All About FSSAI Registration Process
Page Contents

All About FSSAI Registration Process
The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) is an organization that monitors and governs the food industry in India. It is a self-governing body established by the Government of India’s Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
The FSSAI was established under the Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006 (FSS Act), which is a consolidated statute in India governing food safety and regulation.
It helps to ensure that food products are subjected to quality assurance, thereby reducing food adulteration and the sale of sub – standard products.
It is in charge of registering and licencing Food Business Operators (FBO) in India, as well as establishing the rules and regulations for conducting food business in India.
FSSAI Registration/License:
Every food business operator who manufactures, processes, stores, distributes, or sells food products must obtain an FSSAI Registration or License.
FSSAI Registration differs from FSSAI License in that FBO should obtain the necessary registration or licence depending on the size and nature of the business.
It’s a 14-digit licensing or registration number that displays on every food package. The 14-digit registration number contains information about the assembling state and the producer’s permit.
This registration procedure is intended to increase accountability on the part of the FBO in order to maintain the quality of the food products.
The Food Safety and Standards (Licensing and Registration of Food Businesses) Regulations, 2011, govern the licencing and registration process and standards.
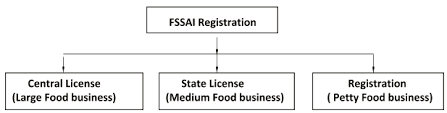
Types of FSSAI Registration
The FSSAI registration or license is based on the size of the business and the location of the premises. The applicant premises may be eligible for a basic license, a central license, or a state license, depending on their installed capacity, turnover, or location.
Procedure acquiring an FSSAI Registration/License
The registration of the FSSAI is commenced by submitting of Form A (registration application) or Form B (State and Central License application) to the Food and Safety Department or online application on the FoSCoS portal.
The appropriate documentation must be presented with the application. At the time of filling out the application, it must be submitted to the Food and Safety Department or uploaded digitally to the FoSCoS portal.
The Department has 7 days from the date of receipt of an application to accept or reject the application, and the denial must be communicated to the applicant in writing.
If the application is approved, the department will provide a registration certificate that includes the applicant’s photo and registration number.
During business hours, the certificate of registration shall be conspicuously displayed at the FBO. A passport photo and a photo ID are the common documents required for basic, state and central registration.
-
Requirement for FSSAI Registration
FSSAI Registration is a basic licence and is necessary for all small food business FBO members. Registration is a basic licence. The following companies cover this category:
- Any FBO with a turnover not greater than Rs. 12 lakh per year.
- Small retailer with food products.
- Anyone who produces or sells food items alone.
- The temporary stall holder makes food sales.
- Anyone who distributes food except caterers at any religious or social meeting.
Small or cottage industries deals in the food industry and the following:
Sl. No |
Business |
Capacity |
| 1 | Food production capacity (other than milk and meat) | Up to 100 kg/ltr per day |
| 2 | Procurement, handling and collection of milk | Up to 500 ltr per day |
| 3 | Slaughtering capacity | 2 large animals or 10 small animals or 50 poultry birds per day or less |
FSSAI License Requirement
Apart from small-scale businesses, all other FBOs must obtain an FSSAI licence. FSSAI Licenses are divided into two categories: State FSSAI Licenses and Central FSSAI Licenses, depending on the size of the firm, whether it is small or large.
FBO with large manufacturing units, importers, exporters, and other large-scale food businesses must obtain FSSAI registration from the central government, while FBO with small to medium-sized manufacturing units, transporters, marketers, traders, and other small to medium-sized manufacturing units must obtain FSSAI registration from the state government.
The FBO must have a turnover of between Rs 12 lakh and Rs 20 crore in order to apply for a State License.
Other prerequisites include manufacturing plants of 2MT per day, dairy plants of up to 5000 liters per day. 3-star and above hotels, refurbishes, re-labellers, clubs, canteens all catering companies have to apply for a license regardless of their turnover.
The license term is not greater than 5 years and not less than 1 year.
The FBO must have a turnover exceeding Rs 20 crores in order to apply for a central license and must operate in two or more states. This license must be requested by all importers and exporters. The maximum tenure shall be five years and the minimum shall be one year.
Required Documents for the Central License:
- Form B has been duly filled out and signed.
- The size and operation-wise area allocation of the processing unit are shown in the diagram.
- Address, contact information, and photo ID for all Directors/Partners/Proprietors.
- The number and installed capacity of the equipment and machinery utilized, as well as the name and list of the equipment and machinery.
- A list of food categories that will be manufactured.
- A responsible person was named and their address was included in an authority letter from the manufacturer.
- Water analysis report to be utilized in the process to ensure mobility
- Milk, meat, and other basic materials are obtained from this source.
- Wherever possible, implement a recall plan.
- 100% EOU certificate from the Ministry of Commerce.
- The FSSAI has issued a NOC/PA document.
- DGFT has produced an IE code document.
- Form IX. Ministry of Tourism certificate.
- Evidence of property possession.
- Proprietorship partnership certificate/affidavit.
- The manufacturer’s NOC and copy of a licence.
- System plan or certificate for food safety management.
- City or local authority NOC.
- Supporting document on sales and transportation evidence
- Form of declaration.
- Documents necessary for State License obtainment.
- Full and signed Form B properly.
- Processing unit plan that shows the size and operational allocation of area.
- List of managers/partners, owner with address, contact details and photo identification.
- The name and description of the equipment and machinery used, as well as the number and installed capacity.
- A list of food categories that will be manufactured.
- The manufacturer’s authority letter designated a responsible person’s name and address.
- Water analysis report to be used in the process to confirm portability.
- Possession of the premises must be proven.
- A partnership agreement or a proprietorship affidavit.
- NOC and a copy of the manufacturer’s licence
- Copies of certificates obtained under the Coop Act of 1861 and the Multistate Coop Act of 2002.
- Plan or certificate for a food safety management system
There are various forms and documents that must be submitted for license conversion, renewal, and modification.
Types of Businesses that Require FSSAI Registration/License:
An FSSAI Registration/License is required for the following types of businesses:
- Retailers, small retailers, shops, bakery or bakery, etc. Small retailers and retailers
- Temporary stalls or stable facilities for food products such as Gol gappa stall, chat stall, fruits/vegetables retailers, tea stall, snacks, bread stall, pan stall, Samoa stall, chinese food stall, south-eastern Indian food stall, sweet stall, juice shop, etc.
- Hawkers who travel from one location to the next sell packaged or freshly prepared food (usually on foot or moving carts).
- Milk Chilling Units, Petty Milkman, and Milk Vendors are examples of dairy units.
- Units for the Production of Vegetable Oil
- Slaughtering establishments such as meat shops, mutton shops, chicken shops, lamb meat shops, and so on.
- Units for meat and fish processing
- All food manufacturing/processing units that include food repackaging.
- Food that is unique and proprietary.
- Storage facility that is cold/refrigerated.
- Food product transporter with a variety of specialised vehicles such as an insulated refrigerated van/wagon, milk tankers, food waggons, food trucks, and so on.
- Food wholesaler, supplier, distributor, and marketer.
- Hotels, restaurants, and bars are all available.
- Cafeterias and canteens, including mid-day meal canteens
- Caterers and food vending agencies
- Dhabas, PGs that serve food, banquet halls with food catering services, home-based canteens, and food stalls at fairs or religious institutions are all examples of food stalls.
- Food importers and exporters, as well as food ingredients.
- Cloud kitchens are e-commerce food vendors.
- Each of the above-mentioned business types requires a different sort of FSSAI license/registration according on their eligibility conditions. The FSSAI lists the eligibility requirements for each type of business and license/registration.
Advantages of Obtaining an FSSAI Food License
Obtaining a license can provide legal benefits to the food business, build goodwill, ensure food safety, raise consumer awareness, and help in business expansion. It also facilitates in the regulation, manufacture, storage, distribution, and sale of imported food.
FSSAI: Food Safety and Standards Authority of India has notified the Final Food Safety and Standards (Food Product Standards and Food Additives) *Amendment Regulation, 2017 in the official gazette of India w.r.t oils, fats, oats and pasta applicable from 1st July, 2017.
Penalty for Non- Compliance
Penalty for various type of non-compliance are given as below:
| Sl. No | Particulars | Fine |
| 1 | Misleading advertisement or false description | 10 Lakh |
| 2 | Misbranded Food | 3 Lakh |
| 3 | Failure to comply with Food safety officer direction | 2 Lakh |
| 4 | Unhygienic processing or manufacture | 1 Lakh |
| 5 | Extraneous matter in food | 1 Lakh |
| 6 | Sub-standard food | 5 Lakh |
| 7 | Food quality not in compliance with act | 2 Lakh Petty manufacturer – 25,000/- |
Renewal of FSSAI License
To establish a food business, you’ll need an FSSAI license, and you’ll also need to renew it. Because the license is valid for one year or five years, the company must apply for renewal 30 days before the existing license expires.
Read our articles: