E-invoice Process is initiated by the GSTN
Page Contents
What is an E-invoice Process is initiated by the GST Network?
- E-invoice is not a bill that you can download or create from the Official website of the GST department, but it is a system of digitally validating all B2B invoices via the GST Network (GSTN). Creating e-invoices directly from the portal isn’t feasible.
- Invoices Authentication or E-invoicing is needed to ensure that the invoices created by your accounting system are valid for processes such as the creation of e-way bills and filing of GST returns. The procedure requires the submission to the GST Portal of company bills created by various accounting system to verify them in a common way.
- So the invoices generated by various GST return filing software may have various forms, the software can not all be directly generated to the GST system. The government has therefore decided to adopt a standard format (Schema), requiring all accounting software to follow a common format that can be uploaded for verification and confirmation to the GST portal.
Note: “The roll-out of e-invoicing will be relevant to corporations with a turnover of more than 500 crs from 1 October onwards.”
Benefit of the GST E-Invoicing System?
A few of the key benefits of e-invoicing are as follows:
- The processing and validation of B2B invoices from the common portal would ensure the automated preparation of GST ANX-1 and ANX-2 in the new format. IT also makes GSTR 1 auto ready for B2B supplies.
- E-invoicing may be further used for providing only vehicle information for generating e-way bills.
- Invoices submitted for verification by vendors shall be exchanged directly with purchasers for reconciliation.
- The output tax directly matches the input credit liability. For Debit / Credit Notes, Invoices, and other qualifying documents, e-invoice can be generated.
- Debit / Credit Notes, Invoices, and other qualifying documents can be generated by e-invoice.
Introduction of e-Invoicing
- While invoices generated by each system look more or less the same, it can not be understood by the computer system while the business users can fully understand it. For example, an accounting software-generated invoice “A” can not be viewed by a system that provides accounting software “B.”
- Now there are hundreds of accounting/billing software generating invoices and they all use their own formats to store the data. Just because of that, the GST program is unable to read and understand these invoices whereas the invoice data remains the same.
- To shorten the long story, the same information is being presented in different invoice formats today and there is no way a system can understand that.
- Therefore, there is a need to standardize the format where an invoice’s electronic data is exchanged with others to ensure data connectivity.
Applicability of E-invoice under GST
How do we implement e-invoicing?
Initially expected to introduce the e-invoice under GST on April 1st, 2020. However, the new date for launching e-invoicing is 1 October 2020, as per the 39th GST Council meeting held on 14 March 2020.
To ensure that companies have enough time to adapt to the new electronic invoicing system, the GST Council has approved the implementation of e-invoicing. To begin with, that will be implemented on a voluntary basis.
- It can be introduced on a voluntary (trial) basis starting 1 January 2020 * for taxpayers with a turnover of more than 500 crores.
- Those with a turnover of more than 100 crores may adopt it from February 1, 2020 (on a voluntary trial basis).
- The updated date for compulsory implementation of e-invoicing is 1 October 2020
*The latest e-invoicing date is revised as per the 39th meeting of the GST Council.
Who will upload the e-invoice?
- Under the e-invoice rule, the seller will electronically upload the invoice to the IRP system and collects the IRN (Invoice Reference Number) in the form of a physical copy of the invoice given to the recipient.
- The IRP program is also configured to send the digitally signed e-invoice with QR code via e-mail to both the manufacturer and the recipient.
Documents required to send to the GST system?
The definition of e-invoice is protected according to the following articles. This means the creator of this document has to upload it to the IRP system.
-
-
- Supplier invoice
- The Supplier credit note
- Supplier debit note
- Any other document which is required by law to be published by the document creator.
-
How E-Invoice vary from current invoicing practice?
- E-invoice is a system in which a unique invoice reference number (IRN) must be electronically uploaded and verified to the invoice. It will have no effect on the existing physical (printed) or electronic (ex.pdf version) invoice issuing process.
- The users will continue to see the physical or electronic (PDF / Excel) output of the invoices in the same way that occurred before the e-Invoice format was implemented into the program.
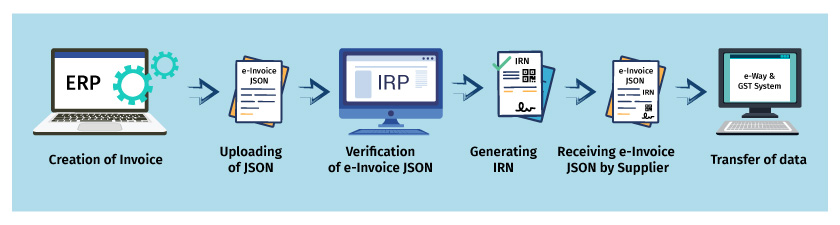
Procedure for generating GST e-invoice
- It is the duty of the taxpayer or companies to produce the invoice / s, and then send them for approval to the Invoice Registration Portal (IRP).
- The portal will return the invoice to the manufacturer, along with a unique reference number, digital signature, and a QR code, after successful verification. The e-invoice will also be exchanged with the corresponding buyer on the provided e-mail ID
Stage-1: Formation of an Invoice
- The seller/supplier will use his / her accounting or billing software to create an invoice in the prescribed format (e-invoice schema). It must have the required details.
- For each B2B invoice, the supplier’s accounting program must produce a JSON. The JSON file is imported into the IRP.
Stage-2: Generation of an IRN
- The next step will be to use a standard hash-generation algorithm to create a unique invoice reference number (IRN) by the vendor.
Stage-3: Uploading the Invoice
- Now the seller will upload JSON to the Invoice Registration Portal, either directly or via third-party software, for each of the invoices, along with IRN.
Stage-4: Sign and Authenticate
- If it’s not already uploaded by the supplier, IRP will validate the hash / IRN attached to JSON, or generate an IRN.
- Then, it verifies the file against GST’s central registry.
- Upon successful verification, JSON will have its signature attached to the invoice and a QR code.
- The earlier created hack will become the new E-invoice IRN. The e-invoice will be the unique identifier for the whole financial year.
Stage-5: Data-sharing
- The data uploaded will be shared with both the E-way bill and the GST program.
Stage-6: Download via e-invoice
- The portal will forward the digitally signed JSON back to the seller along with IRN and QR code. The invoice is also sent to the customer on their registered email I d.
To whom e-invoice is applicable?
Electronic Invoicing shall apply to all businesses whose aggregate turnover exceeds “10 Crore Rupees” in an FY with effect from 1 Oct 2022.
- The Year 2021 in Goods and Services Tax has started with a bang. below things have been made applicable from 1st January 2021 like E-Invoicing for Registered person above INR 100 Crs, Reduction of the limitations of Rule 36(4) from 10 percent to 5 percent, Introduction of restriction of 1 % in utilisation of Electronic Credit ledger, Increase in Distance limit from 100 kilometers to 200 kilometers for 1 days validity.
- Apart from the same, the Government has also extended to 28 February 2021 only 2 Months of GST Annual Return Filing, which means more stress and much more work for both Corporate India & Professionals.
In Summary :
- To sum up, E-invoice is a standardized process or schema for the exchange of data between different manufacturers’ GST billing applications.
- The basic goal behind the tax departments’ adoption for the e-invoice program is the ability to pre-populate the returns and reduce the challenges of reconciliation.
- That is done through the IRP design process, which shares the invoice data with the GST system and also with the e-way bill system. Thus, one-time invoice uploading would ensure that most of the information needed in returns are auto-populated, and also in the e-way bill.
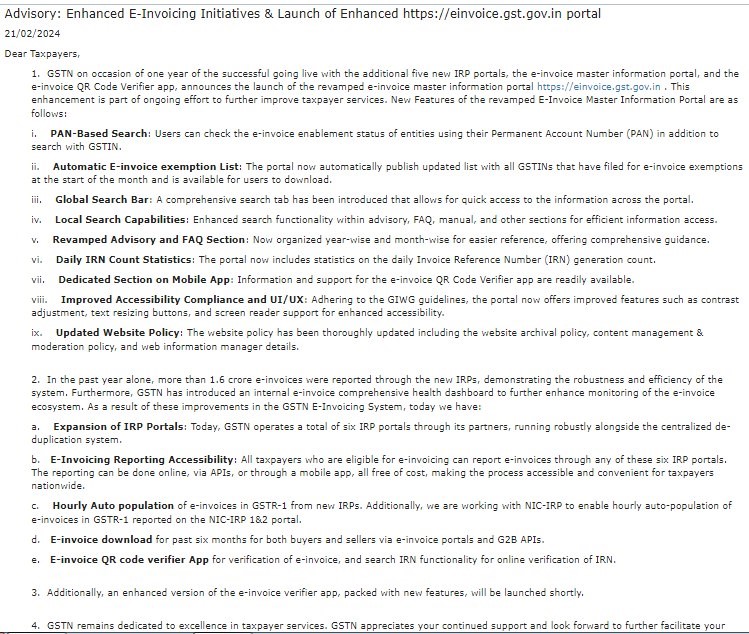
GSTN Advisory on enhanced e-Invoice initiative & Launch of Enhanced
Also, Read the related Blogs: