CBDT Started mobile App called -AIS for Taxpayer
Page Contents

What is AIS?
AIS is a detailed financial summary of a taxpayer for a specific financial year. It is accessible via the Income Tax Portal and serves as an extension of Form 26AS. Uploaded within 3 months from the end of the month in which the Income Tax Department receives the information. AIS is a trigger for inquiry, not a presumption of income. The Annual Information Statement (AIS) and Taxpayer Information Summary (TIS) give the Income Tax Department deep data visibility, but data visibility is not income determination. AIS is merely an input layer, a starting point for inquiry, never a substitute for assessment.
What AIS Actually Does :
- Aggregates third‑party reported information
- Flags mismatches or potential anomalies
- Seeks clarification from the taxpayer
AIS is informational, not adjudicatory. It neither determines income nor creates tax liability.
What an AIS Response Should Contain
A proper AIS explanation must clarify the true nature of each transaction, including whether it is income, a capital receipt, reimbursement, exempt income, or a timing difference. Importantly, the reply must not imply admission or acceptance of taxability. Following are the parts of AIS.
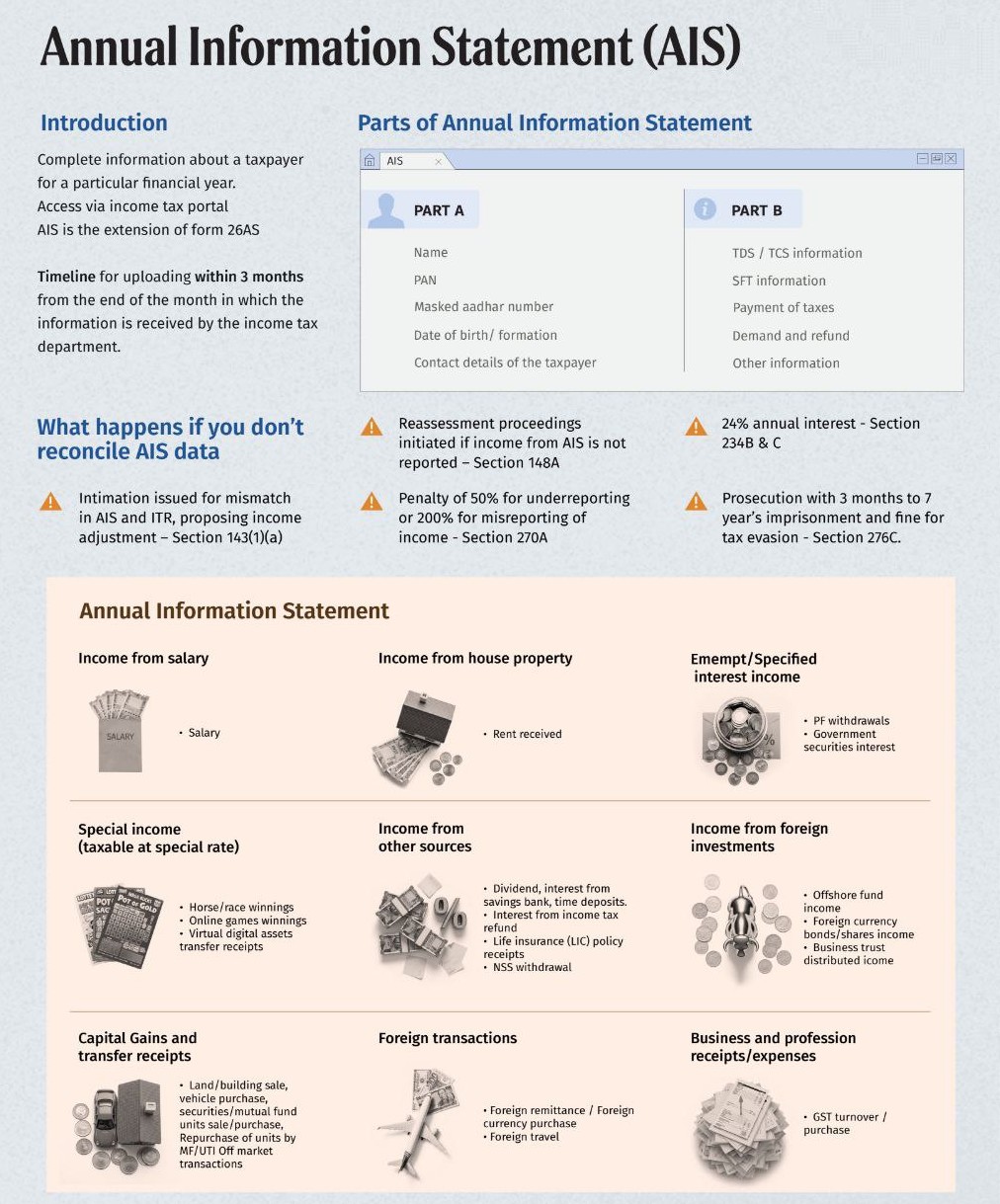
Part A – Basic Details:
- Name
- PAN
- Masked Aadhaar Number
- Date of Birth/Formation
- Contact Details
Part B – Financial Information:
- TDS/TCS Information
- SFT (Specified Financial Transactions)
- Payment of Taxes
- Demand and Refund
- Other Information
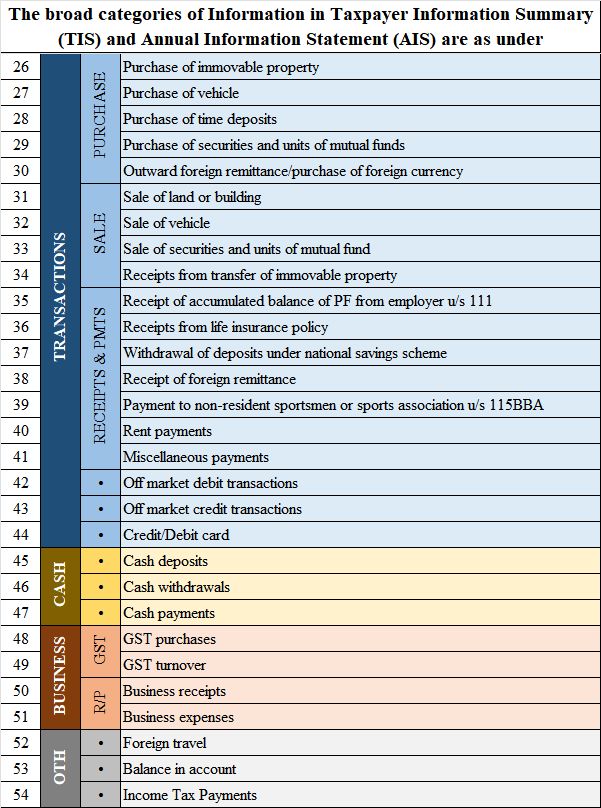
Income Categories in AIS
- Salary Income—e.g., Salary received
- House Property Income—e.g., Rent
- Exempt/Specified Interest—e.g., PF withdrawals
- Special Income—e.g., Horse race winnings
- Other Sources—e.g., Dividends
- Foreign Investments—e.g., Offshore fund dividends
- Capital Gains—e.g., Sale of land/building
- Foreign Transactions—e.g., Remittances
- Business/Profession – e.g., GST turnover
CBDT started a mobile application called “AIS for Taxpayer” for assessees to provide TDS and AIS :
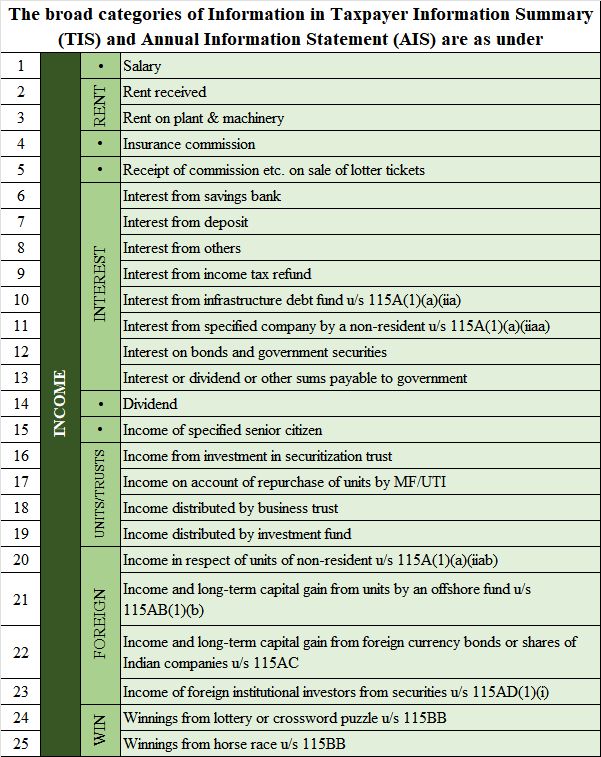
As we know, income tax tries to give an income tax statement in Form No. 26AS. The annual information statement is a much more detailed one with more details included. ex: All mutual fund transactions & Saving account Interest during the year, etc. Now, the Annual Information Statement will capture all the PY financial transactions of the in respect of the below transactions:
- Interest on SB A/c and Deposits.
- Dividends
- Insurance
- Mutual Funds
- Shares
- Salary or Business income
- Purchase of property
- Stocks
- Credit Cards
Selected financial transactions:
Apart from the above list, it is just an indicative transaction list. It is the taxpayer’s overall financial profile & will be getting fine-tuned to include more classes of transactions.
- The new form 26AS will also provide details on “specified financial transactions” that include transactions for the purchase/sale of goods, properties, services, work contracts, investments, expenditures, and receipt or approval of any loan or deposit of the value that may be approved but not less than Rs 50,000.
- FM also suggested steps to ensure full compatibility by extending the scope of monitoring and reporting on subsequent transactions in New Form 26AS
Income Tax Form 26AS
- Details on this Form 26AS at year-end will not be a one-time affair. This will be a live 26AS, as this will be updated regularly within 3 months from the end of the month that such information is gathered.
- For that specific year, Form 26AS will now be a full taxpayer profile as opposed to the previous Form 26AS, which only provided taxpayer information via TDS/TCS or self-assessment. This form will also have the e-mail, mobile no., and Aadhar no. of the taxpayer.
- An enabling provision has also been notified authorizing the CBDT to authorize DG Systems or any other officer to upload information received from any other officer, the authority under any law, in this form.
- Any negative action initiated or found or order carried under any other legislation, such as custom, GST, Benami Law, etc. as well as data on turnover, import, export, etc.
- The above proposed details will also be placed in this form 26AS, so that the taxpayer & tax authorities will understand and have access to the complete database.
- This 26AS form will provide information obtained from any other nation by the Tax Deptt under the agreement/exchange of taxpayers due to income data outside India.
- The implication of this new form 26AS is that financial institutions or any other authority or customer, buyer, etc. will now ask for form 26AS while performing research of the person/corporation worried so as to ensure that there are no significant problems about such kinds of corporations & related people.
- It will now make it impossible for any taxpayer to keep secrets from any bank/financial institution/authority about any proceedings against any statute or tax demand, tax disputes, etc.
- The government has also suggested deducting TDS/collecting TCS at higher rates for those who do not file TDS/TCS returns on income tax (ITR).
- There is also a proposal for the obligatory filing of ITR by those who have their bank transactions above INR 30 lakh, all professionals, companies with revenue above INR 50 lakh, & rent payment above INR 40,000/-
- The new form 26AS will also provide the “selected monetary transactions” information, which includes:
- Buying/selling of goods or real estate transactions, delivering of services
- Transactions made by way of an expenditure or expense.
- Receiving or approving any loan or deposit of the amount specified but not less than Rs 50,000.
- Transactions under contractual works,
- Demand & Refund under the income tax act
- Pending and completed proceedings, which may include assessment, re-evaluation under sections 148, 153A, and 153C, revision, and appeal.
What an AIS Response Cannot Do
An AIS reply does not Convert gross credits into taxable income. Cure the absence of a charging section, Replace statutory assessment procedures and Shift the burden of proving taxability onto the assessee
Data ≠ Income. An AIS entry does not create taxable income by itself.
Assessment Still Requires Judicial Application
A lawful assessment requires classification of the receipt, application of the correct charging provision, and a reasoned conclusion based on evidence. Automated feeds, algorithms, and third‑party reporting may trigger an inquiry but cannot decide taxability.
The Emerging Concern in AIS :
A worrying shift is visible; assessments are becoming explanation‑centric rather than finding‑centric. This inverts the legal framework where the revenue must first establish taxability, and the assessee responds to findings, not assumptions. AIS may initiate a question, but only law and evidence can conclude taxability. AIS can trigger questions, not conclusions. Taxability still begins and ends with law, not data.
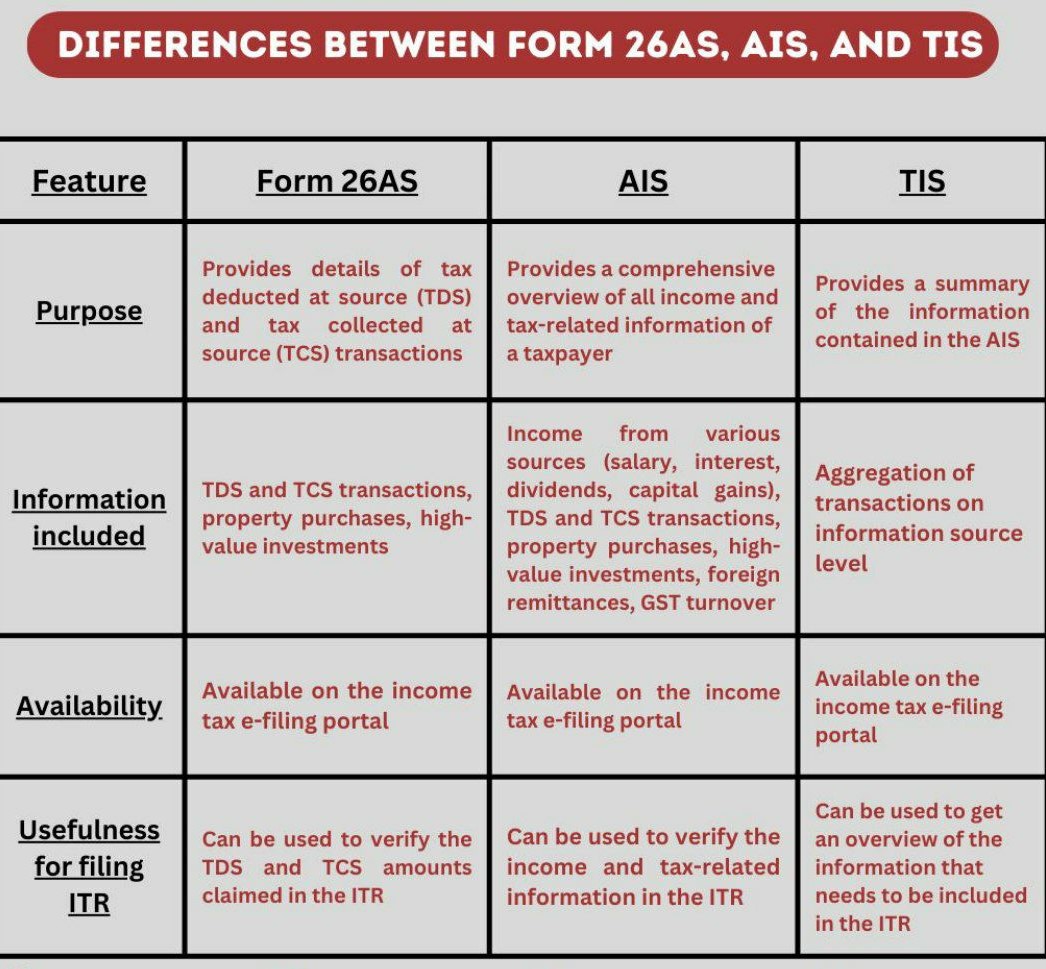
Differences between Form 26AS & AIS
- Below are a few considerable differences between Form 26AS and AIS. The new Annual Information Statement (AIS), which provides an income tax assessment with a clear understanding of the FT made during a FY, was started by the Tax Dept in 2021 and is accessible on the Income Tax Compliance Portal. But 26AS has the complete details of income demand & detailed information about TDS, TCS, etc., only.
- As per the Income Tax Online Portal Frequently Asked Questions on Annual Information Statement, “Annual Information Statement is much more of an extension of Income Tax Form 26AS. Income Tax Form 26AS shows complete information of high-value Annual Information Statements and property purchases. Moreover, it includes dividend, rent received, savings account interest, sale & purchase transactions of immovable properties or securities, interest on deposits, foreign remittances, Goods and services tax sales, etc.
- The Annual Information Statement gives us the taxpayers, the option to provide responses on the transactions reported. Moreover, TIS additionally reports the aggregate transactions at the level of the information source.
New tab inserted to access “AIS” directly
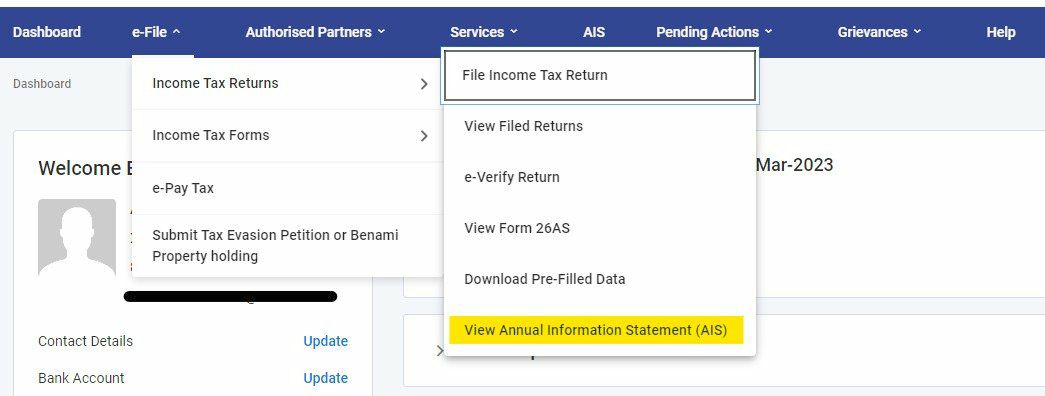
Now AIS can be viewed through 2 way
- Through separate tab “AIS”
- Through e-File>Income Tax Returns>View AIS
The Central Board of Direct Taxes releases new functionality in Annual Information Statement to display the status of feedback given by Taxpayer
Taxpayers can submit their transactions & submit feedback in AIS.- Kind attention taxpayers
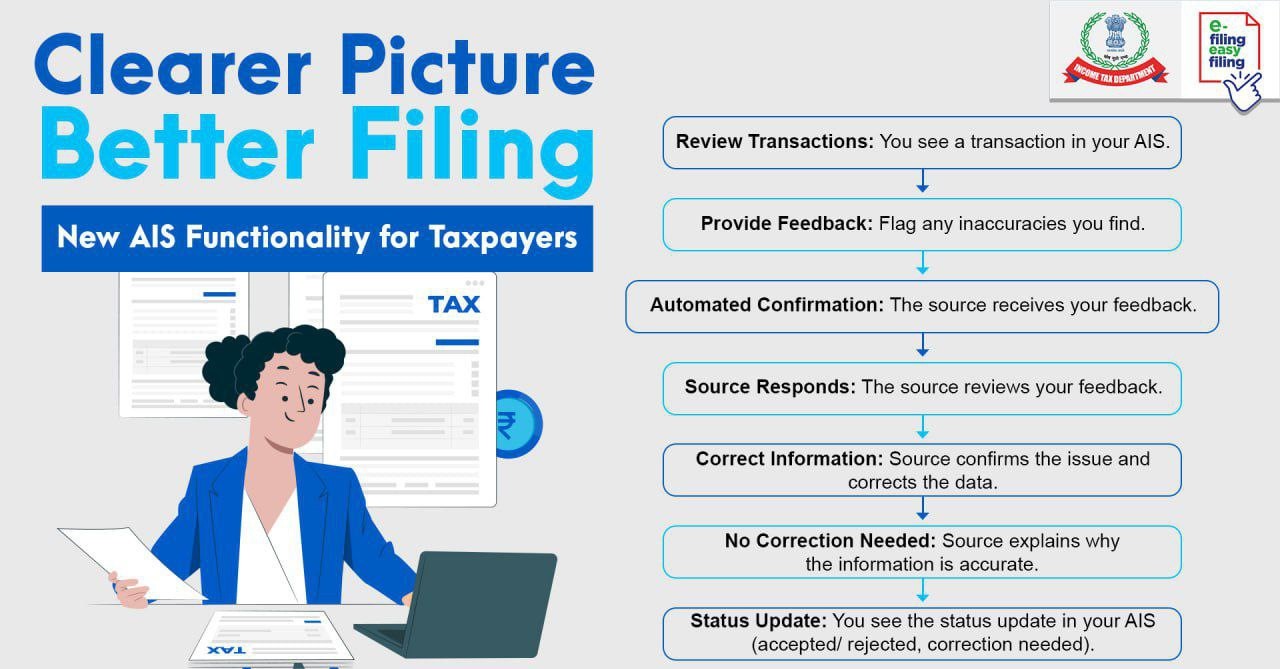
Now you can review your transactions and submit feedback in AIS.
- Taxpayers can submit feedback, which is taken up with the source for confirmation
- The source responds to feedback with details.
- If the details provided are correct and there is a mistake in AIS, the source will correct it.
- Taxpayers can see the status of the information confirmation process.
- The status will show if the feedback has been acted upon, either partially accepted/fully accepted or rejected.
- This is an initiative towards ease of compliance and enhanced taxpayer services.
Consequences of Not Reconciling AIS with ITR
- Section 143(1)(a): Intimation for mismatch proposing income adjustment.
- Under Section 148A: Reassessment proceedings for unreported AIS income.
- Section 270A: Penalty:
- 50% for underreporting
- 200% for misreporting
- Under Sections 234B & 234C: Interest at 24% annually.
- Section 276C: Prosecution (3 months to 7 years imprisonment + fine).
Popular Article :