Overview of GST Audit & its Procedures
Page Contents
Overview of GST Audit & its Procedures
Requirement of GST Audit and meaning
- The audit in accordance with GST includes an examination by a registered individual of the GST of records, returns and other documents.
- It also ensures that declared turnover is correct, taxes paid, reimbursed, and input tax credit used and other such compliances are evaluated by a qualified expert pursuant to the GST Act.
- GST is a taxation trust system in which a taxpayer must self-evaluate his/her tax liability, pay taxes and file returns. So a robust audit mechanism is necessary to ensure that the taxpayer properly assessed his tax liability.
- The government has taken several measures to correctly implement GST, one of which is an audit.
On 1st Feb 2021, Union Budget 2021:
- GST audit requirement has been removed from the GST law by professionals such as Chartered Accountants and CMAs. This was amended in Sections 35 and 44 of CGST Act.
- According to the amendment, taxpayers only have to submit GSTR-9 annual self-certified returns to the GST portal, completely abolishing the GSTR-9C reconciliation statement requirement.
- Moreover, the Govt still has to clarify the fiscal year and the date on which this removal is applicable. Note that GSTR-9C is still subject to change for Financial Year 2019-20.
Key Objective GST Audit:
A GST audit’s main goal is to establish a reconciliation between the information declared in GSTR 9 – Annual return and the audited financial statements.
- To Taxpayer the compliance of Registered Taxpayers (RTP) with the provisions of the GST Act & GST rules made thereunder.
- To make ensure & promote the correctness of
- input tax credit availed,
- turnover declared,
- refund claimed and
- taxes paid,
This can be a difficult task, and even if such information is found, its accuracy must be validated using audited financial statements.
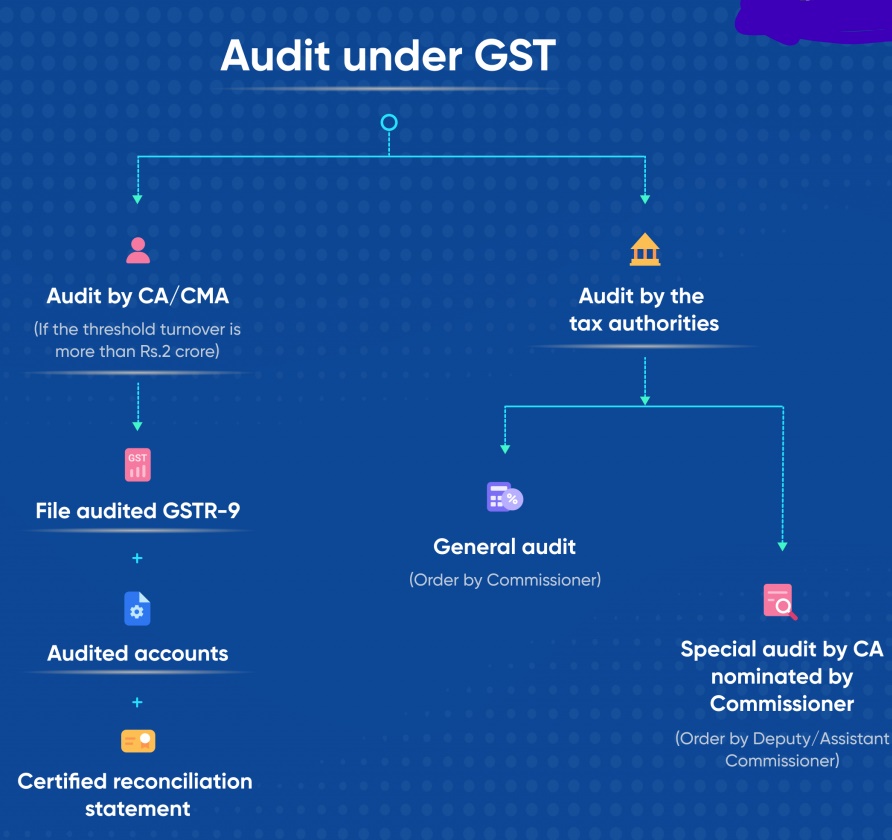
Who are all subject to the Goods and Service Tax audit?
- GST Audit applies to any registered taxable person whose annual aggregate turnover (Value of all taxable supplies whether it is inter-state or intra-state + exempt supplies + supplies made outside India) exceeds INR 2 Cr during a Financial Year.
- The GST taxpayer may be able to get his account and any other documents audited by a chartered accountant (CA) or by a Cost and Work Accountant (CWA).
- Each state shall be audited separately under GST. For that reason, there is a separate GST audit under the same permanent account number for every single registration (PAN).
Kind of GST Audit
| Kind of GST Audit | Who required to be Performed | When required to Initiated |
| General Audit/Normal audit | Commissioner of SGST/ CGST or any Officer authorized by him | On order of Commissioner by giving 15 days prior notice |
| Turnover based Audit | CWA or Chartered Accountants appointed by the taxpayer | If the Turnover exceeds 2 crores the taxpayer has to get his accounts & records audited |
| Special audit | Chartered Accountants or CWA appointed by the taxpayer which is nominated by Commissioner | On order of Assistant/ Deputy Commissioner with prior approval of Commissioner |
In case the businesses have a turnover of less than INR 5 Cr, filing of GSTR-9C for Financial Year 2020-21 is waived off.
Turnover-based GST Audit U/s 35(5) of CGST Act
- When a GST Registered taxpayer’s Annual Aggregate turnover exceeds Rs. 2 crores in a Financial Year a practicing CA or CWA audits his accounts every year
- It required to be noted that 12-month period from April to March of the next calendar year shall be the financial year.
- Special Note: In a press release dated 3 July 2019, the government clarified the turnover ceiling for the financial Year 2017-18.
- The period from 1 July 2017 to 31 March 2018 shall apply and the first quarter of Financial Year 2017-2018 shall be excluded. And
- GSTR-9C for Financial Year 2018-19 is withdrawn for businesses with an annual turnover below Rs 5 crore.
Annual Aggregate turnover is calculated as below:
-
- Annual Aggregate turnover = Value of all taxable (inter-state and intra-state) supplies + Exempt supplies + export supplies of all goods and services
- Total turnover calculation shall be PAN-based, i.e. all business entities registered under the GST of the PAN are responsible for the GST audit of a fiscal year once the PAN turnover is greater than Rs. 2 crores.
- GSTR-9C for Financial Year 2018-19 is withdrawn for businesses with an annual turnover below Rs 5 crore.
Following Items excluded while calculating Annual Aggregate turnover:
- Goods supplied to or received back from a Job Worker.
- Activities which are neither supply of goods nor service under schedule III of CGST Act.
- All taxes and cess charged under Goods and Service Tax like CGST, SGST or IGST, Compensation Cess.
- Inward supplies on which tax is paid under reverse charge mechanism (RCM).
Following Items included while calculating Annual Aggregate turnover:
- Goods supplied to/received from job worker on a principal-to-principal basis.
- All taxable (inter-state and intra-state) supplies other than supplies on which reverse charge is applicable.
- Value of all export/zero-rated supplies.
- All exempt supplies. E.g. Agricultural produce supplied along with branded ready-to-eat food.
- Supplies between separate business verticals.
- All taxes other than those covered under GST Eg: Entertainment Tax paid on the sale of movie tickets.
- Supplies of agents/ job worker on behalf of the principal.
How to Conduct GST Audit & handling Issue of GST Audit report

Points to be kept in mind/ remembered for GST Audit:
- At least 15 days must be given for collection, compilation, preparation and arrangement of documents for audit from receipt of an audit notice
- Adjournment can be sought in case of unavoidable circumstances.
- The registered person can submit his say throughout the audit proceedings in written form
- GST taxpayer must given the opportunity of hearing.
- The GST audit shall be finished within the prescribed period, i.e. three months.
- In case any non-payment of tax is found out, such tax may be paid in conjunction with interest before issuance of the Show Cause Notice. In such cases, no penalty may be imposed
- GST audit findings must be notified in Form GST ADT-02 within 30 days of the end of the audit.
GST Audit program may be prepared considering the various aspects to be covered in the report, i.e., checks to be performed to verify the following:
- Whether the books of account and related records maintained are sufficient for verification of the correctness, completeness and accuracy of the returns.
- Is the annual return filed reflects the correct figures and includes all the transactions effected during the year that require disclosure.
- Whether the value of outward supplies and inward supplies declared in the annual return includes all the outward supplies and inward supplies, respectively, affected during the year.
- Is inclusions and exclusions to/from the value of supply are in accordance with the provisions of the law.
- Whether the exemptions claimed in the annual return are in conformity with the provisions of the law;
- Is amount of Input tax credit determined as eligible and ineligible has been determined in accordance with the provisions of the law.
- Whether the classification of outward supplies, rate and amount of tax thereon, and nature of tax, is correct.
- Is all the other information given in the return is correct and complete.
Preparedness of GST Audit includes
- Preparation and making reconciliation of on internal reconciliation,
- Ensure proper presentation of all relevant documents;
- Above all, review of the legal positions under GST. In this respect, some instances are as follows:
- The transactions for which GST has not been released (for example, GST on transactions covered by Schedule – I of the CGST Act (i.e. supplies without reference) cannot be released);
- Where the input tax credit for goods/services covered in Section 17(5) of the CGST Act is misused (for example, the input tax credit for goods/services inadvertently exploited)
- If input tax credit is reversed, whenever necessary, and if the reversal is correct in the case of misallocation of GST advantages (e.g., reversals of input tax credits to the level of making the supplies exempt under Rule 42 and 43 of the CGST Rules) (e.g. claiming refund of IGST paid in respect of exports subject to the provisions of GST).
- The authorized representative (who is aware of all facts and legal positions) of that registered individual must be identified to represent the GST Dept at the time of an audit.
GST Audit should be done Seriously and time-consuming with the full knowledge of fact and legislation, including the corresponding updates about the GST law.
GST Auditor Appointment:
- A partner or proprietor, or BOD (Board of Directors) in case of a Company should appoint a GST Auditor at the starting of the FY.
Forms for Annual return and GST Audit:
| Various kind of taxpayer | Applicable Form to be filed |
| Cases where Applicable for GST Audit | |
| Taxpayers whose turnover exceeds Rs. 2 crores in FY | Form GSTR-9C |
| Cases Whether or not applicable to GST Audit | |
| A registered person who is a Taxpayer under Composition Scheme | Form GSTR-9A |
| A registered person who is a Regular taxpayer filing GSTR 1 and GSTR 3B | Form GSTR-9 |
| GST registered Person who are E-commerce operator | Form GSTR-9B |
What are Accounts to be to be audited/reviewed by GST Auditor:
Below are important information records & accounts for review:
- ITC(Input tax credit) availed & Utilized
- Sales Register
- Purchase Register and Expenses ledgers
- Stock Register
- E-way bills generated during period under Audit, if in compliance with rules.
- Output tax payable and paid.
- Any documents that record communications from the GST department relating to the Financial Year.
- Output tax payable and paid.
GST Auditor’s Review of Comments:
- Any tax liability pending payment by a taxpayer identified by the reconciliation exercise and the GST audit observations shall be reported by the auditor. As requested by the auditor in form DRC-03, taxpayers can pay taxes.
GST Audit Report Submission & Annually Return:
- The GSTR-9C finalized may either be certified by the same Chartered Accountants or CWA that performed the GST audit.
- If GST Auditor finds any problem or mismatch in these books of accounts or related records of taxpayer, the GST Auditor shall add a comment in GST Audit Report.
- Furthermore, GST Registered person can rectify such a mismatch reported by GST Auditor in Form 9C.
GST Auditor or the certificatory must report and certify as follows:
- Whether the Financial Statements are drawn up or not in accordance with the account books maintained at the taxpayer’s principal place of business or additional business.
- Whether all accounts and records required are kept or not.
- List audit comments, reservations or comments where applicable.
- Certify the correctness of the GSTR-9C information.
- The filing of GSTR-9C for Financial Year 2018-19 shall be waived for companies that have an annual turnover of less than Rs 5 crore. For more information, see our article on GSTR-9C content.
Rectifications to Returns After GST Audit
- If any taxable person, after furnishing a GST return discovers any omission/incorrect details (from results of audit), he can rectify subject to payment of interest.
- However, No rectification will be allowed after that.
Return adjustments following the GST Audit.
- If any taxable person after furnishing a GST return discovers any omission/incorrect details (from audit findings), he or she may correct subject to interest payment.
- However, no rectification will be permitted after the earlier of:
(i) the actual date of filing o the relevant annual return. Or
(ii) the due date for filing of return for the month of September or 2nd Quarter following the end of the Financial Year,
GSTR 9 filing mistakes
- GSTR-9 table 8A requires a reconciliation report, which is related to mismatching Input tax credit.
- Filing GSTR-9 for all your clients with so much of the information can be a time-consuming and cumbersome activity.
Due dates for submission of GST Audit report:
- GST-9 and GSTR-9C are due on or prior to 31 December* of the following fiscal year for submission of the GST audit report. Special Note: *GSTR-9 submission made optional for Financial Year 2017-18 and Financial Year 2018-19 to businesses with turnover up to Rs 2 crore^s.
- GSTR-9 filing due date for Financial Year 2020-21 extended up to 28th February 2022.
Notes : Important issue in filling GST Audit Filling Form 9C under the GST
What are the applicability of pay Additional GST Tax via DRC-03?
Conditions or Prerequisites before submissions of DRC-03
Under the Gst Form DRC-03 is used for making a voluntary payment of GST. In case of Voluntary payment of GST can be made either:
- Before the issuance of show cause notice
- Within thirty days of issue of show cause notice, in case the SCN is already issued
Take a note That: All payments must be made with either input tax credits or cash balances from the electronic credit ledger or the electronic cash ledger. However, the Input tax credit cannot be used in the case of interest and penalties. It is compulsory to be paid in full and in cash.
What happens once you submit the DRC-03?
- The status of the submission will be modified to “Pending Tax Officer Approval.”
- GST taxpayer receives an acknowledgement in the form GST DRC-04 from the tax officer (Acknowledgement of Acceptance of voluntary payment).
- There are no restrictions on a taxpayer making another voluntary contribution while the tax officer’s acknowledgement is still pending.
Penalty for failure to submit a GST Audit report:
No particular provision exists with regard to GST Audit Noncompliance. However general penalty is therefore applicable i.e INR 25,000. GSTR-9C for Financial Year 2018-19 is discontinued for businesses with annual turnover below Rs 5 crore.
Popular Articles: