDINANCE.
SECTION 54K, READ WITH REGULATION 42 TO 47
APPROVAL OF RESOLUTION PLAN BY COC
ANY PLAN INVITED FROM OUTSIDE THE BUSINESS IS REQUIRED TO BE SPECIFIED AS THE SIGNIFICANTLY BETTER THAN THE BASE PLAN, FOR ITS APPROVAL.
WHERE NO PLAN IS RECEIVED FROM THE OUTSIDER, THE RP SHALL CONTINUE WITH THE IMPLEMENTATION OF BASE PLAN.
THE COC IS REQUIRED TO SCRUTINIZE THE PLAN, NOT ONLY FOR SATISFACTION OF THEIR CLAIM, BUT ALSO IN RESPECT OF OPERATIONAL CREDITOR’S CLAIM.
SECTION 54K (8) TO (12), READ WITH REGULATION 48
POST APPROVAL
SUBMISSION OF PLAN TO NCLT
RESOLUTION PLAN, APPROVED BY COMMITTEE OF CREDITORS SHALL BE SUBMITTED TO THE ADJUDICATING AUTHORITY, WITHIN 90 DAYS FROM THE COMMENCEMENT DATE.
AFTER RECEIVING THE ORDER OF APPROVAL FROM NCLT, THE RP IS REQUIRE TO IMPLEMENT THE RESOLUTION PLAN.
IN CASE THE SAME IS REJECTED BY THE NCLT, AND THE COC PASS A RESOLUTION FOR TERMINATION OF THE PIRP, THE SAME BE TERMINATED.
ALONG WITH THE RESOLUTION PLAN, THE RESOLUTION PROFESSIONAL SHALL ALSO SUBMIT A COMPLIANCE CERTIFICATE TO NATIONAL COMPANY LAW TRIBUNAL IN FORM P-12.
SECTION 54L, READ WITH REGULATION 49
OTHER PROVISIONS
MEETING AND COMMUNICATIONS
THE MEETINGS OF COC TO BE HELD EITHER IN ELECTRONIC OR PHYSICAL MODE OR IN A COMBINATION OF BOTH; & ALL COMMUNICATIONS BE MADE BY ELECTRONIC MEANS.
REGULATION 3
ESSENTIAL SUPPLIES OF GOODS AND SERVICES
THE ESSENTIAL GOODS AND SERVICES, TO THE EXTENT THESE ARE NOT A DIRECT INPUT TO THE OUTPUT PRODUCED OR SUPPLIED BY THE CORPORATE DEBTOR, BE PROVIDED TO THE BUSINESS DURING PIRP.
PIRP COST
AS DISCUSSED ABOVE, EVERY STEP REQUIRE SOME COST TO BE INCURRED LIKE RAISING INTERIM FINANCE, FEE PAYABLE TO IP, COSTS INCURRED IN RUNNING THE BUSINESS OF THE CORPORATE DEBTOR FEE PAYABLE TO THE AR OF CLASS OF CREDITORS, AND SUCH COSTS DIRECTLY RELATED TO THE PRE-PACK INSOLVENCY RESOLUTION PROCESS, AND APPROVED BY THE COMMITTEE.
THE AMOUNT OF FEE TO BE PAID TO THE RP, SHALL CONSTITUTE THE EXPENSES AND FEES FOR THE PERIOD, AFTER THE COMMENCEMENT OF PIRP.
HENCE, THERE IS A REQUIREMENT TO WIDEN THE PIRP COST DEFINITION, TO COVER THE COSTS INCURRED ON AND FROM THE DATE OF APPROVAL BY THE FINANCIAL CREDITOR’S.
SECTION 5 (23C) R/W
REGULATION 6
ACCESS TO BOOKS OF ACCOUNTS AND RECORDS
THE RESOLUTION PROFESSIONAL IS ALLOWED TO ACCESS THE BOOKS OF ACCOUNT, RECORDS, AND OTHER DOCUMENTS, TO THE EXTENT RELEVANT FOR DISCHARGING HIS DUTIES.
IT INCLUDES ACCOUNTS HELD BY -
(A) MEMBERS, PROMOTERS, PARTNERS, DIRECTORS AND JOINT VENTURE PARTNERS OF THE CORPORATE DEBTOR.
(B) PROFESSIONALS AND ADVISORS APPOINTED BY THE CORPORATE DEBTOR
(C) DEPOSITORIES OF SECURITIES.
(D) REGISTRIES THAT RECORDS THE OWNERSHIP OF ASSETS.
(E) CONTRACTUAL COUNTERPARTIES OF THE CORPORATE DEBTOR.
REGULATION 9
APPOINTMENT OF OTHER EXPERTS FOR ASSISTANCE TO RP
THE RESOLUTION PROFESSIONAL MAY APPOINT A PROFESSIONAL FOR ASSISTANCE WITH RESPECT TO PIRP.
THE RP IS NOT ALLOWED TO OUTSOURCE, ANY OF HIS PRIMARY DUTIES. THEY CAN ONLY TAKE ADVICE IN RESPECT OF THE SAME.
SECTION 54F (3) (E) READ WITH REGULATION 10.
DISCLOSURE OF PIRP COST
THE RP IS REQUIRED TO DISCLOSE, ALL THE COST PERTAINING TO PIRP, AS PER THE CODE OF CONDUCT AS SET OUT IN THE IBBI (INSOLVENCY PROFESSIONALS) REGULATIONS, 2016.
REGULATION 11
PRESERVATION OF RECORDS AND ACCOUNTS
THE RP IS REQUIRED TO PRESERVE THE RECORDS, IN PHYSICAL AS WELL AS ELECTRONIC FORM. THE RECORDS SHALL RELATE TO THE PROCESS OF THE CORPORATE DEBTOR AS PER THE RECORD RETENTION SCHEDULE.
THE BOARD SHALL ISSUE A CIRCULAR PROVIDING FOR THE MANNER IN WHICH THE RECORDS OF THE PRE-PACK INSOLVENCY RESOLUTION PROCESS SHALL BE PRESERVED.
REGULATION 12

















