Budget 2021- key highlight
Page Contents

BUDGET 2021- KEY HIGHLIGHT
In Union Budget 2021 speech, finance minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced plenty of tax reforms but kept the personal income tax slab unchanged. Highlights from Budget 2021 are as follows:
Fiscal deficit:
- Finance minister Nirmala Sitharaman estimated the fiscal deficit for FY21 at 9.5% of GDP, with the fiscal deficit goal for FY22 at 6.8% of GDP. Hope to get back to the fiscal consolidation route by FY26. By FY26, the fiscal deficit would be below 4.5 per cent.
- Gross expenditure for FY22 at Rs 34.83 lakh crore.
Expenditure on Capital:
- According to the Finance Minister, FY22 capital expenditure raised seems to be up 34.5 % (vs FY21 BE) at Rs 5.54 lakh crore for 2021-22. Rs 44,000 crore will be given to the Department of Economic Affairs in FY22 under capital expenditure. Capital investment for FY21 is seen at Rs 4.39 lakh crore.
PM Atmanirbhar Swasth Bharat Yojana
- Over the next period, the ‘PM Atmanirbhar Swasth Bharat Yojana’ will be launched with a total outlay of Rs 64,180 crore. Of this total amount, She also announced that Rs 35,000 crore will be spent on the Covid-19 vaccine alone and was committed to spending more if needed.
- The Scheme will concentrate on the development of healthcare capabilities. More than 17,000 rural and 11,000 urban wellness centres would be supported by the main interventions under the scheme.
- The country’s health budget has been hiked by 138 % keeping the coronavirus pandemic in mind since last year and is currently at Rs 2,23,846 crore.
Fuel and Liquor cess:
- A number of items, including fuel and liquor, were announced today by Agri Infrastructure and Development Cess, but the finance minister also said there would be no additional burden on the overall customer.
- A budget of Rs 2.5 per litre of Agri infra cess was imposed on petrol, Rs 4 on diesel, and 100% on alcoholic beverages.
Voluntary Scrapping policy
- Announced Voluntary Vehicle Scrapping Scheme for private and commercial vehicles.
- Private cars over 20 years of old and commercial vehicles over 15 years old should undergo fitness tests.
- Vehicle fitness checks are to be carried out in automated fitness centres.
- This would hopefully encourage fuel-efficient, environmentally friendly vehicles and thereby reduce vehicle pollution and oil import bills.
Highway works:
- The Centre has pledged to allocate 8,500 km of national highway projects by March 2022 and to complete an additional 11,000 km of the National Highway Corridor.
- The Minister claimed that this would be in addition to the more than 13,000 km of roadwork awarded under the Centrally Sponsored Bharatmala Pariyojana Project, of which 3,800 km have already been completed.
- In TamilNadu, 3500 km corridor has been proposed at an investment of 03 lakh crore
- Kerala, 1100 km have been proposed at an investment of 65000 crores
- In Assam, 1300 km of national highway will be built in the coming three years.
- West Bengal, 675 km highway works, including the re-development of the Kolkata-Siliguri highway, have been proposed at an Investment of 25,000 crores Note: all 4 states have elections coming up
Foreign ownership:
- The foreign ownership limit of insurance companies increased from 49% to 74%. Foreign ownership and control with safeguards would also be allowed by the amendment to the Insurance Act 1938. “Under the new structure, the majority of on-board directors and key leaders will be resident Indians, with at least 50 per cent of directors being independent directors and a specified percentage of profits retained as a general reserve.
- Increasing the FDI limits for the insurance industry from 49% to 74% would help insurance companies to collect funds to ensure that their solvency is sustained in line with increasing business needs.
- This can also contribute to enhancing sector M&A while clearing the way for PE funds to reach space. It will also increase foreign inflows and help to attract more foreign firms.
Power Sector:
- By setting up a fund of INR3,000 bn over five years, the budget has proposed a scheme to assist discoms for infrastructure development. Importantly, budgetary changes would be tied to the system. DISCOM reforms will be a valuable benefit for the power sector and will help to attract investment not only in the distribution sector but also in the generation and transmission industries.
- The budget also announced the creation of a system to include options for customers to select from more than one Distribution Company. If this is done in the right spirit, real rivalry in the power delivery market would be brought about and made more effective.
- Budget has granted the two renewable energy development agencies, Solar Energy Corporation of India (SECI) and the Indian Renewable Energy Development Agency (IREDA) has provided a higher allocation of INR25bn
- The budget also announced the launch of the 2020-21 Hydrogen Technology Mission to produce hydrogen from renewable sources of energy.
- Assets worth INR70bn in the transmission sector will be allocated to the Power Grid Infrastructure Investment Trust (InvIT) for these assets to be monetized. This would help finance revenue-generating connectivity initiatives such as inter-state transmission networks, thus helping to develop infrastructure in this crucial field.
Indian stock market reacts positively to the first hour of the Budget speech.

- Indian indices on Monday settled more than 5% higher as investors cheered budget announcements. At 48,600, the Sensex finished 2,315 points higher, while the Nifty improved 646 points to settle at 14,281. Domestic index rises were largely driven by banking, financial, and car stocks. After the FM announced measures to clean up the NPAs in the sector, the Nifty Bank reached its all-time peak up to 9 percent.
- Whereas, the Nifty Auto index contributed 4% to the scrappage policy announcement. IndusInd Bank, ICICI Bank, Bajaj Finserv, SBI, and L&T were the top gainers on the Nifty50 index, while the losses were led by UPL, Dr. Reddy’s, Cipla, Tech Mahindra and HUL.
Disinvestment Plan:
- The government has set a Rs 1.75 lakh crore disinvestment target for 2021-22. This is lower than Rs 2.1 lakh crore in 2020-21, which it hoped to benefit from disinvestment.
- Adverse market conditions have impacted the disinvestment plans of the government in 2020-21 due to the pandemic and are projected to fall well short of the target.
- Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman, introducing the Union budget for 2021-22, said that strategic sales of IDBI Bank, BPCL, Shipping Corp, Container Company, Neelachal Ispat Nigam Ltd, Pawan Hans, Air India, among others would be completed during this year.
- Two public sector banks and one general insurance company for stake sale
- Will bring LIC IPO in this fiscal year
Education:
- 15000 schools will be qualitatively strengthened
- 100 new Sainik schools to be set up
- 750 Eklavya schools to be set up in tribal areas
- Rising the unit cost of each school to Rs 38 crore
- To Rs 48 crore for hilly and challenging areas
- Focus on developing comprehensive tribal student infrastructure facilities
- 4 crore SC students to be benefits
- Central University in Leh the city of Ladakh
- Rs 35219 crore over 6 years to be benefit scheduled Caste students
Government cuts import tax on gold and silver
- Government cuts import tax on gold and silver to 7.5% from 12.5%. It was the long pending demand to reduce the import duty on gold and silver. It is a welcoming move for the Domestic organized sector.
- From April to December 2020-21, gold imports with a deficit effect fell by 27.20 per cent to USD 16.8 trillion.
- Over the period too, imports of silver dropped 67% to approximately USD 762,31 million.
- India is the biggest gold importer and largely supplies the jewellery industry with demand. Volume is 800-900 tonnes of gold imported last year by the government
- In the nine months of the current fiscal, jewellery exports decreased by around 40 per cent to about US$ 17 billion.
- By cutting off the import tax on gold and silver would help in promoting domestic manufacturing and boosting/enhancing the exports.
Direct Tax Changes in Union Budget 2021:
Many such direct tax changes have been incorporated, to a certain extent providing support for individual taxpayers and start-ups. The individual and corporate tax rates for the FY 2021-22 (AY 2022-23) remained unchanged. In a big change, the tax audit ceiling under section 44AB has been enhanced from INR 5 Cr to INR 10 Cr (only where 95 % of payments are digitised), providing relief to many corporate homes. Other proposed amendments are as tries to follow:
Income tax reforms- Taxpayers should be aware of that: Union Budget 2021
- The time period for the re-opening of the assessment is shortened to three years. Originally, it was 6 years. Re-opening of the assessment up to 10 Yr’s will be allowed if there is proof of undisclosed income of INR fifty lakh or more for a financial Year.
- Taxpayers expected some major announcements about income tax in the Union Budget 2021 but were dissatisfied on the budget day. But, FM N. Sitharaman revealed in her Budget Speech some changes to the income tax laws that could be of concern interested to taxpayers.
The following are the modifications to the income tax rules announced in the budget 2021 :
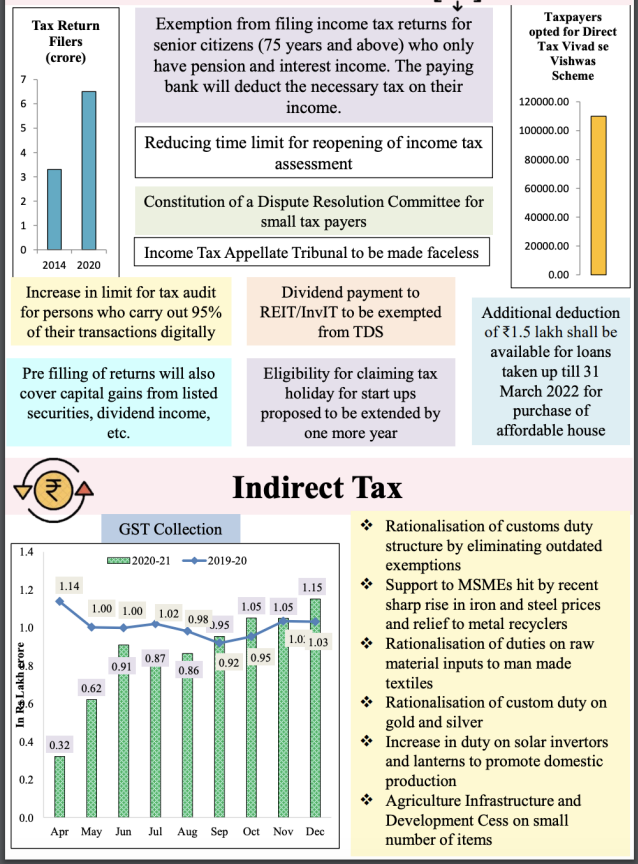
1) Union Budget 2021 goals to relieve the burden of compliance on senior citizens 75 Yr’s of age or older. Accordingly, Budget 2021 proposed to exclude these senior pensioners from filing ITR’s if the full amount of the tax payable had already been deducted by the paying bank.
This exception extends only to senior citizens who have only interest income rather than pension income. so No tax filing for seniors older than 75 with a pension, interest income only.
It is being planned to dispute settlement committee for small taxpayers. Anyone with a taxable income of up to Rs 50 lakh will be entitled to approach the dispute resolution committee with a contested income of up to Rs 10 lakh.
2) The time period for the re-opening of the assessment is cut off to three years. Initially, it was six years. Re-opening of the assessment up to 10 Yr’s would be allowed if there is proof of undisclosed income of INR Fifty lakh (or more) for a year.
In addition, Union Budget 2021 suggested the full removal of prudence in the re-opening assessment. Only cases flagged by the mechanism will be reopened.
3) Budget 2021 proposed that the ITAT should be faceless and without jurisdiction. “A National Faceless Income-tax Appellate Tribunal Centre will be established & all relevant communication between the Tribunal & appellant will be made electronically.
Wherever individual hearing is required, it will be done via video-conferencing,” said the Finance Ministers in their Budget Statement.
4) Budget 2021 made interest income taxable. With this in mind, the Employees Provident Fund contribution does not have the status of Exempt-Exempt-Exempt(EEE) status except for employees with a large salary.
Indirect Tax Changes Proposed in Budget 2021
Budget 2021 is hailed as a very development-oriented budget that aims for creating and augment social infrastructure. However Indirect Tax proposals indicate the intent of the government to tighten the compliance mechanism and increase the scope of GST through various retrospective amendments.
The industry needs to be extra cautious while preparing their returns and even basic documents like Invoices, E-way Bill etc. GST which was earlier presented by the government and tax professionals alike as Good and Simple Tax has not remained so simple.
Key amendments proposed by the CGST Act, 2017 :
-An added requirement set out in Section 16 specifically provides that ITC may be used only if the invoices/debit notes are provided by the supplier in its GSTR-1 and the details have been expressed to the recipient pursuant to Section 37.
-The necessity under Section 35(5) for annual accounts to be audited and the reconciliation statement filed by the designated professional (subject to condition) has been deleted.
-Requirement to provide GSTR-9 Annual return form to be substituted by a self-certified reconciliation statement.
-The requirement for charging interest on net cash liability (inserted in Section 50 of the Finance Act 2019) was made retroactively applicable from 1 July 2017.
-Judicial commissioner is authorised to obtain information from any person on any issue dealt with in link with the Act and the use of such data would be subject to an opportunity to be heard by the person concerned.
-The scope of the “Supply” term provided for in Section 7 is further extended to include transactions involving the supply of goods or services by any person, other than an individual, to its members or constituents, or conversely, for consideration. For this clause, supplier & recipient will be deemed as 2 Distic persons. The same is proposed to be retrospectively applied from 1 July 2017.
-Proceedings involving the seizure and confiscation of goods and conveyances in transit to be treated as a separate proceeding from the collection of taxes.
-Appeal against the order of the adjudicating authority in connection with the seizure and confiscation of goods and conveyances in transit (provided by section 129) may be produced only if 25% of the penalty is paid by the appellant.
IGST Act, 2017- Key amendments introduced :
- The option of a zero-rated supply on payment of an integrated tax would be limited only to the specified class of taxpayers or the stipulated supply of goods or services to be notified in due time.
- In the case of the export of goods, the foreign exchange remittance would be linked to the refunds claimed for such supplies.
- Zero-rating of supplies made to a special economic zone would only be valid if such supplies are for authorised operations.
Customs Act, 1962 – Key amendments proposed:
- Evaluation of more than 400 old customs exemptions formulated via extensive consultations as of 1 October 2021. It is proposed that the revised customs duty structure should be free of distortions.
- Any fresh exemption from customs duty will, from now on, be valid until 31 March going to follow two years from the date of its issue.
The views expressed herein are those of the authors and cannot be used in the framework of opinions or for the reason of compliance without an honest evaluation.
A few of the articles on which rate of Customs Duty are revised are as below:
-
- Reduced duty on copper scrap from 5 percentage to 2.5 percentage
- Basic and Special additional excise duty on petrol and high-speed diesel oil (both branded and unbranded) is reduced
- Increased duty on solar inverters from 5 Percentage to 20 percentage
- Raised duty on solar lanterns from 5 percentage to 15 percentage
- The basic customs duty on gold and silver was reduced.
- Department will rationalise duty on textile, chemicals & other products
- The revised rates will be applicable from 2nd Feb 2021 onwards.
Popular blog:-
