Residential Status under the Income Tax Act
Page Contents
RESIDENTIAL STATUS UNDER INCOME TAX ACT
Tax incidence on an assessee depends on his residential status. For instance, whether an income, accrued to an individual outside India, is taxable in India depends upon the residential status of the individual in India.
Similarly, whether an income earned by a foreign national in India (or outside India) is taxable in India, depends on the residential status of the individual, rather than on his citizenship.
Therefore, the determination of the residential status of a person is very significant.
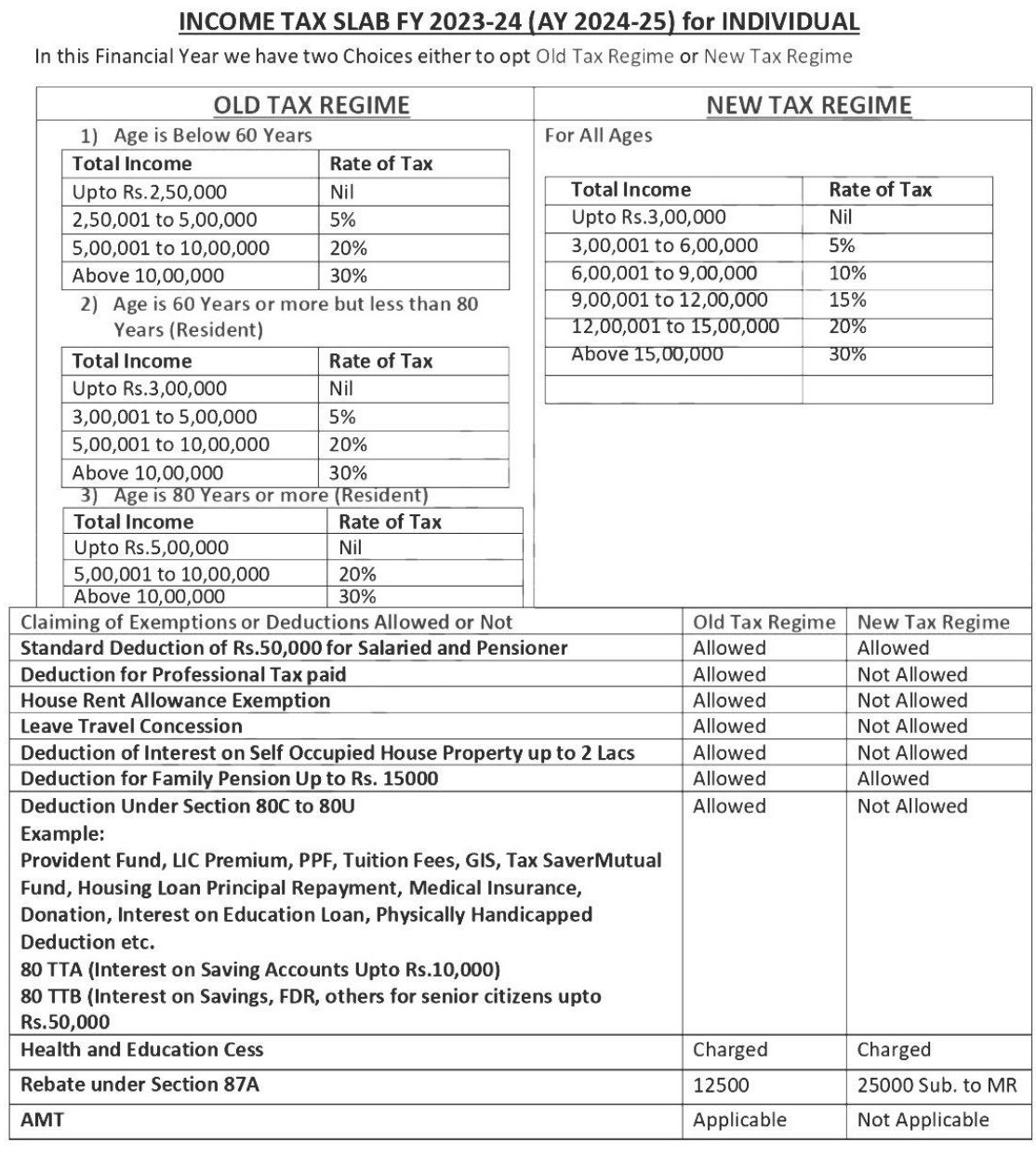
RESIDENTIAL STATUS Of INDIVIDUAL
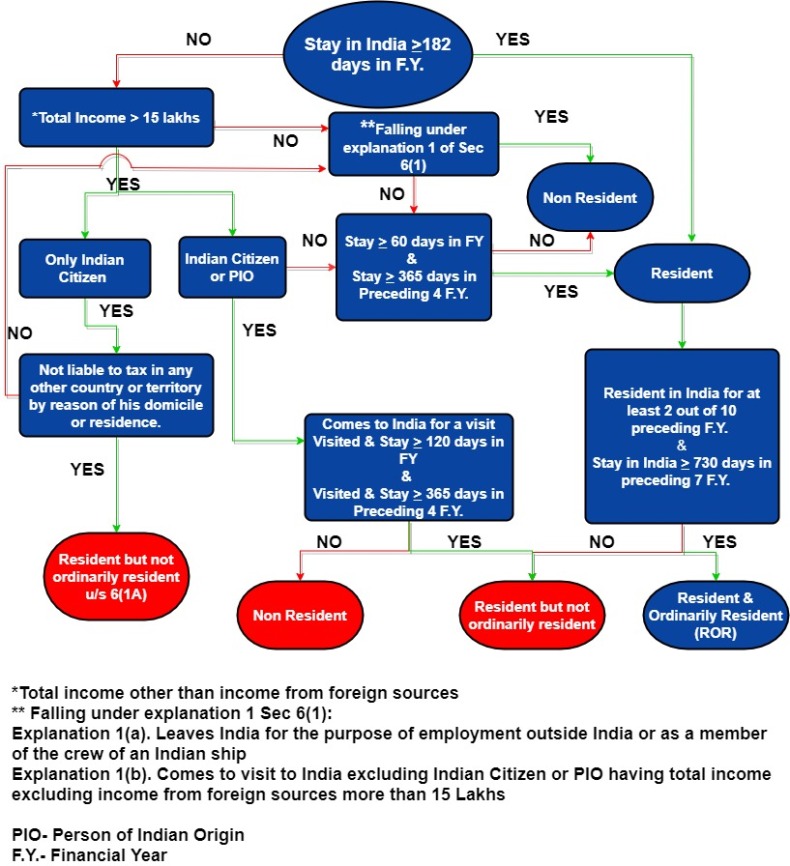
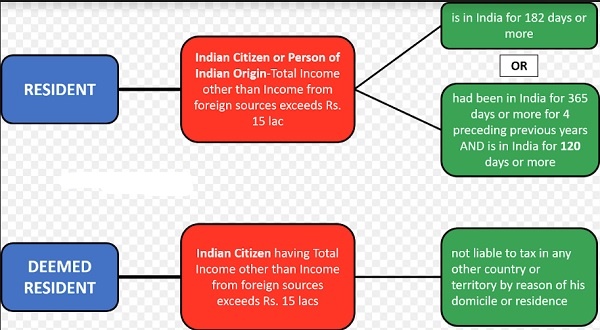
An Individual is said to be a resident Indian for the purpose of Income tax if one of the following Basic conditions are satisfied.
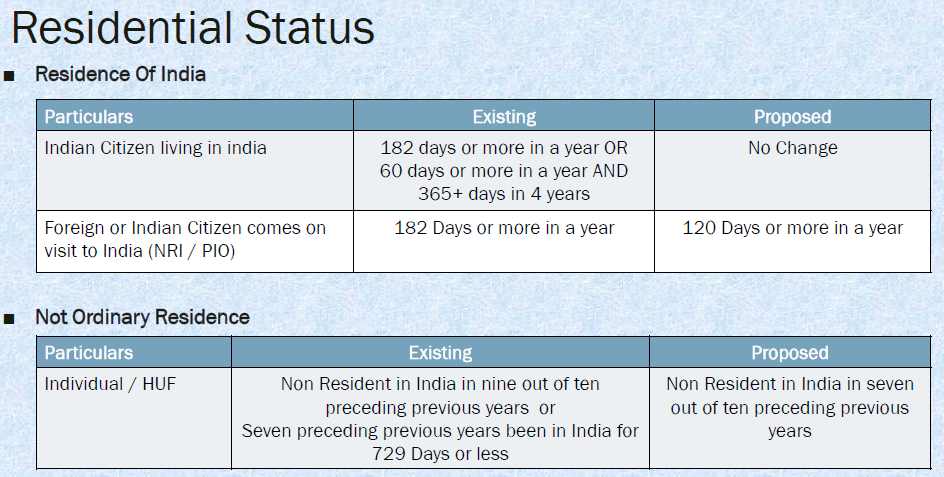
- An Individual is in India for a period of 182 days in the financial year in which he is getting his salary income or,
- An Individual is in India for a period of 60 days or more during financial year in which he gets his salary and 365 days or more during 4 years immediately preceding to that financial year.
Read our articles:
- How to file a return of TDS online
- New TDS deduction No cash transactions exceeding 1 Crore -Section 194N
If one of the above conditions are satisfied then he is resident of india as per income tax. Non-Resident in India if he satisfies none of the basic conditions.
RESIDENT AND ORDINARILY RESIDENT OR RESIDENT BUT NOT ORDINARILY RESIDENT
If the Individual fulfils one the following conditions then he said to be resident but not ordinarily resident of India:
- An Individual is a non-resident in India for 9 years out of 10 years immediately before relevant financial year.
- An Individual is in India for a period less than 729 day during 7 years immediately before the relevant financial year.
Else, he is considered as a resident and ordinarily resident in India.
These conditions need to be tested every year for every Individual.
- When you are calculating the number of days, you have to include the day you left India and the day you arrived in India as part of your total stay in India.
- Stay in India includes stay in territorial waters of India i.e. up to 12 nautical miles into the sea.
- The stay need not be continuous. All different periods of stay in India have to be added up.
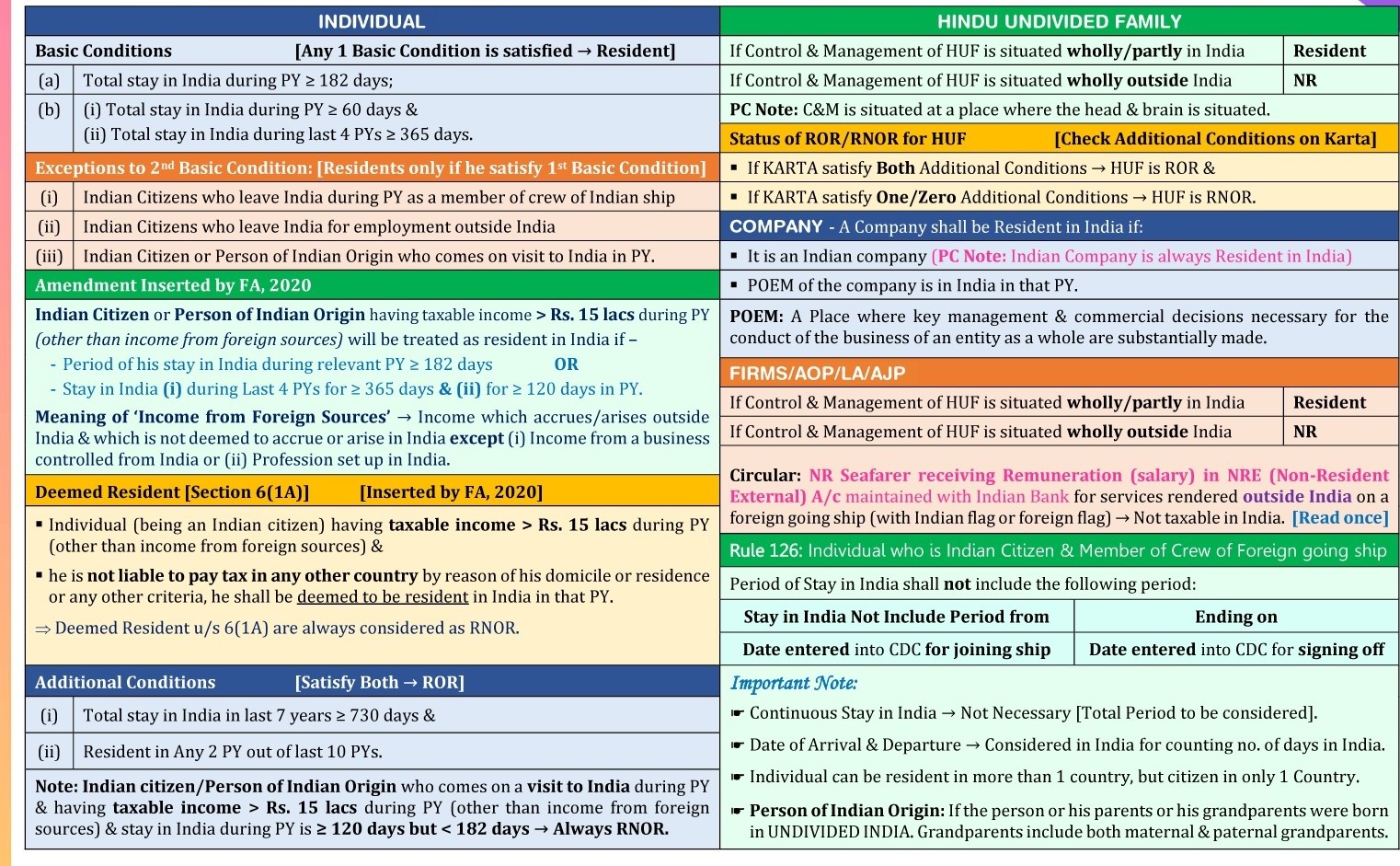
RESIDENTIAL STATUS OF HUF
A Hindu undivided family is said to be a resident in India if the control and management of its affairs is wholly or partly situated in India.
A Hindu undivided family is a non-resident in India if the control and management of its affairs is wholly situated out of India.
In order to determine whether a Hindu Undivided Family is a resident or a non-resident, the residential status of the karta of the family during the previous year is not relevant
Residential status of a company
An Indian company is always resident in India. A foreign company is resident in India only if during the previous year, control and management of its affairs is situated wholly in India.
Conversely, a foreign company is treated as non-resident if during the previous year, control and management of its affairs is either is wholly or partly situated out of India.
A company can never be ordinarily or not ordinarily resident in India.
Other person
Every other person is resident in India if control and management of his affairs is, wholly or partly, situated within India during the relevant previous.
On the other hand, every other person is non-resident in India if control and management of its affairs is wholly situated outside India.
Nature of income & its Taxability income to be taxed in India
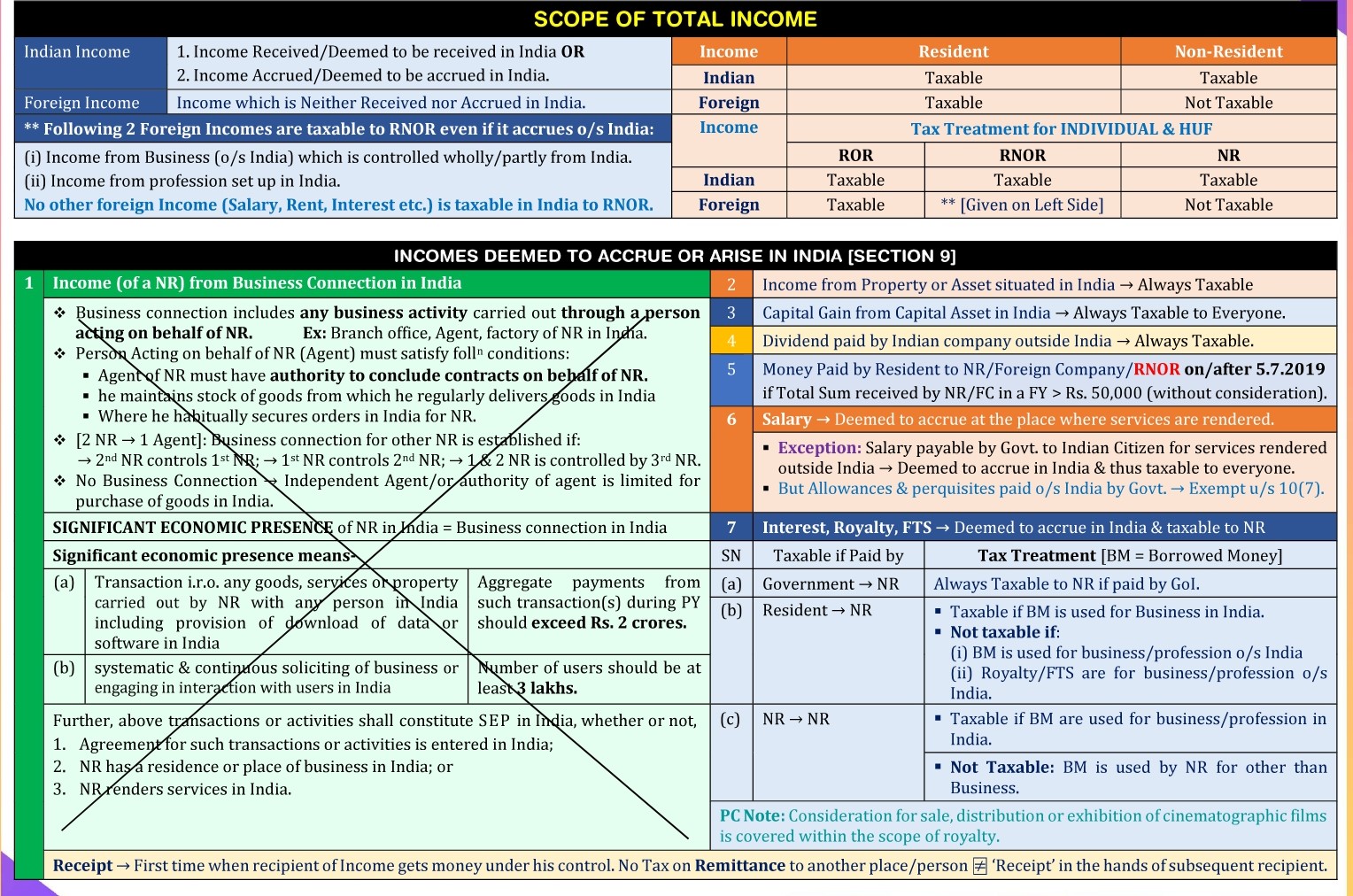
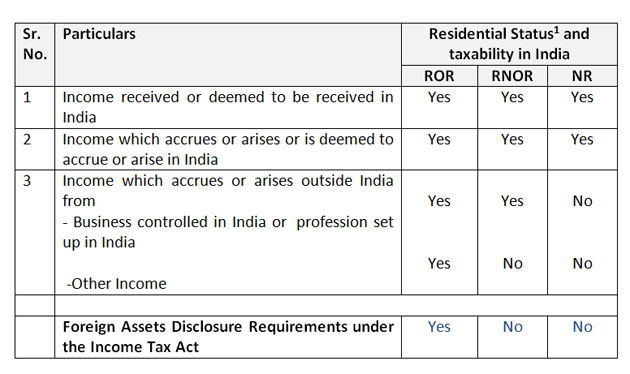
- If you are a NR (Non Resident)
a) You are liable to pay tax “only” on the income earned in India.
b) You are “not taxed” on any income earned outside India “nor” on the income earned outside India out of a business controlled from India or a profession set-up in India2. If you are RNOR (resident but not ordinarily resident)
a) You are liable to pay tax on the income earned in India on the income earned outside India out of a business controlled from India or a profession set-up in India
b) You are “not taxed” on any income earned outside India3. If you are ROR (resident and ordinarily resident)
You are liable to pay tax on all types of incomes i.e.
a) what you earn in India
b) earnings outside India out of a business controlled from India or a profession set-up in India,
c) and also on all other incomes earned outside India