GST Offenses, Penalties, Appeals Under GST
Page Contents
BRIEF INTRODUCTION
As per the Union Budget 2021, which was presented on 1st February 2021, the following provisions were inserted in respect of penalty and appeal –
- The section 50 of the CGST Act 2017, was amended and it provides for a retrospective charge of interest on net cash liability and the said charge shall be effective from 1st July 2017.
- Where the orders involve detention and seizure of goods and conveyance under section 130, an amount equal to 25% of penalty needs to be paid for making an application of appeals under section 107 of the CGST Act.
It is to be noted that for the effective implementation of any tax law, there is a need for having a strict action against tax offenders. Thus, to have effective implementation of India’s new GST tax regime, the government implemented a three-pronged approach involving interest, monetary penalties, and prosecution.
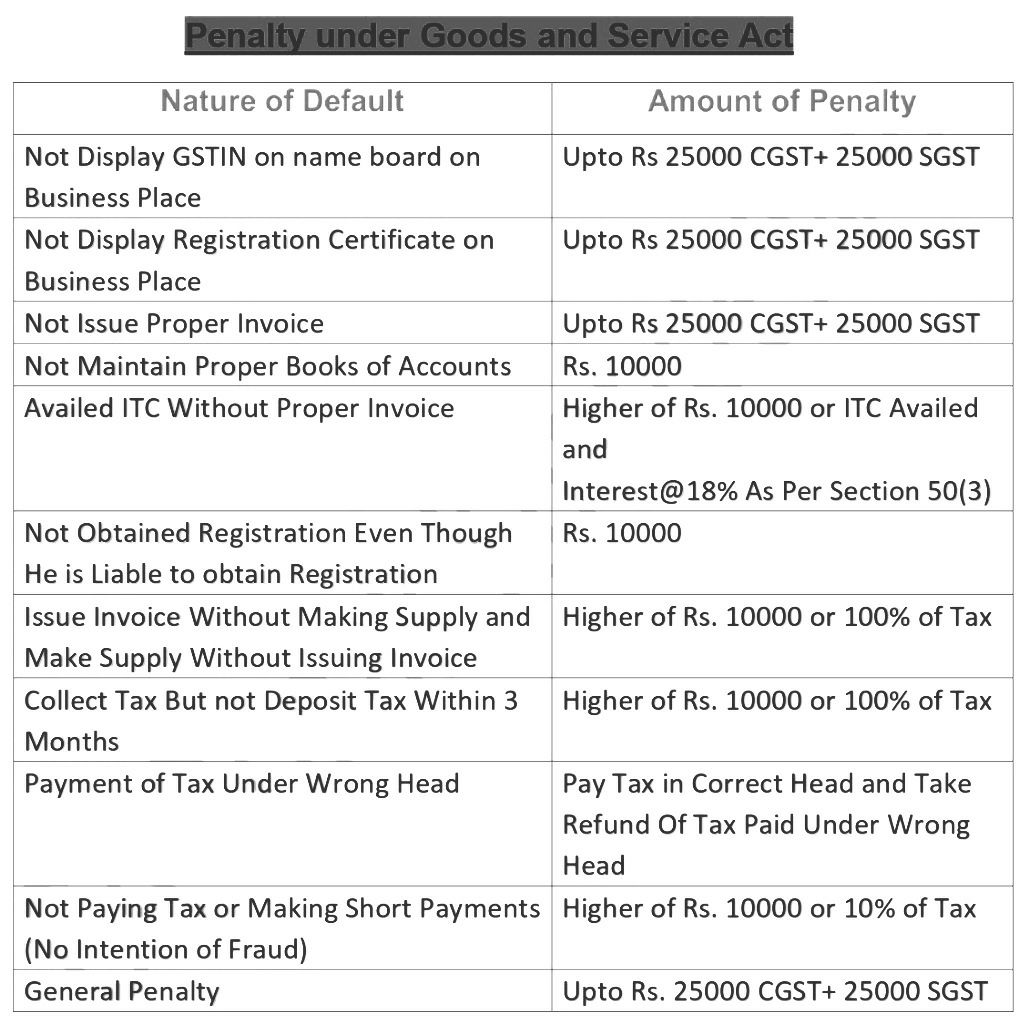
PENALTY
Where any offense has been committed, a penalty is required to be paid under GST laws. The penalty depends upon the various parameters –
-
- Under Sec 122(1), the following defaults involve a penalty of Rs 10,000 or the amount of tax involved, whichever is higher.
-
-
- Supply of goods/services without issuing an invoice or issuing an incorrect or false invoice.
- Issuing an invoice without supplying goods and/or services.
- TDS deducted but not deposited with the government.
- TCS collected but not deposited with the government.
- TDS deducted in contravention with the provisions.
- TCS collected in contravention with the provisions.
- Claiming of full or partial input tax credit without receiving the goods and/or services.
- Refund of tax obtained by fraud.
- Distributing the input tax credit in a manner against the prescribed standards.
- Submitting fake financial records, or producing fake accounts, documents ad returns.
- Liable to take registration, but fails to take one.
- False information is furnished in the registration application.
- Not allowing an officer from performing their duties.
- Transfer of taxable goods through conveyance, without proper documents
- Suppressing the turnover, with the intention to evade tax
- Failure in maintaining proper books of accounts and documents
- Supplying of goods where the goods are liable for confiscation
- Failure to furnish information as required by the CGST/SGST officers.
- Issuance of invoice or document using GSTIN of another person.
- Tampering with material evidence crucial for proceeding.
- The Tampering with any goods, detained, seized, or attached, as an evidence in a proceeding.
-
- Where any information is required from an electronic commerce operator under Sec. 122, and the supplier fails to furnish the required information, a penalty of Rs 25000 be levied.
- CGST Act provides for a reduction in penalties where the default involve failure to pay or underpays the tax owed erroneously, provided the same is not done deliberately by fraud, wilful misstatement, or the suppression of facts. In this case, the penalty levied could be reduced to 10 percent of the tax to be paid, provided the same shall not be less than Rs 10,000.
- Offence where the person is not involved in any evasion directly but is a party to evasion or fails to attend summons or produce necessary documents. Penalty would be up to Rs 25,000.
- Default in providing the information return, a penalty of Rs 100 per day, subject to a maximum of Rs 5,000 rupees.
- Person fails to furnish statistics or wilfully furnishes false statistics; the penalty would be –
-
- First-time offense – Rs 10,000
- Continuing offense – Rs 10,000 plus Rs 100 per day starting from the second day of default, subject to maximum of Rs 25,000 rupees.
- Where no specific penalty provided in the law, the amount of penalty be Rs 25,000.
It can be seen that the amount of penalty in GST regime has increased substantially than that in the earlier tax laws. This shows that the government is pretty much serious regarding proper GST compliance. However, the government has provided for certain relief and exemption for penalty as well. These are as follows –
-
- The penalty shall not be levied, where the amount of default of tax is less than Rs 5,000 rupees and documentation errors are easily rectifiable.
-
- Proper safety nets have been established, to determine the degree and severity of a breach.
-
- Penalty be imposed only after issuing a show cause notice or giving the assessee, a chance to be heard.
-
- Any sought of voluntary disclosure by a person to a tax authority, regarding any default, be considered as a mitigating
factor for levy of penalty.
- Any sought of voluntary disclosure by a person to a tax authority, regarding any default, be considered as a mitigating
LATE FILING OF RETURN
The default related to late filing attracts late fees. The amount being Rs. 100 per day of default. The said amount is applicable for each type of GST, thus the effective rate comes out to be Rs. 200/day, subject to the maximum of Rs. 5,000. However, no late fee is levied on IGST.
Apart from the late fee, an interest @ 18% per annum is also required to be paid.
NON-FILING OF RETURN
Where the GST return is not filed, the provision for subsequent filing of other returns is not provided. Thus, late filing leads to a piling of burden, resulting in heavy fines and penalty.
INSPECTION
Under the GST Act, the inspection can be initiated where, the Joint Commissioner of SGST/CGST, have the reasons to believe that to evade tax, a person has suppressed any transaction or claimed excess input tax credit. In such a case, the Joint Commissioner can authorize any other officer, to inspect places of business of the suspected evader.
SEARCH & SEIZURE
The Joint Commissioner has the authority to order for a search. However, the same can be ordered, where he has the reasons to believe that –
- some goods have been confiscated.
- There is any documents or account which is hidden somewhere and the same useful during proceedings.
GOODS IN TRANSIT
Under this, the person carrying the goods of value exceeding Rs. 50,000 is required to carry the following documents:
- The invoice or bill of supply of the goods/service along with the delivery challan.
- Copy of e-way bill, properly filed by the supplier and the transporter.
The proper officer can intercept goods in transit and have an inspection of the goods and the documents. Where the goods are found to be in contravention of the GST Act, such goods, related documents, and the vehicle will be seized. And the goods be released only on payment of tax and penalty.
CONFISCATION OF GOODS OR CONVEYANCE
The following defaults lead to the confiscation of goods and/or conveyances and involves a penalty of Rs 10,000 or an amount equal to the tax evaded.
- Failing in accounting for the goods on which the tax is to be paid.
- Supplying or receiving goods in contravention with any provisions or rules.
- Supply undertaken with the intention to evade tax.
- Supplying any goods liable to tax without registering them.
- Using a conveyance to deliver taxable goods in breach of any provisions or rules.
It is to be noted that the prosecution provisions are much harsher than the monetary penalty.
PERIOD OF IMPRISONMENT
| TYPE OF OFFENCE | AMOUNT OF DEFAULT. | PERIOD OF IMPRISONMENT | APPLICATION OF FINE |
| CERTAIN OFFENSES SPECIFIED IN THE ACT | EXCEEDING RS 500 LAKHS | UP TO 5 YEARS AND NON-BAILABLE | APPLICABLE |
| CERTAIN OFFENSES SPECIFIED IN THE ACT | EXCEEDING RS 200 LAKHS UP TO RS 500 LAKHS | UPTO 3 YEARS | APPLICABLE |
| ANY OTHER OFFENSE | EXCEEDING RS 100 LAKHS UP TO RS 200 LAKHS | UPTO 1 YEAR | APPLICABLE |
| ASSISTS THE COMMISSION OF CERTAIN SPECIFIED OFFENSES | UP TO 6 MONTHS | APPLICABLE | |
| REPETITION OF OFFENSE
|
UPTO 5 YEARS | APPLICABLE |
COMPOUNDING OF OFFENCES UNDER GST
Compounding of offenses is a method to avoid litigation. Where any prosecution for an offense is pending in a criminal court, the accused is required to appear before the Magistrate at every hearing through an advocate. Such an activity involves time and money.
Now, in the compounding, the accused is not required to appear personally and can discharge the liability by making the payment of compounding fee that is capped to the maximum fine as applicable under GST.
Thus, compounding will save time and money. However, the compounding under GST shall not be available where the amount involved exceeds 1 crore.
PROSECUTION
Prosecution involves conducting of legal proceedings against someone in respect of a criminal charge. Where a person with a deliberate intention to fraud, commits an offence, shall be liable to prosecution under GST, and shall face criminal charges. Some of these cases are as follows –
- Issuance of invoice without supplying any goods/services and claiming the input credit or refund by fraud.
- Obtaining refund under CGST/SGST by fraud.
- submission fake financial records/documents or files, and fake returns to evade tax.
- Assisting another person to commit fraud under GST.
ARREST
Where the Commissioner of CGST/SGST believes that a person has committed a certain offense, he can make an order for the arrested under GST Act. The arrested person shall be informed about the grounds for the arrest and once arrested, the said person be appeared before the magistrate within 24 hours of arrest.
GST Appellate Tribunal age limit raised to 70, ensuring longer service for taxpayers.

APPEALS
Where a person is unhappy with any decision or order passed against him under GST can apply for the appeal against such decision. The first appeal can be made against the order of the adjudicating authority and the same be filed with the First Appellate Authority.
Where the aggrieved person is not happy with the decision of the First Appellate Authority they can appeal to the National Appellate Tribunal, if still not satisfied, they can go to the High Court, and if still unsatisfied, the last resort is to appeal to the Supreme Court.
To avoid such a long process of appeal and litigation, the taxpayer may apply for the advance ruling under GST, where they can seek clarification from GST authorities on GST treatment before starting the proposed activity.
Popular blog:-

