GST Liability on mobile application developers
Page Contents
All about Goods and Services Tax Liability on mobile application developers
- Almost every one uses some kind of application in their everyday life, which is created by application developers and made available to end-users through online stores such as the Google Play store.
- Now, there’s a crucial question that needs to be addressed and should come into the thoughts of application developers is whether they are liable to register under GST & what they must do to comply with the GST regulations.
- Complete understanding on GST application on mobile application developers will be given as below:
Q1) How would the transaction of selling the application be treated provide the fact that the application can be sold within India & worldwide?
- To begin, selling applications online through an electronic shop appears to be very similar to selling anything else on the electronic market.
- However, the most crucial factor that distinguishes this transaction is that, because the product is intangible, it may be sold from anywhere in the world and does not involve physical delivery.
- When the Internet is utilized as a medium, the supply is classified as OIDAR (Online Information Database Access and Retrieval) Services under the GST.
Q2) Whether applications sold on the online platforms are taxable under Goods and Services Tax?
We can start with a fundamental principle: every supply that is taxable under GST the place of supply should be in India. To evaluate its taxability in India, we must first ascertain the source of supply.
a) The application developer is located in India, and the consumers are also from India:
- IF it is domestic supply, than it’s taxable under GST as the place of supply.
b) Application developer is situated in India, and the users are also based outside of India:
- Because the customers are situated outside of India, selling the application would be considered an export of services (if all other export conditions are met), and it would be exempt from GST in India.
- If you are already registered for GST, however, GST compliance is still required.:
c) Consumers are in India, yet the application developer is situated outside of India:
- Because the consumers are in India, the source of supply is also in India.
- If the consumer is a GST registered person in India, the supply will be subject to reverse charge, and the registered consumer would be responsible for GST compliance.
- Whereas, if a consumer in India is not registered under GST,the GST act places responsibility on the application developer, who will be required to complete a simplified GST registration and comply with GST regulations.
d) The app developer is located outside of India, and the users are likewise situated outside of India:
- GST has no jurisdiction over this.
Q3) Do application developers need Goods and Services Tax registration?
Now that we’ve talked about taxability, it’ll be easy to figure out whether or not we require to register for GST.
a) The application developer is based in India, as are the consumers:
- GST registration is mandatory if you render OIDAR services in India to Indian consumers (threshold turnover exemption is not applicable).
(b) Application developer is based in India & consumers are also based outside of India:
- Because your customers are located in India, you are an exporter of services (if all other export conditions are met). If your turnover exceeds Rs 20 lakhs, you must register for GST.
(c) In case the application developer is located outside of India, yet the consumers are located in India:
- Form GST REG-10 is mandatory for GST registration under the simplified GST registration scheme.
d) The app developer is located outside of India, and the consumers are likewise located outside of India:
- A GST registration. is not mandatory
Q4) What is the responsibility of application developers with respect to Goods and Services Tax?
We now know that in cases a, b, and c, as mentioned in the preceding paragraphs, we need to register for GST. Let’s look at your obligations as a GST registered person now.
(a) Application developer is located in India as are the consumers:
- Responsibilities will be the same as any other Indian seller. You must charge GST on every applications you sell, produce tax invoices, pay your tax due every month, and file GST returns on a regular basis.
- Similarly, you may be able to claim an eligible Input tax credit on expenditure or purchases incurred in the course of your business.
(b) Mobile application developer is located in India, and the consumers are outside of India:
- The most crucial task at hand is to assess whether if you meet all the conditions to conclude the supply as an export.
- Most important requirement that may not be met in practice is “that you must receive payments from consumers in foreign currency.”
- If this criterion is not met, the service will not be considered export and you will be expected to comply as if you were making a local supply.
- In case all of the requirements are fulfilled and it is determined that the supply is an export of services, you are not required to charge GST, but you must file GST returns reflecting the export of services.
- This type of service export can be done with or without payment of taxes (which would require LUT) You can claim ITC on expenses or purchases made in the course of your business and receive a refund.
c) The application developer is located outside of India, yet the consumers are located in India:
- You must register for GST under the simplified system and will be responsible for paying IGST and submitting a monthly return in form GSTR-5A.
d) The app developer is located outside of India, and the users are likewise located outside of India:
- GST has no jurisdiction over this.
Q5) What other services can be treated the same way?
Via these Blogs, we’ve focused on apps available through the Google Play Store. Similar treatment can be applied to other OIDAR services. An example of such services is shown below:
(I) offering cloud computing services
(ii) the distribution of e-books, software, movies, music & other intangibles via telecommunication networks or the internet
(iii) transmitting data or information in electronic form via a computer network, whether retrievable or not.
(iv) online supplies of digital content (music, movies, television shows, and the like)
(v) the storage of digital data
(vi) Supply of software and updating thereof
vii) online gaming.
TDS application of app developers/freelancers
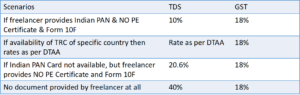
- As per above pic we have to incur a tax of 58% on any payment, we make if no documents provided by developer.
- the Indian Payment Gateway levied a commission fee of Rs. 24,000 on software developers and freelancers.
- App developers and freelancers have paid the Payment Gateway INR 24,000 for their services. TDS is required by law to be deducted from this payment by app developers/freelancers.
GST Applicable to app developers- Conclusion
- Goods and Services Tax Under GST law, this is considered a service supply. Goods and Services Tax registration is not required if total revenue from app developers/freelancing activity is less than Rs.20,00,000, and one is not responsible for GST.
- A person who is registered for GST or who is liable for registration, on the other hand, must pay 18 percent Goods and Services Tax on the above services.
- Exports are zero-rated & input taxes paid in the form of IGST are refundable.
- For the period preceding the Goods and Services Tax implementation, i.e. July 1, 2017, app developers/freelancers who provided software services such as designing, app development, website design, and so on paid a service tax of 15%.
Popular Article :

