Formation Of Charitable Trust in India
Page Contents
Formation of Charitable Trust in India
Brief Introduction
- A Trust is a sought of obligation or responsibility placed on one in whom confidence or authority is place; it’s a confidence reposed in a person by conveying to him the legal title to property which he’s to carry for the advantage of others.
- Hence, the “Trustee” has been vested with various responsibilities and the same includes protection of the rightful ownership in respect of the Trust property, along with the preservation of the property and channelization of the income of the Trust property, as per the intentions of the creator of the Trust.
- During this article, we glance at the procedure for forming a charitable trust in India.
Meaning of Trust
As per Indian Trusts Act, 1882, a Trust has been defined as an entity, being established with an obligation annexed with the ownership of property and the same arises out of confidence reposed in and accepted by the owner, for take the advantage of trust himself, or for another and himself.
- The one that reposes or declares the confidence is named the “Author of the Trust”.
- The one who accepts the confidence is named the “Trustee”.
- A person for whose benefit the confidence is accepted is named the “Beneficiary”.
- The subject matter of the trust is named “Trust Property” or “Trust Money”.
- The instrument if any, by which the Trust is registered is termed as the instrument of Trust or trust deed.
Documents needed for Trust Registration
Following list of documents which 1 should have for Trust Registration:
- ID proof such as Election Voter ID, Adhaar Card or Driving License, Passport of minimum of 2 members.
- ID proof of the settlor
- 2 photographs of which 1 must be of passport size
- Proof of registered address such an water bill or electricity
- ID proof of each of the 2 witnesses & their photo
Essential Elements for the Formation of Trust
The following elements are essential for the formation of a Charitable Trust:
- The Author or Settlor
- The Trustee
- Beneficiary
- Trust Property or subject matter of the proposed trust
- The objects of the Trust
Pre-Requisites of Trust Registration
As per Section 6 of The Indian Trusts Act, 1882 a Trust is formed when the Author of the Trust indicates with reasonable certainty by any words or acts the following:
- Author’s intention to create a Trust
- purpose of proposed Trust
- Beneficiary
- Trust Property
- Transfer of Trust Property to Trustee.
Who can create a Trust?
A trust can be established by:
-
- Any individual, AOP, HUF, firm, or other organization that is capable of contract.
- If a trust is to be formed on behalf of or for the benefit of a minor, permission from the a Principal Civil Court of Original Jurisdiction is needed.
It also depends on the law in effect at the time and the specific time to which the author of the trust may intend to dispose of his property.
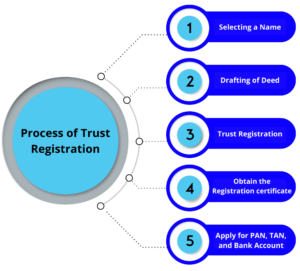
Procedure Of Trust Registration
below is step which we required to take for Trust Registration in India:
Kind of Trusts
-
Public Charitable Trust
- For forming a charitable trust, the procedure is quite different from the point of view of private Trust, since they’re governed by different laws.
- The formation of trust is governed by a general law, however, the formation of a non-public Trust is governed by Indian Trusts Act, 1882.
- A public institution is established in the form of either as a Trust, a Society or as a section 8 Company. Generally, such institutions take the shape of a Trust, where the same is required to be established primarily by one or few persons. During this guide, we only cover the procedure for forming a non-public trust.
-
Private Charitable Trust
In order to form a non-public Trust, the foremost requirement is of an Author who is required to express with reasonable certainty, an intention to form a Trust.
A Trust is also declared either by words, spoken or written or by acts. Where a Trust is declared by Trust words, the language used must be clear enough to point out an intention to make a Trust.
For this, no formal language is required, in order to constitute a good declaration of Trust, however, the language must make it clear that:
-
- The Author intended to constitute a Trust binding in law on himself or the person to whom the property was given.
- The Author intended to bind definite property by the Trust.
- Author intended to learn a definite person or persons in an exceedingly definite way.
Compulsory Registration for a Private Trust
According to Section 5 of the Act, whenever it relates to:
- Immovable property: A private trust must be established through a written non-testamentary instrument. The non-testamentary instrument must also be signed and recorded by the author of the trust or the trustee. Registration is not required if the non-testamentary instrument is created by a will.
- Moveable property: A movable property trust can be established in the same way that an immovable property trust is established, or by transferring ownership of the property to the trustee. As a result, registration is not necessary.
Trust Deed
A Trust are often formed by words or act and there’s no requirement for a trust deed.
However, it is desirable to have a trust deed. When a non-public Trust pertains to an immovable property a written and executed trust deed is important and shall also require to be registered except where the Trust is made by a will. Just in case of charitable trust immovable property, a written trust deed need not be mandatorily registered,
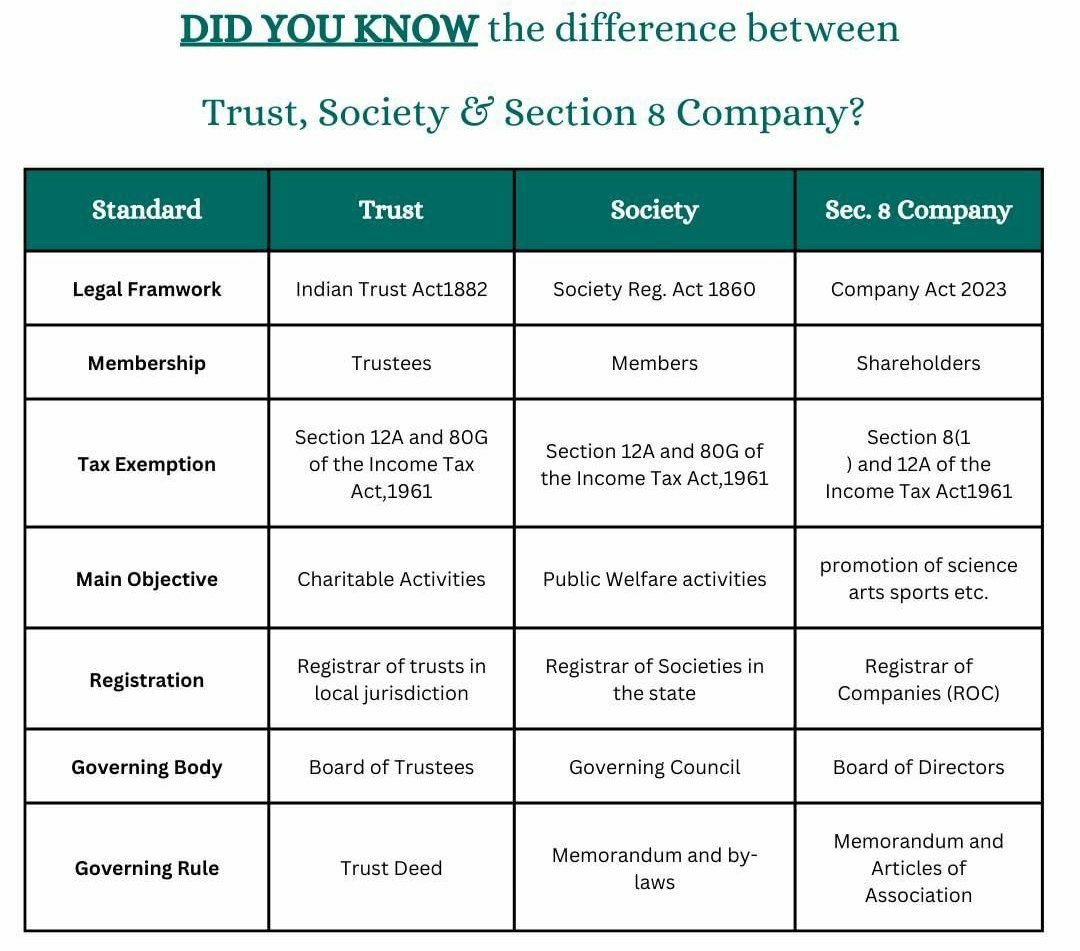
What is the difference between trust NGO and Section 8 company?
Reasons For forming a Trust
Charitable Trusts are formed in India for one or more of the subsequent reasons:
- Discharge of the Charitable or religious sentiments of the Author, in a very way that ensures public benefit.
• For claiming exemption from income tax, as the case could also be, in respect of incomes applied to charitable or religious purposes.
• For welfare of family members or other relatives, being dependent on the settlor of proposed Trust
• For the right management and preservation of property.
• For regulating the affairs of a provident fund, superannuation fund or gratuity fund or the other fund constituted by someone for the welfare of its employees. - Tax benefit of Trust
Conclusion
The word “trust” refers to a legal entity that fulfills society’s needs. Register a Trust if you want to also contribute to a social cause. Even though the process of forming a trust appears simple, preparing the necessary documentation for Trust Registration can be a challenging task.
As a consequence, obtaining legal advice from a firm like RJA experts is a wise decision. Not only will our expert assist in the drafting of the required documents, but he will also assist in the formation of the Trust Deed.
Hope the information will help you in your Professional endeavors. For help, contact: singh@carajput.com or call at 9555555480

