Meaning of Turnover in Income Tax Act, Companies Act & GST
Page Contents
As per companies act, 2013: –
“Turnover” means the gross amount of revenue recognized in the profit and loss account from the sale, supply, or distribution of goods or on account of services rendered, or both, by a company during a financial year.
From the above clause, it is clearly understood that the turnover of a company is defined on the basis of the amount of realization made during the financial year rather than the value of goods sold or service rendered during the financial year.
The New Definition of turnover under companies act {Section 2 (91)} which says that calculation of realization of amount made from the sale of goods or rendering of service during the financial year is require to be done on cash basis.
It means sales of goods and rendering of service on credit term basis during the year is not included in turnover.
In Companies Acceptance and Deposit Rule, 2014
Define eligible company means company having turnover of not less than Rs. 500 crore or more.
Every company having net worth of rupees five hundred crore or more, or turnover of rupees one thousand crore or more or a net profit of rupees five crore or more during the immediately preceding financial year shall constitute a Corporate Social Responsibility Committee of the Board consisting of three or more directors, out of which at least one director shall be an independent director.
As per Guidance Note issued for Financial Statements: –
Turnover means the aggregate amount for which sales are effected or services.
As per Accounting Standards Interpretation (ASI)-29: –
Recognized as revenue in the statements of the contractors as per the requirement of AS-7”
As per The Statement on the Companies (Auditors’ Report) Order, 2003 issued by the Institute in April 2004, while discussing the term ‘turnover’ in paragraph 23 states `as follows: –
The term, “Turnover”, has not been defined by the Order. Part II of Schedule VI of the Act, however, defines the term “turnover” as the aggregate amount for which sales are affected by the company.
It may be noted that the “sales effected” would include sale of goods as well as services rendered by the company.
In an agency relationship, turnover is the amount of commission earned by the agent and not the aggregate amount for which sales are affected or services are rendered.
The term “turnover” is a commercial term and it should be construed in accordance with the method of accounting regularly employed by the company.
As per income tax act, 1961: –
Section 44AB:
An assessee is required to get his accounts audited when his turnover/sales from business is more than Rs 1 crore
Section 44AD:
Businesses, whose annual gross turnover does not exceed Rs. 2 Crore, are eligible under this scheme.
Derivatives, futures and options :
Such transactions are completed without the delivery of shares or securities. Turnover in such type of transactions are to be determined as follows: –
- The total of favorable and unfavorable differences shall be taken as turnover.
- Premium received on sale of options is also to be included in turnover.
- In respect of any reverse trades entered, the difference thereon should also form part of the turnover.
Delivery based transactions:
Where the transaction for the purchase or sale of any commodity including stocks and shares is delivery based whether intended or by default, the total value of the sales is to be considered as turnover.
Gross Receipt: the following items of income would be included: –
- i) Cash assistance received or receivable by any person against exports under any scheme of the Government of India;
(ii) Any duty of customs or excise or service tax re-paid or repayable as drawback to any person against exports under the Customs and Central Excise Duties and Service tax Drawback Rules, 1995;
(iii) The aggregate of gross income by way of interest received by the money lender;
(iv) Commission, brokerage, service and other incidental charges received in the business of chit funds;
(v) Reimbursement of expenses incurred and if the same is credited to a separate account in the books, only the net surplus on this account should be added to the turnover for the purposes of Section 44AB;
(vi) The Net exchange rate difference on export sales during the year on the basis of the principle explained in.
(v) Above will have to be added;
(vii) Hire charges of cold storage;
(viii) Liquidated damages;
(ix) Insurance claims – except for fixed assets;
(x) Sale proceeds of scrap, wastage etc. unless treated as part of sale or turnover, whether or not credited to miscellaneous income account;
(xi) Gross receipts including lease rent in the business of operating lease;
(xii) Finance income to reimburse and reward the less or for his investment and services;
(xiii) Hire charges and instalments received in the course of hire purchase;
(xiv) Advance received and forfeited from customers.
(xv) The value of any benefit or perquisite, whether convertible into money or not, arising from business or the exercise of a profession.
The following items would not form part of “gross receipts in business” for purposes of section 44AB.
(i) Sale proceeds of fixed assets including advance forfeited,
(ii) Sale proceeds of assets held as investments;
(iii) Rental income unless the same is Assessable as business income;
(iv) Dividends on shares except in the case of an Assessee dealing in shares;
(v) Income by way of interest unless Assessable as business income;
(vi) Re Imbursement of customs duty and other charges collected by a clearing agent;
(vii) In the case of a recruiting agent, the advertisement charges received by him by way of reimbursement of expenses incurred by him;
(viii) In the case of a travelling agent, the amount received from the clients for payment to the airlines, railways etc. where such amounts are received by way of reimbursement of expenses incurred on behalf of the client.
(ix) In the case of an advertising agent, the amount of advertising charges recovered by him from his clients provided these are by way of reimbursement.
(x) Share of profit of a partner of a firm in the total income of the firm excluded from his total income under section 10(2A) of the Income-tax Act;
(xi) Write back of amounts payable to creditors and provisions for expenses or taxes no longer required.
Read more about: What is core Business Activity GST
Read more about: All about GST Offenses, Penalties, and Appeals
As per GST Act: –
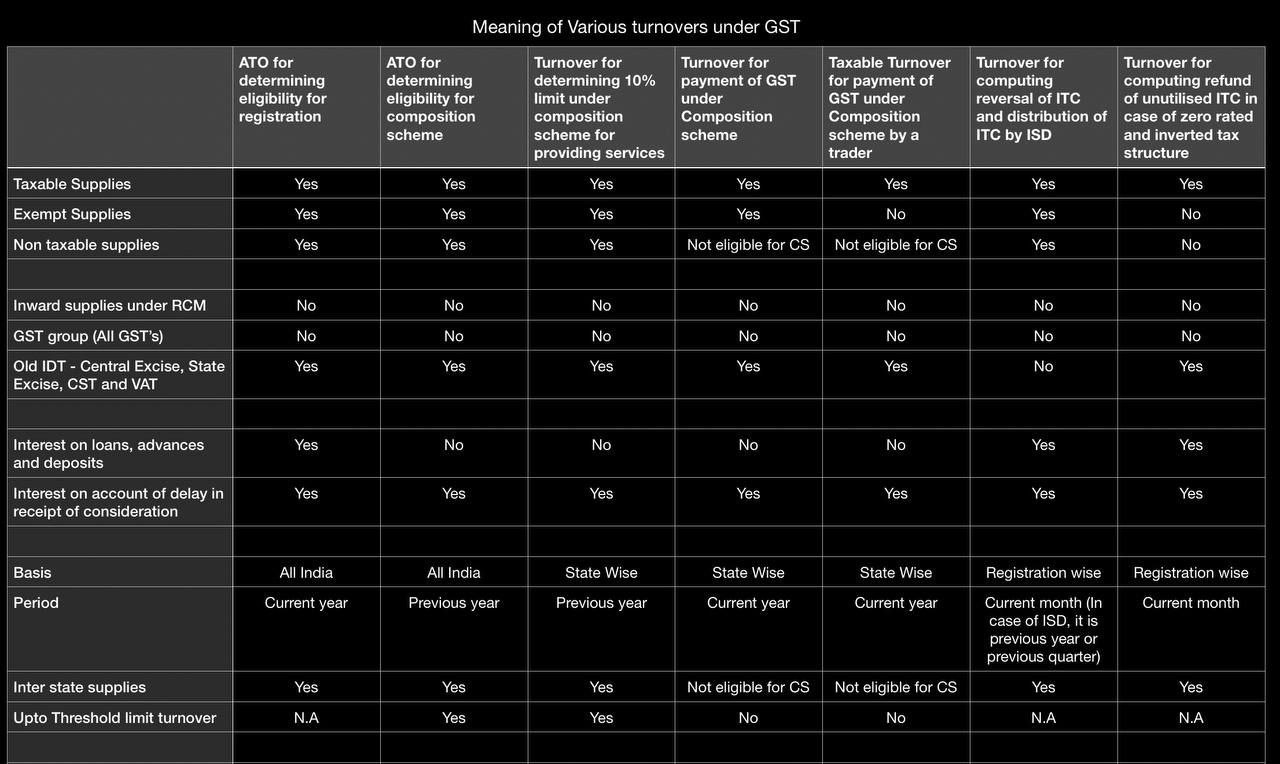
In past, CST/VAT was levied on sale of goods, Service Tax was levied on sale of services while Excise Duty was levied on manufacture.
Under the proposed current GST regime, these and certain other levies are proposed to be subsumed and Tax is leviable on supply of goods or services or a blend of both.
The concept of “supply” and what forms part of Turnover, would be included. The scope of “supply” is quite wide and includes:
- sale, transfer, barter, exchange, license, rental, lease or disposal made or agreed to be made;
- importation of service, whether or not for a consideration; and
- specified in Schedule I, made or agreed to be made without a consideration.
Under the proposed GST regime, “Turnover in a State” has been defined as “the aggregate value of all taxable and non-taxable supplies, including exempt supplies and exports of goods and/or services made within a State by a taxable person and inter-state supplies of goods and/or services made from the State by the said taxable person excluding taxes.
In summarized form “Turnover”:
Includes:
Supplies in Goods or Services or in both effected within state or outside the state.3
Stock Transfer, Barter, Gift in kind, Samples, Exchange of services, etc.3
Exempted supplies, supplies made in the course of export.3
Excludes: Taxes Leviable under the GST Enactments.7
Turnover Redefinition brings certain changes:-
- For Small business exemption is Aggregate Turnover over Rs.9 lakhs for registration and Rs.10 lakhs for levy of Tax. Impact of these are as follows:-
More businesses coming into the Taxation regime.3
Improved benefits with respect to Input Credits.3
Compliance requirements for Small Businesses.7
- For Persons exclusively dealing in exempted goods/services or Exports would be mandatory to take GST registration.
- For North-eastern States Aggregate Turnover over Rs.4 lakhs for registration and Rs.5 lakhs for levy of Tax (as against 9 and 10 lakhs respectively)
As per Amendments in GST law limits of turnover are as follows: –
- Limit of turnover for opting for composition scheme to be raised from Rs. 1 crore to Rs. 1.5 crore. Present limit of turnover can now be raised on the recommendations of the Council.
- Composition dealers to be allowed to supply services (other than restaurant services), for up to a value not exceeding 10% of turnover in the preceding financial year, or Rs. 5 lakhs, whichever is higher.
- Exemption limit for registration in the States of Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, Himachal Pradesh, Meghalaya, Sikkim and Uttarakhand to be increased to Rs. 20 Lakhs from Rs. 10 Lakhs
- Council approved quarterly filing of return for the small taxpayers having turnover below Rs. 5 Cr.


