Key provisions of NRI Taxability
Page Contents
Key provisions of NRI Taxability
-
PERMANENT ACCOUNT NUMBER
-
- PAN card number is a ten-digit number designed with the unique alphanumeric combination. This number is required to be taken by all entities requiring payment of tax in India.
- It is issued by the Indian Income Tax Department.
- PAN card also serves as the national identification number in India.
NRI PAN CARD FEATURES
-
- APPLICATION FORM: A person can apply for obtaining a PAN card by filing an application (i.e., Form 49AA in case of Non-Residents).
Details to be provided in the form correctly filled up & signed by the applicant along with 2 passport size photographs and the application be submitted online on the NSDL portal.
-
- MEANS OF ID AND ADDRESS PROOF: PAN number serves as the ID or Address Proof of the person in whose name PAN has been issued.
- REQUIREMENT: Every person required to undertake any financial transaction or is required to pay tax in India is compulsorily required to have a PAN card.
- ITR FILING: As discussed in above point, a person requiring to file ITR in India is required to have a PAN card.
- MEANS OF TRANSACTION TRAIL: PAN card also provides a means for identification for all financial transactions and helps in keeping a watch on the same.
- CHANGES IN PAN CARD: PAN is a very crucial document and the same be kept in updated form.
NSDL portal also provides for PAN Correction/Change Application to het the latest information updated in the prescribed form with the IT Department.
INCOME TAX SLAB RATES FOR NRI
-
- Every person earning income from any source in India, including the incomes which accrue or deemed to accrue in India, are liable to pay Income Tax on such income.
- Same applies to an NRI, they are also liable to pay tax on their income, which is earned in India for example Interest Income from investment made in India, Rental Income from any property situated in India etc.
- India Taxation rates are progressive in nature i.e., with the increase in income, tax rates also increase gradually.
- In the Union Budget which is announced every year in the month of February, Finance Act is modified by passing the modification bill in order to give effect to the Income Tax Act, 1961.
- Tax slabs for resident individual of India below the age of 60 years and that of a NRI are same.
-
NRI TAX SLABS WITH EFFECT FROM AY 2021-22
| TAXABLE INCOME (RS) | TAX RATE |
| 0 – 2,50,000 | NIL |
| 2,50,000 – 5,00,000 | 5% |
| 5,00,000 – 7,50,000 | 10% ON EXCESS OF 5,00,000 + 12,500 |
| 7,50,000 – 10,00,000 | 15% ON EXCESS OF 7,50,000 + 37,500 |
| 10,00,000 – 12,50,000 | 20% ON EXCESS OF 10,00,000 + 75,000 |
| 12,50,000 – 15,00,000 | 25% ON EXCESS OF 12,50,000 + 1,25,000 |
| ABOVE 15,00,000 | 30% ON EXCESS OF 15,00,000 + 1,87,500 |
- Example
- Following are the details of Mr. X, Y and Z. They all are NRI and are having the following income and deductions in the FY 2020-21
| PARTICULARS | X (RS) | Y (RS) | Z (RS) |
| GROSS TOTAL INCOME | 4,50,000 | 8,50,000 | 14,50,000 |
| DEDUCTIONS | 1,50,000 | 1,50,000 | 1,50,000 |
| TAXABLE INCOME | 3,00,000 | 7,00,000 | 13,00,000 |
| TAX LIABILITY | NIL | 32,500 | 1,37,500 |
-
ADDITIONS TO TAX LIABILITY
-
- HEALTH AND EDUCATION CESS: On the above tax liability, a Health and Education Cess @4%, is charged on the value of the tax liability including Surcharge, if any. This cess is applied on the tax liability of every person irrespective of their age and residency.
- SURCHARGE APPLICABLE: A fixed percentage of Surcharge is levied on the tax liability; in case the total taxable income of the individual exceeds the limit prescribed. The rates are as follows –
10% for Income exceeding Rs 50 Lakh and up to Rs 1 crore.
15% for Income exceeding Rs 1 Crore and up to Rs 2 crores.
25% for Income exceeding Rs 2 Crore and up to Rs 5 crores.
37% for Income exceeding Rs 5 Crore
Such rate of surcharge is applied and added to the value of Tax liability.
- From the above data, the tax slab and rates applicable to NRI is pretty much clear and the same be used to answer the following questions –
-
- What rate of tax is applicable to NRI in India?
- Is there any special tax treatment for NRI?
- Up to what income is exempt for NRIs in India?
-
Read our articles: How to file a return of TDS online
-
TRANSFER OF IMMOVABLE PROPERTY BY NRI AND TAX IMPLICATIONS
- NRIs can acquire immovable property in India by different means as prescribed under the FEMA act. Now where the NRIs wish to sell this immovable property, they are required to keep the taxation aspect in mind Because of sale transaction by NRIs,
- There are lots of tax issues arise before them. Same common questions arising in their mind could be –
- What will be the taxation aspect involved in such transfer?
- How will the capital gain be calculated and what rate be applicable?
- What are the stamp duty regulations to be applied?
- In what way can the capital gain be reduced or what advantages can they take while making the payment for tax?
- How will the expenses to be made while transferring the property be handled?
- Will there be any TDS provision that will arise?
- How will the cost of acquisition be identified in case the property is received as a gift or inherited to them?
-
FEATURES OF TRANSFER OF IMMOVABLE PROPERTY
-
GAINS ON SALE
– Immovable property comes in the definition of capital asset as prescribed in the law. Being a capital asset, any gain arising on the transfer of same be termed and taxed as a capital gain.
-
COMPUTATION –
The amount of capital gain is determined by reducing the value of sale consideration by the cost of acquisition and the expenses incurred for undertaking the sale of such property.
- In case the amount of sale consideration is less than the acquiring cost and expenses on sale, there exist a capital loss, otherwise, it will be a capital gain.
-
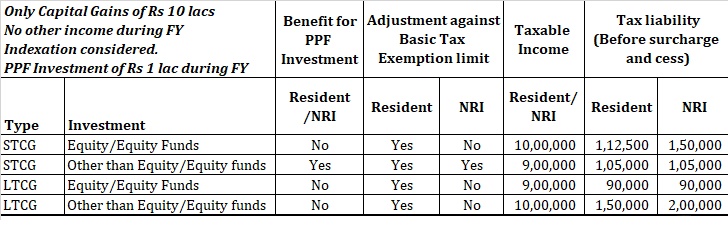
INDEXATION BENEFIT –
Indexation benefit refers to the benefit provided for calculation of cost of acquisition, by increasing such cost by taking the inflation index as base.
- Such a benefit is available is the asset is a long-term asset i.e., it was hold by the owner for at least 3 years.
-
INHERITED OR GIFTED PROPERTY –
where the immovable property was acquired by NRI by way of Inheritance/Gift,
- then the benefits of previous owner will pass on to the person who acquires such property, in terms of holding period and cost of acquisition.
-
STAMP DUTY VALUATION –
As per the provisions of Section 50C of the Income Tax Act, an individual shall not sell a property for a consideration, where stamp duty is more than the 110% of the consideration.
- In such a case, the stamp duty value is considered as the actual amount of consideration for determining the capital gain.
-
MEANS TO REDUCE TAX LIABILITY
– a person can reduce their capital gain tax, by adopting certain tax planning tools, like
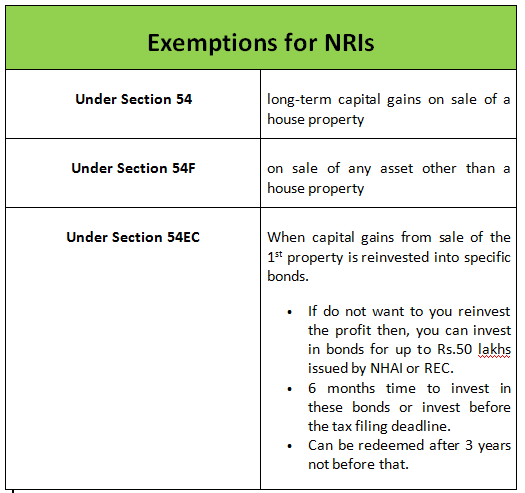
- Investing in Long Term Specified Bonds (i.e., 3-year lock-in bonds of NHAI/REC)
- Purchasing a new house property within specified time period.
-
TDS IMPLICATIONS –
As per section 195 of Income Tax Act, 1961, buyers of the immovable property need to deduct TDS from the payment to be made to NRIs/PIOs.
- Read our articles: New TDS deduction No cash transactions exceeding 1 Crore -Section 194N
INCOME TAX RETURN FILING FOR NRI
-
- Income Tax Return Filing comes under the annual compliance by the Income Tax authorities in India. Every taxpayer of India is required to file an annual income tax return.
- NRIs are also not exempt, rather their filing is more important.
COMPONENTS OF ITR FILLING ON NRI
- Some common source of income derived by NRIs in India are –
-
- Interest received from balance kept in NRI accounts.
- Rent received from House Property situated in India.
- Capital Gains arising from sale of securities of Indian Companies.
- Dividend income received by investing in shares and mutual funds in India.
- Capital Gain arising from sale of immovable property situated in India.
PROCESS OF FILING OF ITR FOR NRI
-
- The person is required to collect all the documents supporting the source and nature of the income to be disclosed.
- Next, they need to prepare their ITR return on the Income Tax portal. The same can be done by themselves or with the help of some expert.
- After preparation of ITR, the same be submitted with the requisite amount of tax, as calculated by the inbuilt tax calculator.
- After making payment of tax, the ITR form will be submitted to the IT department for verification purposes.
- Online verification of ITR and supporting documents be done and the same be communicated by the online mode using Emails.
DUE DATE FOR FILING ITR FOR NRI
- In India, individuals including NRIs who come under the Non-Audit class are required to file their ITR by July 31 of Assessment Year.
- With the outbreak of Covid 19, this date has been extended to Nov 30, 2020 by the Finance Minister, hence, the extended due date for filing FY 2019-20 is Dec 31, 2020 and for those whose accounts require audit, the due date is extended up to Jan 31, 2021.
Benefits to NRI on Filing of ITR
-
LEVY OF INTEREST PENALTY
In case an assessee fails to file their ITR within the prescribed time, an interest @1% is charged for every month of default and part thereof.
-
PENALTY FEE
Along with interest penalty a fee be also charged with an amount ranging from RS 1,000 – 10,000.
-
DELAY IN REFUND PROCESSING
In case the amount of tax paid is less than the actual tax liability, the IT department issues a refund for the same. In case the ITR is filed after the due date, the refund also gets delayed.
-
VERY LESS TIME AFTER THE DUE DATE
- a person is in receipt of plenty of time to file their return. Where it is not done in the prescribed time, the time after due date is very less for late filers.
-
CARRY FORWARD OF LOSS
In case of business income, an assessee is allowed to carry forward their loss of current year for 8 succeeding assessment years.
the same is disallowed in case the assessee fails to file ITR within due date in each of the AY.
-
PROSECUTION AND SCRUTINY
In late filing of ITR, the chances of prosecution and scrutiny of documents by the department is pretty high
Time Limit to file Updated ITR Returns For AY 2021-22

Popular Articles :
Tax filing Changes are taken into account when filing ITR for FY-2019-20
Section 54F, read with section 263, of the Income-tax Act, 1961