Overview on GST Unified Indirect Tax Mechanism
Page Contents

Overview on GST unified indirect taxation mechanism
Goods and Service Tax is a unique unified indirect taxation mechanism that replaced various indirect taxes levied by State & Central Govt of India. Under the GST regime, GST is a destination-based tax on consumption of services & goods that is levied on every value addition. the tax is levied at every point of sale GST simplifies taxation process & helps in ease of doing business in India. Under Goods and Service Tax, both State & Central Govts share authority to levy & collect taxes on Services & Goods. GST levied at all levels right from goods manufacture up to final consumption with credit of taxes paid at earlier stages available as set off. GST includes 4 GST kinds namely SGST, CGST, Integrated Goods and Services Tax (IGST) & UTGST. The taxation rate under SGST, CGST, IGST, UTGST is different. Goods and services are classified into different tax slabs, including 5%, 12%, 18%, & 28%.
A simple GST formula arises: GST Amount value = (Original Cost X GST Rate % )/100.
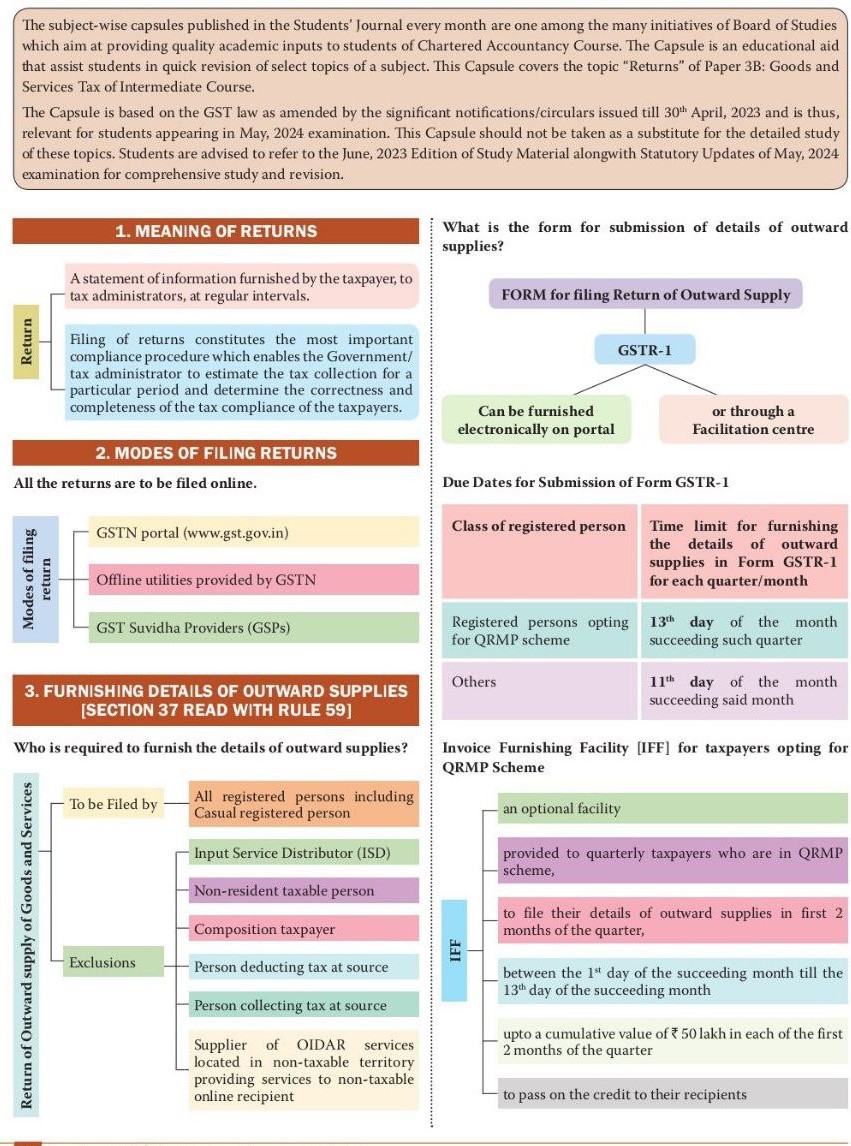
Main objective of the Goods and Service Tax Law
- GST Taxation Process is simplified.
- Logistics productivity is enhanced.
- Simple & Easy online indirect taxation process.
- More FDI is attracted.
- Cascading effects on indirect taxation are reduced.
- All have features of Composition scheme.
- Throughout country, a uniform indirect taxation rate is implemented.
- Subsume most indirect taxes into a single unified indirect taxation mechanism & widen the tax base in India.
- Indirect tax management is applied effective.
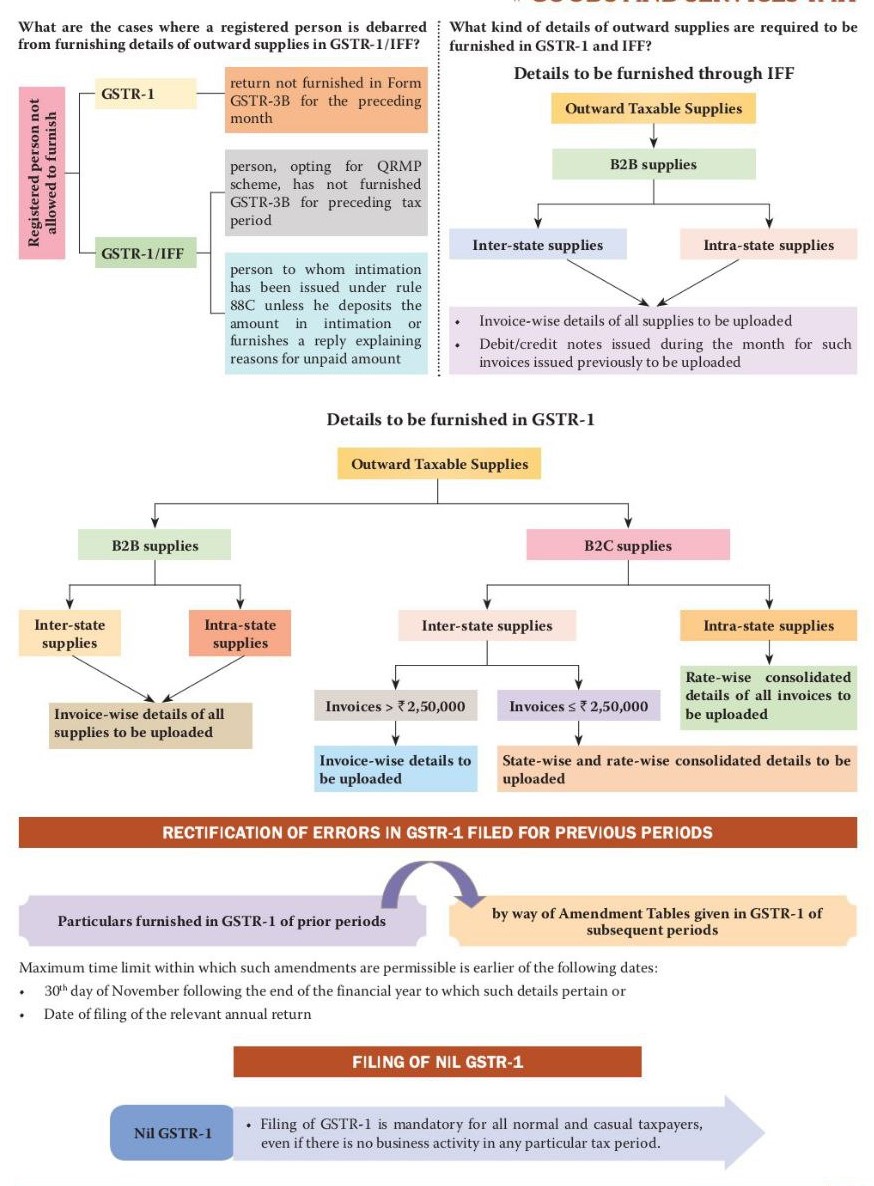
Common Mistakes in avoid GST Compliance:
- Wrong entry of Invoice Details in GSTR-1 can result in the denial of input tax credits for recipients for a smooth input tax credit process
- Confusing zero-rated and nil-rated supply treatment, It is compulsory to file accurately report zero-rated & NIL rated supplies to avoid GST audit scrutiny.
- No Purchases or Sales than Ignorance To File Nil Gst Return Failure to do so can result in penalties and potential cancellation of GST registration.
- Non-Payment of RCM where recipients are responsible for paying the tax obligations can lead to interest payments and the loss of ITC.
- Neglecting Failure to Reconcile the monthly GSTR-3B RETURNS & GSTR-1 is a significant mistake.
- Delays or failure to submitting GST Returns within the Timeline date can result in the cancellation of GST registration and financial penalties.
- Misplacement of export sales details can lead to complicate in claiming GST refund.
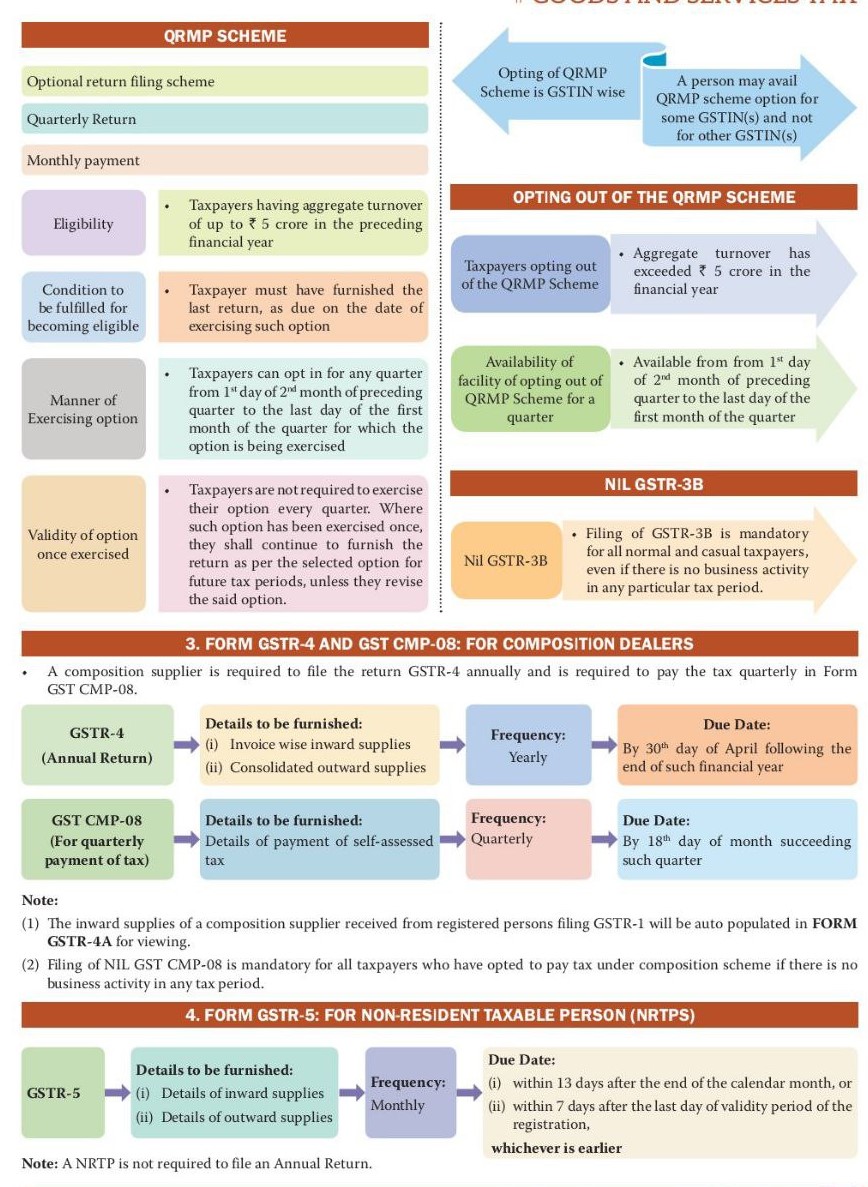
CONCLUSION:
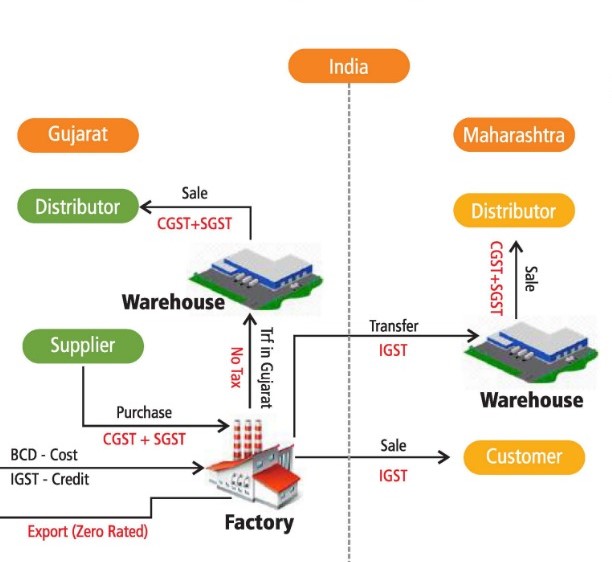
Maintaining compliance, averting needless reconciliation processes, and avoiding legal issues all depend on timely and accurate filing of GST returns. Taxpayers can make sure that submitting their GST returns is easy by being aware of and avoiding the typical pitfalls covered in this article. It’s also essential to be familiar with the relevant GST return types according to their particular business features. With careful planning and adherence to the guidelines, taxpayers can properly file their GST returns. Following chart present the complete GST Overview :
How to Contact GST Consultant Near me – At Rajput Jain and Associates, we consistently strive to satisfy clients by completing their work accurately & efficiently. We always consider all of clients’ issues. You may contact us or give us a call at +91-9555 555 480, if you need our assistance. for GST advice.
