Proposed GST Law Procedures & Compliances
Page Contents
Proposed GST Law Procedures & Compliances
- After a lot of deliberation, Govt. has finally unveiled the proposed common indirect tax regime- Goods and Services Tax (GST). Battered with a multiplicity of Indirect taxes in the current regime,
- India Company has more than welcomed the GST as it brings within its ambit the flavor of ‘ease of doing business’ in India, seamless credit flow, and a vision of a common market across India.
- The draft Indian Model GST Law (‘Model GST Law’) which was made public on 3rd December 2015, underlines an overview of the Final GST Law. In this article, we have outlined the key compliances proposed in the Model GST Law.
- The Report of Sub-Committee released in the public domain outlines the various facets of the Model GST Law. Though recently the Ministry of Finance confirmed that the said report is not the Draft GST law and the Draft GST law may take one more month before it is released on the public domain.
- The above said report acts as a base document from which a clue can be taken about the ideology of the Indian Government in the formulation of the framework of the GST Law.
Registration in GST regime:
- GST law on registration provides that a taxable person in the GST regime will be required to take State-specific registration. Further, multiple registrations in a State for business verticals would also be permitted.
- As per Schedule III of the GST law, every person who is registered or holds a license under an earlier law (i.e. current indirect tax regime) would be liable to be registered under the GST regime.
- For new assessee (who has not registered under current indirect tax regime) a threshold (to be calculated on all India basis) of Turnover (as per section 2 (73) of the model GST law) including exports and exempted supplies below which any person engaged in the supply of Goods or Services or both will not be required to take registration.
- Given above, there could be ambiguity if a person already registered under earlier law if falls under threshold exemption limit of turnover under GST then whether he is liable for registration under GST law?
- As regards registrations, one can also apply voluntarily for GST registration. However, in case of a person engaged in inter-state supplies, casual taxable persons, or a person liable to GST under reverse charge, irrespective of turnover, registration would be compulsory.
Payments in GST regime
- GST law provides that the taxable person will be required to make payment of tax (i.e. CGST, SGST, IGST, and Additional Tax) including interest, penalty or fee through electronic cash/credit ledger.
- It is important to know that cross utilisation of electronic cash/credit under IGST for CGST and SGST payment, electronic cash/credit under CGST for IGST payment and electronic cash/credit under SGST for IGST payment will be allowed.
- However, the cross utilization of cash/credit under CGST for payment of SGST and vice versa will not be allowed
Read our articles: Top Taxation Relaxation to MSMS
Highlights of International Taxation.
- As per section 47(6) of the Model GST law, where the amount available in the electronic cash or the credit ledger falls short of the aggregate of tax, interest, penalty fee or any other amount due the said amount would be liable to be debited in the following order:
-
-
- Interest liability related to returns of previous tax periods
- Tax liability related to returns of previous tax periods
- Tax liability of current tax periods
- Any other amount
- Tax deduction at source
-
- The Central or State Govt may mandate to deduct tax at the rate of 1% from the payment made or credited to the supplier of taxable goods and/or services as notified by the Central or a State government, where the total value of such supply, under the contract, exceeds ₹ 10 lacs.
- The value of supply for TDS would be excluding the tax indicated on the invoice.
- The tax deducted would be paid by the deductor within 10 days after the end of the month in which such deduction is made in the manner prescribed.
- The deductor would furnish a certificate to the deductee within 5 days from crediting such tax at source to the appropriate government and default in the furnishing of such certificate would be liable to the late fee as prescribed under the Act.
- Every deductor would be liable to take registration within the specified period as prescribed and furnish the return in the form within due date as prescribed, failing which he would be liable to pay a late fee of as prescribed under the Act.
Returns in GST regime
Every GST registered assessee will be required to file returns (including NIL returns). It is pertinent to note that there could be as many as 8 returns as under:
| Type of Return | Description | Due date of filing |
| GSTR 1 | Outward supplies made by the taxpayer | 10th of the succeeding month |
| GSTR 2 | Inward supplies made by the taxpayer | 15th of the succeeding month |
| GSTR 3 | Monthly return (inward supplies + outward supplies) | 20th of the succeeding month |
| GSTR 4 | Quarterly return for compounding Taxpayer | 18th of next month from the end of the quarter |
| GSTR 5 | Periodic Return by Non-Resident Taxpayer | Last day of registration |
| GSTR 6 | Return for Input Service Distributor (ISD) | 15th of succeeding month |
| GSTR 7 | Return for Tax Deducted at Source | 10th of succeeding month |
| GSTR 8 | GST Annual Return | By 31st December of next FY |
- The return (including NIL return) filing formalities may increase by manifolds as far as periodicity, a No of forms, & multiplicity of compliances are concerned.
- Compliance requirements may further become cumbersome as invoice level details are expected to be provided in the returns.
- For example, a service taxpayer, covered by the Central Service Tax legislation, is currently required to file half yearly return and within the GST regime, the same Service Tax assessee might be required to file as many as 61 returns (5 returns per month i.e. GSTR 1, 2,3,6,7 and GSTR 8 annual return).
Rectification of Errors in returns:
- Rectification of errors for any omission or incorrect particulars (other than as a result of the audit, inspection, or enforcement activity by the tax authorities) would be allowed in the return period in which such omission/incorrect particulars to specific restriction such as rectification/omission may not be allowed after filing of the return for the month of November following the end of the FY etc.
- Given the aforesaid restrictions, it would be advisable that the taxpayers would need to have a robust mechanism to capture correctly the details of invoices, revenue, input invoices, and other data in the original return itself.
- The taxpayers will have to strengthen their reporting processes and controls.
- Thus given the drastic change & increase in the No of compliances, it is advisable to work towards analyzing the impact of the GST on business operations to ascertain the impact on tax, finance, working capital, contracts, operations, and compliances to anticipate the changes in advance and gear up accordingly.
You may also like following Post Complete Guidance on TDS applicable on Goods and Services Tax
Specific Relevant Extract of Finance Release : Ministry of Finance
Extension of the deadline for filing applications for revocation or cancellation of registration under the GST Act, as well as the deadline for filing late fee amnesty applications.

- The Govt provided relief to taxpayers by decreasing / waiving the late fee for non-furnishing Form GSTR-3B for the tax periods from July 2017 to April 2021, if the returns for these tax periods are filed between 01.06.2021 & 31.08.2021.
- Deadline to apply for the late fee amnesty scheme has been extended from August 31, 2021 to Nov 30, 2021.
- Based on the numerous representations received, the govt has also extended the deadlines for filing an application for revocation of cancellation of registration to Sept 30, 2021, where the deadline for filing an application for revocation of cancellation of registration is between March 1, 2020 & August 31, 2021.
- Only those registrations that have been cancelled under clause (b) or clause (c) of sub-section (2) of section 29 of the CGST Act would be eligible for the extension.
- For the period of 27.04.2021 to 31.08.2021, businesses can file FORM GSTR-3B and FORM GSTR-1/ IFF utilising an electronic verification code (EVC) instead of a Digital Signature Certificate (DSC).
- This has been extended till October 31, 2021. [Refer to Central Tax Notification No. 32/2021, dated August 29, 2021].
- The extension of the late fee amnesty deadline & time limit for filing an application for revocation or cancellation of registration will benefit a large No of taxpayers specify small taxpayers, who have been unable to file their returns on time due to a variety of factors, including the COVID-19 pandemic.
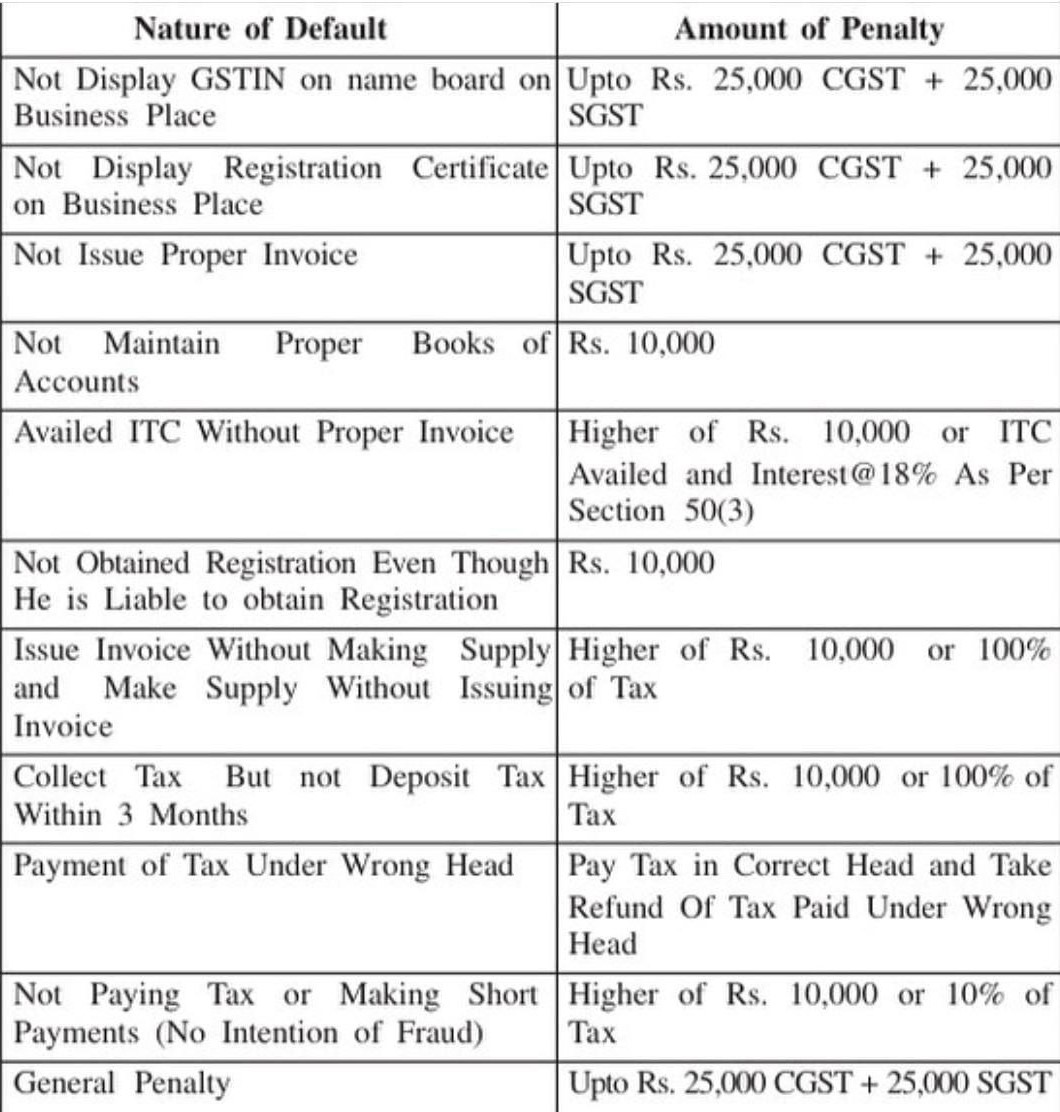
GST Penalties :
You may also : Key takeaways about TDS under GST
For query or help, contact: singh@carajput.com or call at 9555555480

