INDIA LIAISON OFFICE MANAGEMENT
Page Contents
India Liaison office management
Foreign companies planning to set up their business operations in India need to start a liaison office. The main purpose of starting a liaison office is to explore possible business opportunities in India by gathering relevant business information.
This helps the companies to develop a business strategy to tap the existing business potential in India. A liaison office also acts as a marketing channel to provide business information about the parent company and its products to the prospective clientele in India.
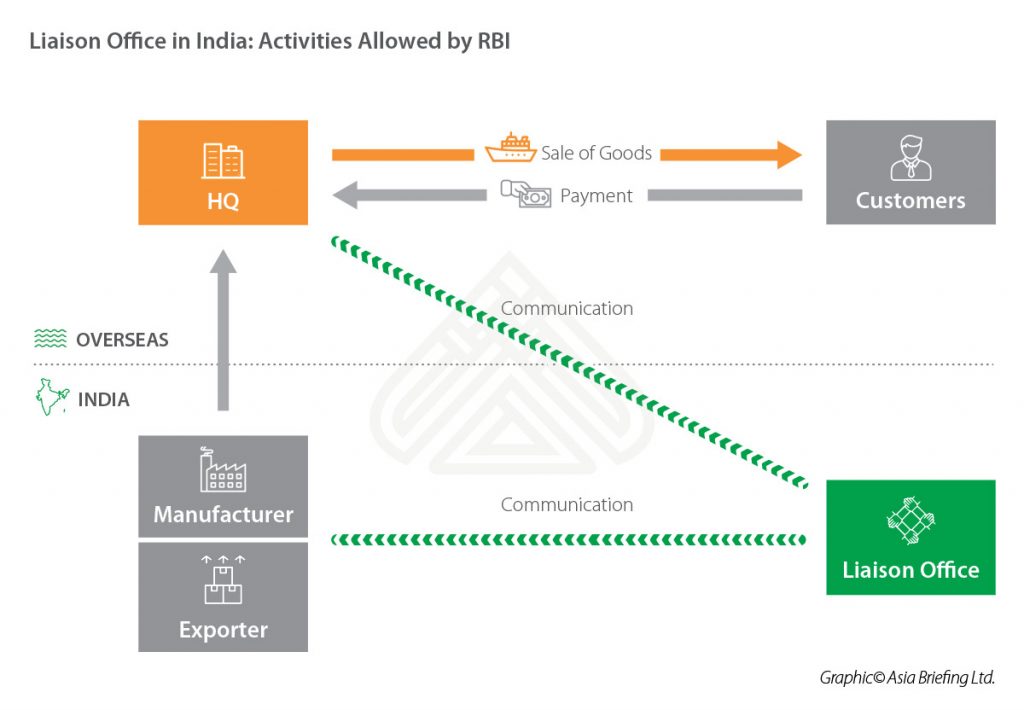
As the name suggests the Liaison office is set up by a foreign company in India to carry out the liaison activity for its business. The company cannot have any revenue for the Indian Liaison office.
It has to meet all its expenses of the Indian office through remittances from the Head office. The Liaison office is not allowed to earn any income in India
liaison office is suitable for a foreign company to test and understand the Indian market, as it does not allow the companies to do business but just to be in the market and understand the Indian market or carry out the Research & Development activities or to understand the problem of existing clients of the company and serve them better.
Application for Liaison office Licenses is approved by the RBI , but as per the recent changes, the applications for Liaison office are routed through the A.D i.e Authorized Dealers.
Due to this the timeline for setting up the liaison office has increased tremendously. Further, the documentation required for the same has also increased.
GENERAL FEATURES OF LIAISON OFFICE
- The name of the Indian liaison office shall be the same as the parent company.
- Governing body for the Liaison office License is Reserve Bank of India.
- It is suitable for foreign Companies looking to setup a temporary office in India to liaison its existing business with Indian clients.
- This office does not have any ownership, it is just extension of the exiting company in the foreign country.
- All the expenses of the Liaison office are met by the head office, hence the funds shall be received from head office account only.
- Licence for the Liaison office is given for three years and shall be renewed every 3 years.
- Read the related blogs below;
ACTIVITIES ALLOWED TO LIAISON OFFICE IN INDIA
- Representing in India the parent company/group companies.
- Promoting export / import from / to India.
- Technical/financial collaborations between parent/group companies and companies in India.
- Acting as a communication channel between the parent company and Indian companies.
CONDITION FOR SETTING UP LIAISON OFFICE
- The company looking to start a Liaison office in India shall have a profitable track record during immediately preceding three years in the home country.
- The Net Worth i.e total of paid-up capital and free reserves, less intangible assets as per the latest Audited Balance Sheet or Account Statement certified by a Certified Public Accountant or any Registered Accounts Practitioner by whatever name shall be not less then of equal to USD 50000/- .
DOCUMENTS REQUIRED FOR LIAISON OFFICE SETUP
Currently as per the RBI Requirement the application for the branch office and Liaison office is submitted through the Authorized dealer. The authorized dealer means the various institution having banking licenses.
The applicant of the Branch/Liaison office has to opt for the any of the Authorized Dealer , it is always preferable for the company to opt for the same authorized dealer as it is dealing in the home country.
- Form FNC 1 Three copies
- Letter from the principal officer of the Parent company to RBI.
- Letter of authority from the parent company in favor of Local Representative.
- Letter of authority/ Resolution from the parent company for setting up a liaison office in India.
- Comfort letter from the parent company intending to support the operation in India.
- Two copies of the English version of the Certificate of Incorporation, Memorandum & Articles of association (Charter Document) of the parent company duly attested by the Indian embassy or notary public in the country of registration.
- Certification of Incorporation – Translated & Duly Notarised and Certified by Indian Consulate
- The Latest audited Balance sheet and annual accounts of parent company duly Translated notarized for past Three years. & Certified by Indian Consulate & Directors
- Name, Address, email ID, and telephone number of the authorized person in Home Country.
- Details of Bankers of the Organization the Country of Origin along with the bank account number
- Commitment from the Organization to the effect that it will be open to report / opinion sought from its banker by the Government of India / Reserve Bank of India
- The expected funding level for operations in India.
- Details Relating to address of the proposed local office, number of persons likely to be employed, number of Foreigners among such employees and address of the head of the local office, if decided
- Details of Activity carried out in Home Country by the applicant organisation in brief about the product and services of the company in Brief.
- Bankers Certificate
- Latest Proof of identity of all the Directors – Certified by Consulate and Banker in Home Country
- Latest Proof of address all of the Directors – Certified by Consulate and Banker in Home Country
- Details of the Individuals / Company holding more 10% of Equity
- Structure of the Organization w.r.t. Shareholding pattern
- Complete KYC of Shareholders holding more than 10% Equity in the Applicant Company
- Resolution for Opening up Bank Account with the Banker
- Duly Signed Bank Account Opening Form for Indian Bank
NOTE – THE ABOVE LIST IS NOT EXHAUSTIVE AND MAY DIFFER DEPENDING UPON THE REQUIREMENT FROM THE AUTHORISED DEALER.
BRIEF SUMMARY OF STEPS TO GET RBI LICENCES
- Selection of Authorized Dealer by Client, As the same AD will have the bank account of the Company.
- Working on the documentation required for the Liaison office.
- Submission of documents to the AD.
- Scrutiny of documents by the AD
- Providing clarification and additional documents to AD
- Submission of the final application to RBI by the AD.
- Follow up and getting the Licenses from AD.
PROCEDURE AFTER GETTING THE RBI LICENCE
Every Liaison office registered with RBI shall get itself registered with the Ministry of Corporate Affairs, It is a registration by the Liaison office as an establishment of a foreign company in India.
On such registration, a CIN i.e. Corporate Identity Number is allotted by the Registrar of Companies. The following documents shall be filled with the Registrar of Companies :-
- Form 44
- Charter, statutes or memorandum and articles of association or other Instrument constituting or defining the constitution of the company(In the manner provided under Rule 16, 17 of the Companies (Central Government’s) General Rules and Forms, 1956)
- If the above documents are not in English then the translated version of the documents.
- Director(s) details individuals
- Director(s) details bodies corporate
- Reserve bank of India approval letter
- Secretary(s) details
- Power of attorney or board resolution in favor of the authorized representative(s)
OTHER BUSINESS LICENCES APPLICABLE TO LIAISON OFFICE
- PERMANENT ACCOUNT NUMBER PAN NUMBER
- TAX DEDUCTION NUMBER TAN NUMBER
- SHOP & ESTABLISHMENT REGISTRATION
ANNUAL ACTIVITY TO BE CARRIED OUT BY LIAISON OFFICE
- Maintenance of Books of Account
- Getting Annual Accounts audited
- Filling of Annual Activity Certificate with RBI
- Filling of Annual Return and Balance sheet with Registrar of Companies
- Intimating any change in the constitution of Foreign Company to RBI & ROC
- Intimating any change in Directors of Foreign Company to RBI & ROC
- Intimating each and every change in the Liaison office to RBI & ROC
- No additional place of business can be started unless approval is taken from RBI.
Goods and Services Tax on liaison office: AAR-Karnataka decision:
- The basic activities of the liaison office (LO) do not amount to supply of service as per the Goods and services tax Act.
- the liaison office is neither required to be registered under GST nor liable to pay Goods and Services Tax on liaison office activity. (Fraunhofer- Gesellschaft Zur Forderung Derangewandten Forchunge)
CLOSURE OF LIAISON OFFICE
Generally, the Liaison office licenses is given for three years, if at any time the Company plans to close the Liaison office setup in India it shall file the necessary documents with the Authorized Dealer, and the application for the closure shall be forwarded by the Authorized Dealer.
- Copy of the Reserve Bank’s permission/ approval from the sectoral regulator(s) for establishing the BO / LO.
- Auditor’s certificate-
- i) indicating the manner in which the remittable amount has been arrived at and supported by a statement of assets and liabilities of the applicant, and indicating the manner of disposal of assets;
- ii) confirming that all liabilities in India including arrears of gratuity and other benefits to employees, etc., of the Office have been either fully met or adequately provided for; and
- iii) confirming that no income accruing from sources outside India (including proceeds of exports) has remained un-repatriated to India.
- No-objection / Tax Clearance Certificate from Income-Tax authority for the remittance/s.
- Confirmation from the applicant/parent company that no legal proceedings in any Court in India are pending and there is no legal impediment to the remittance.
- A report from the Registrar of Companies regarding compliance with the provisions of the Companies Act, 1956, in case of winding up of the Office in India.
- Any other document/s, specified by the Reserve Bank while granting approval.
FAQ’s ON LIAISON OFFICE
-
How can foreign companies open Liaison/Project/Branch office in India?
Foreign companies can set up Liaison/Branch Offices in India after obtaining approval from Reserve Bank of India.
Reserve Bank of India has given general permission to foreign companies to establish Project Offices in India subject to certain conditions.
2.What is the procedure to be followed for obtaining Reserve Bank’s approval for opening Liaison Office/ Representative Office?
A Liaison office can carry on only liaison activities, i.e. it can act as a channel of communication between Head Office abroad and parties in India. It is not allowed to undertake any business activity in India and cannot earn any income in India.
Expenses of such offices are to be met entirely through inward remittances of foreign exchange from the Head Office abroad. The role of such office is therefore, limited to collecting information about possible market opportunities and providing information about the Company and its products to the prospective Indian customers.
The companies desirous of opening a liaison office in India may make an application in form FNC-1 along with the documents mentioned therein to Foreign Investment Division, Foreign Exchange Department, Reserve Bank of India, Central office Mumbai.
Permission to set up such offices is initially granted for a period of 3 years and this may be extended from time to time by the Regional Office in whose jurisdiction the office is set up. Liaison/ Representative offices have to flee an Activity Certificate on an annual basis from a Chartered Accountant to the concerned Regional Office of the Reserve Bank of India, stating that the Liaison office has undertaken only those activities permitted by Reserve Bank of India.
-
What is the procedure for setting up Project Office?
Foreign companies are granted projects in India by Indian entities. General Permission has been granted by Reserve
Bank of India Vide Notification No. FEMA 95/ 2003-RB dated July 2, 2003 to foreign companies to open Project
Office/s in India provided they have secured from an Indian company, a contract to execute a project in India, and
- the project is funded directly by inward remittance from abroad; or
- the project is funded by a bilateral or multilateral International Financing Agency; or
- the project has been cleared by an appropriate authority; or
- a company or entity in India awarding the contract has been granted Term Loan by a Public Financial Institution
or bank in India for the project.
- However, if the above criteria are not met, or if the parent entity is established in Pakistan, Bangladesh Sri Lanka, Afghanistan, lran or China, such applications have to be forwarded to Central Office of the Foreign Exchange Department of the Reserve Bank at Mumbai for approval.
-
What is the procedure for setting up Branch office?
Reserve Bank permits companies engaged in manufacturing and trading activities abroad to set up Branch Office
in India for the following purposes:
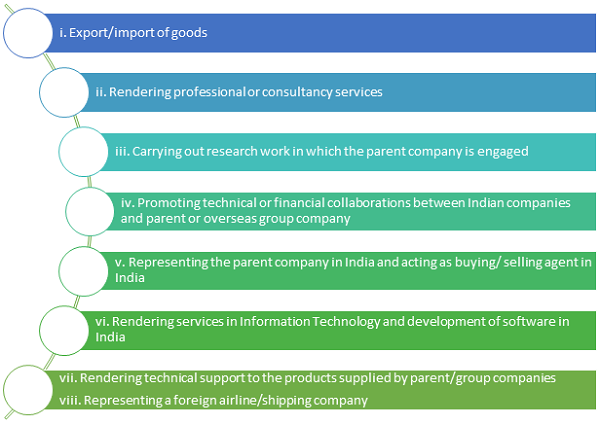
- To represent the parent company/ other foreign companies in various matters in India e.g. acting as buying/selling agents in India.
- To conduct research work in the area in which the parent company is engaged.
- To undertake export and import activities and trading on wholesale basis
- To promote possible technical and financial collaborations between the Indian companies and overseas companies
- Rendering professional or consultancy services
- Rendering services in Information technology and development of software in India
- Rendering technical support to the products supplied by the parent/ Group companies. .
- A branch office is not allowed to carry out manufacturing, processing activities directly/ indirectly. A Branch office is also not allowed to undertake Retail Trading activities of any nature in India. Branch Offices have to submit Activity Certificate
5.What are the forms in which business can be conducted by a foreign company in India?
A foreign company planning to set up business operations in India may:
- Incorporate a company under the Companies Act, 1956, as a Joint Venture or a Wholly Owned Subsidiary.
- Set up a Liaison Office / Representative Office or a Project Office or a Branch Office of the foreign company which can undertake activities permitted under the Foreign Exchange Management (Establishment in India of Branch Office or Other Place of Business) Regulations, 2000.
6.What is the procedure for receiving Foreign Direct Investment in an Indian company?
An Indian company may receive Foreign Direct Investment under the two routes as given under:
- Automatic Route
- FDI is allowed under the automatic route without prior approval either of the Government or the Reserve Bank of India in all activities/sectors as specified in the consolidated FDI Policy, issued by the Government of India from time to time.
- Government Route
- FDI in activities not covered under the automatic route requires prior approval of the Government which are considered by the Foreign Investment Promotion Board (FIPB), Department of Economic Affairs, Ministry of Finance
- The Indian company having received FDI either under the Automatic route or the Government route is required to comply with provisions of the FDI policy including reporting the FDI to the Reserve Bank.
7.What are the instruments for receiving Foreign Direct Investment in an Indian company?
Foreign investment is reckoned as FDI only if the investment is made in equity shares , fully and mandatorily Convertible preference shares and fully and mandatorily convertible debentures with the pricing being decided Upfront as a figure or based on the formula that is decided upfront. Any foreign investment into an instrument issued
By an Indian company which:
- gives an option to the investor to convert or not to convert it into equity or
- does not involve upfront pricing of the instrument as a date would be reckoned as ECB and would have to comply with the ECB guidelines.
The FDI policy provides that the price/ conversion formula of convertible capital instruments should be determined upfront at the time of issue of the instruments.
The price at the time of conversion should not in any case be lower than the fair value worked out, at the time of issuance of such instruments, in accordance with the extant FEMA regulations [the DCF method of valuation for the unlisted companies and valuation in terms of SEBI (ICDR)Regulations, for the listed companies].
8.What are the modes of payment allowed for receiving Foreign Direct Investment in an Indian company?
An Indian company issuing shares /convertible debentures under FDI Scheme to a person resident outside India
shall receive the amount of consideration required to be paid for such shares /convertible debentures by:
(i) Inward remittance through normal banking channels.
(ii) Debit to NRE / FCNR account of a person concerned maintained with an AD category I bank.
(iii) Conversion of royalty / lump sum / technical know how fee due for payment or conversion of ECB, shall be treated as consideration for issue of shares.
(iv) conversion of import payables / pre incorporation expenses / share swap can be treated as consideration for issue of shares with the approval of FIPB.
(v) debit to non-interest bearing Escrow account in Indian Rupees in India which is opened with the approval from AD Category – I bank and is maintained with the AD Category I bank on behalf of residents and non-residents towards payment of share purchase consideration.
If the shares or convertible debentures are not issued within 180 days from the date of receipt of the inward remittance or date of debit to NRE / FCNR (B) / Escrow account, the amount shall be refunded.
Further, Reserve Bank may on an application made to it and for sufficient reasons permit an Indian Company to refund / allot shares for the amount of consideration received towards issue of security if such amount is outstanding beyond the period of 180 days from the date of receipt.
9.Which are the sectors where FDI is not allowed in India, both under the Automatic Route as well asunder the Government Route?
FDI is prohibited under the Government Route as well as the Automatic Route in the following sectors:
- i) Atomic Energy
- ii) Lottery Business
iii) Gambling and Betting
- iv) Business of Chit Fund
- v) Nidhi Company
- vi) Agricultural (excluding Floriculture, Horticulture, Development of seeds, Animal Husbandry, Pisciculture and cultivation of vegetables, mushrooms, etc. under controlled conditions and services related to agro and allied sectors) and Plantations activities (other than Tea Plantations)
vii) Housing and Real Estate business (except development of townships, construction of residential/commercial premises, roads or bridges to the extent viii) Trading in Transferable Development Rights (TDRs).
viii) Manufacture of cigars , cheroots, cigarillos and cigarettes , of tobacco or of tobacco substitutes.
- ix) What are the advantage & Disadvantage of Liaison office?
Advantages of Liaison office:
- Fewer ongoing formalities although there are set-up costs.
- No separate legal entity but does provide a formal presence for UKCo in India.
Disadvantages of Liaison office:
- Cannot trade or generate revenue in India.
- UKCo may be exposed to claims and liabilities in India.
- What are the points to consider while setting-up a of Liaison office?
Five points to consider while setting-up a Liaison Office in India
Any Foreign Entity looking for an office in India as a sourcing division or to facilitate export or to test the Indian market with a prospective business venture to improve the relations with the authorities and business community or to have the presence in the country from worldwide business outlook, Liaison Office (LO) is the best option.
A Liaison Office or a Representative Office can undertake only liaison activities, which means that it can act as a channel of communication between the Head Office (out of India) and parties in India.
It is not allowed to undertake any commercial activity in India. As there is no income of Liaison Office of its own, its expenses are to be met entirely through inward remittances from the parent company outside India received in Convertible Foreign Exchange.
Establishment of Liaison Office/Representative Office in India is governed by Reserve Bank of India (RBI) together with Ministry of Finance, Government of India.The rules and regulations in respect to Liaison Offices are framed under Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 and Circulars/Notifications issued by RBI from time to time.There are 2 routes to establish a Liaison Office in India:
RBI Route
If the industry the Foreign Entity is in, comes in the specified industries for 100% automatic route of investment as per Foreign Direct Investment Policy then the Liaison Office will be approved by the Reserve Bank of India.
Government Route
If the industry the Foreign Entity is in, doesn’t come in 100% automatic route and Non Profit and Non-Government Organization, then the Liaison Office will be approved by Reserve Bank of India in consultation of the Ministry of Finance, Government of India.
In addition to above, Reserve Bank of India has prescribed eligibility criteria for Foreign Entities to apply for Liaison Office. The application of Foreign Entities satisfying the below criteria will be processed:
- Profit making track record during immediate preceding 3 financial years.
- Net worth as per latest audited balance sheet certified by CPA should not be less than US $50,000 or its equivalent amount in home country.
The other prerequisites of Liaison Office application are to have a designated manager of the proposed Liaison Office and a prospective office space of the proposed Liaison Office which can be provided by consultants who help the foreign entities in applying for LO as part of their services which is called Virtual Office or Service Office Services.
The Application has to be made to RBI through Authorized Dealer Category-1 Bank in India. RBI will allot a UIN (Unique Identification Number) on approval of the application. Once approved the intimation has to be given to Registrar of Companies (ROC) and Director General of Police (DGP).
An application has to be sen to the Income Tax Department to allot Permanent Account Number (PAN).
Annual Compliance
A Liaison office has to do minimal annual compliances as compared to other forms of business in India.
As annual compliance, an annual activity certificate issued by a Practicing Chartered Accountant at the end of March 31, need to be submitted to the Authorized Dealer Category-1 Bank, Directorate General of Income Tax (International Taxation), concerned Registrar of Companies and Director General of Police, on or before 30th September of each financial year (In India the Financial Year is April to March) including audited receipts and payments account.
Tenure
Approval is generally given for a period of 3 years and extension is granted on the basis of
- Track record of annual activity certificates.
- Record of the account maintained with the designated bank as per the terms and conditions of original approval.
Additional Activities and Offices
For establishing an additional office, a fresh application duly signed by an authorized signatory of the foreign entity is filed to Reserve Bank of India with a justification to open additional office and identify one of the offices as a nodal office to co-ordinate the activities of all offices.
Conclusion:-
Liaison Offices are very popular forms of business in India for a long time. However, the issue of the taxability of liaison offices still looms over the foreign entities and is not free from ambiguity.
To capture the entities in tax clutches, tax authorities have been contending that the liaison offices are transgressing the list of permitted activities and constitute the company’s permanent establishment in India.
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances; Hope the information will assist you in your Professional endeavors. For query or help, contact: singh@carajput.com or call at 9555-555-480