IBC forms-demand notices, forms
Page Contents
IBC Forms- Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code 2016 – Forms, Demand Notices, Returns
The implementation of the 2016 Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (“IBC”) in India has provided a fundamental change in attitude to addressing the issue of rising non-performing assets (NPA) and assisting the financial sector with early detection, rehabilitation, and restructuring steps of stressed assets.
Various Kinds of Demand Notice Forms are issued under the IBC Code, Insolvency is that state when one is unable to pay the debt.
Demand Notice to recover the debt is sent under of IBC Code, 2016 by the creditor/ Employee/ Workman or any other person to the corporate debtor.
IBC Code also prescribes the procedure to file an insolvency proceeding before NCLT.
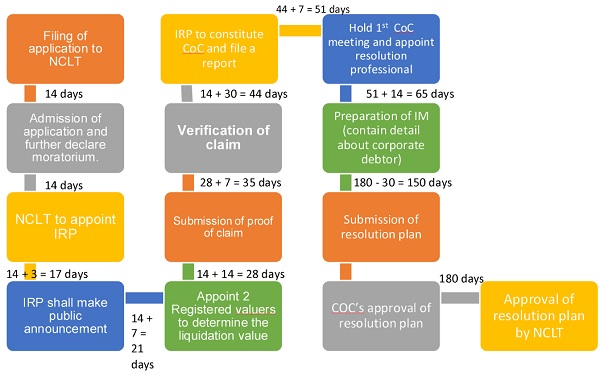
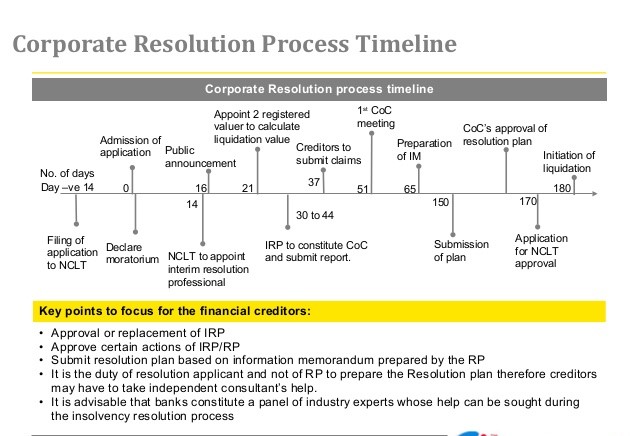
Insolvency Resolution Process for Corporate Person- Time Limits under IBC
Key point Under the IBC
As per IBC sections 7 and 9, it is not mandatory to allow the corporate debtor the chance to be heard until IBC’s application is accepted. And as set out in section 14, once the IBC application is accepted, the management team goes into the hands of the IRP proposed by such an applicant.
Therefore, there are high chances that even a small default could cause a situation where the business goes to hands.
It is because, on the one hand, creditors recover debts from the bankrupt company while, on the other, certain creditors use IBC to intimidate and harass the corporate debtor.
It is a manipulation of new legislation to place pressure on corporate debtors to recover the fraudulent/falsified claims.
The civil recovery issues take a very long time to determine which is a well-known reality. There is a weak credit control in trade, due to poor recoverability.
It has influenced companies, as it also contributes to high demand for capital investment and leading to greater pressure on profitability.
Insolvency & Bankruptcy Code (IBC) has made a big change, and now an operational creditor can take action under IBC to recover their duties in a very cost-effective manner.
Various Forms Specified areas under Insolvency Resolution Process for Corporate Person:
| Forms | Description | Go to |
| Form A | Public Announcements | Click here |
| Form AA | Consent to act as Resolution Professional | Click here |
| Form AB | Consent to act as an authorized representative | Click here |
| Form B | Proof of claim | Click here |
| Form C | Submission of a claim by the financial creditor | Click here |
| Form CA | Submission of a claim by the financial creditor in a class | Click here |
| Form D | Proof of claim by workman or employee | Click here |
| Form E | Proof of claim by workman or employee by an authorized representative | Click here |
| Form F | Submission of a claim by creditors | Click here |
| Form FA | Application for withdrawal of CIRP | Click here |
| Form G | Invitation for expression of interest | Click here |
| Form H | Compliance certificate | Click here |
| Form 1 | Application by financial creditor to initiate CIRP | Click here |
| Form 2 | Written communication by proposed IRP | Click here |
| Form 3 | Form of Demand Notice demanding payment under IBC code, 2016 | Click here |
| Form 4 | Form of Notice with which Invoice demanding payments to be attached | Click here |
| Form 5 | Application of Operational Creditor to initiate CIRP | Click here |
| Form 6 | Application by Corporate Applicant to start CIRP | Click here |
Due dates Under the IBC
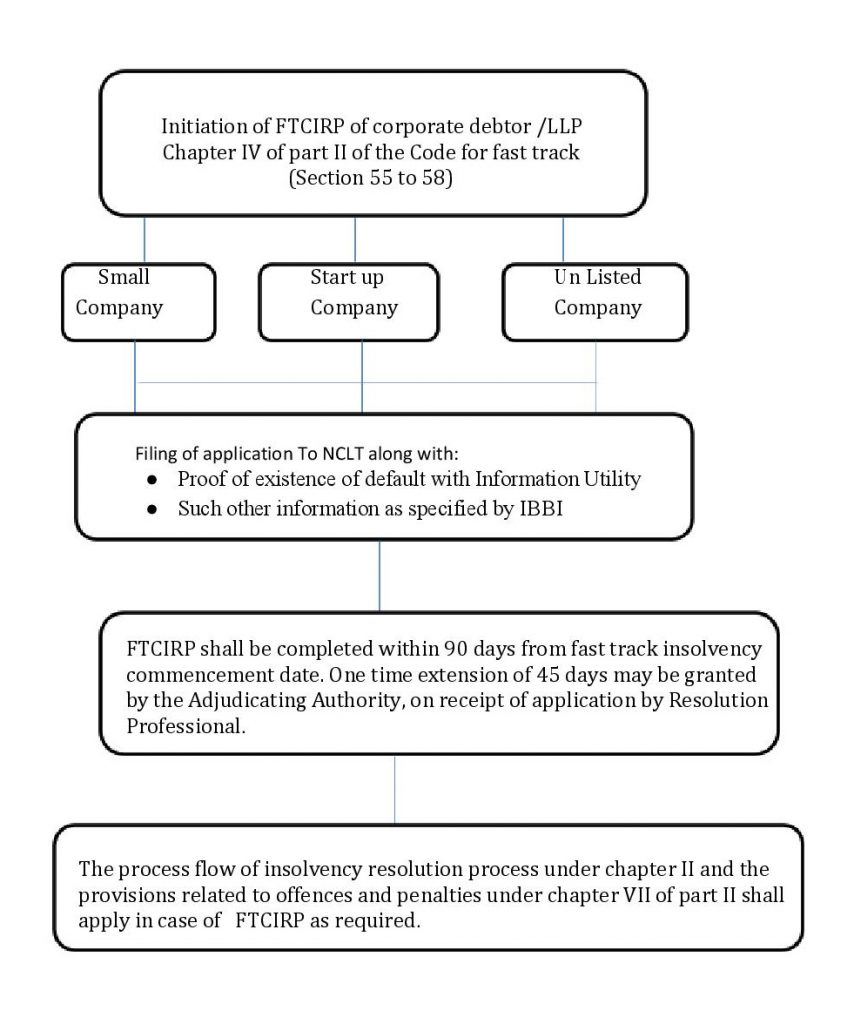
Fast Insolvency Resolution Process for Corporate Person
Section55 to 58The aim of the Fast Insolvency Resolution Process for Corporate Person is to speed up the CIRP of start-ups and small businesses with less complexity and the time taken to complete an insolvency resolution to nearly half as opposed to the standard Code procedure.
The Fast Insolvency Resolution Process for Corporate Person must be done within a period of ninety (90) days, as compared in other situations to one-eighty (180) days.
The adjudicating authority may, however, extend the duration of ninety ( 90 ) days by a further period of up to forty-five (45) days to complete the proceedings.
However, this extension can only be given once and can only be applied for if COC agrees that in a resolution adopted and approved by a majority of 75% of the voting share
The Regulations and the Fast Track Resolution process apply to the following corporate debtor categories-:
(I) a small enterprise as described in the 2013 Companies Act;
(ii) a start-up (other than a partnership) as set out above;
(iii) an unlisted corporation with total assets not exceeding one crore, as stated in the financial statement of the financial year immediately preceding it.
Various Forms Specified areas under Fast Insolvency Resolution Process for Corporate Person :
| Forms | Description | Go to |
| Form A | Public Announcements | Click here |
| Form B | Proof of claim | Click here |
| Form C | Submission of a claim by the financial creditor | Click here |
| Form D | Proof of claim by workman or employee | Click here |
| Form E | Proof of claim by workman or employee by an authorized representative | Click here |
| Form F | Submission of a claim by creditors | Click here |
The Laws as a whole provide for the resolution process from the commencement of the corporate debtors’ insolvency resolution until its completion, with the adjudicating authority’s approval of the resolution plan within the specified deadlines, thus guaranteeing the extremely viable of any case under the fast track procedure.
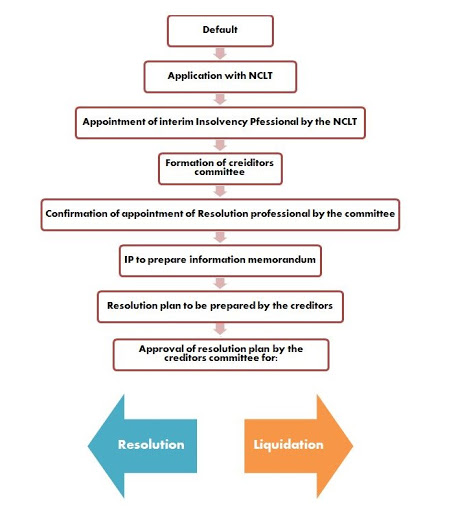
Liquidation Process
Under the following conditions, the winding-up process is activated under section 33 of the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code 2016-
- When no resolution plan is presented by qualified interim resolution as provided by the adjudicating authority at or before the insolvency resolution period expires.
- If the resolution strategy is not consistent with section 31 as provided by IRP.
- When a request from the creditor’s committee is issued for the liquidation of the corporate debtor during the corporate insolvency resolution process, the same shall be conveyed to the adjudicating authority by the interim resolution professional.
- If the corporate debtor refuses to obey the resolution plan authorized by the adjudicating authority and the individual or creditor impacted by this files an application for the liquidation of the corporate debtor and the adjudicating authority considers the corporate debtor responsible.
When the mechanism of liquidation is begun in compliance with the above requirements, the moratorium will begin. During the suspension, a public statement shall be made on the liquidation of the corporate debtor.
As per section 34, a liquidator is named and the fee to be charged to him in respect of the trial is determined. The liquidator fee is part of liquidation assets proceeds. The Professional Counsel also serves as a liquidator until NCLT replaces him.
Liquidation trust shall be established in compliance with section 36 of the Code of Insolvency and Bankruptcy.
Each section is the cornerstone of the corporate liquidation process as it determines which corporate debtor’s assets will form part of the liquidation estate, how the assets will be allocated by the liquidator, and who will retain the estate as a fiduciary for all creditors’ benefit.
Various Forms Specified areas under Liquidation Process :
| Forms | Description | Go to |
| Form A | Performa for Reporting consultations with Stakeholders | Click here |
| Form B | Public Announcements | Click here |
| Form C | Submission of a claim by the financial creditor | Click here |
| Form D | Proof of claim by workman or employee | Click here |
| Form E | Proof of claim by workman or employee by an authorized representative | Click here |
| Form F | Submission of a claim by creditors | Click here |
| Schedule 111 | Form for cashbook, general ledger, bank ledger, register of assets, securities, and investment registers, tenants ledger, etc. | Click here |
The creditors’ claims are then assessed. There are different parts assisting in this process.
Section 38 specifies how financial and operational creditors’ claims should be combined, section 39 specifies how claims should be checked, and section 40 describes the procedure for approving and rejecting claims, and under section 42 of IBC describe how the applications against the liquidator decision shall be processed.
Voluntary Liquidation Process

If the corporate debtor has been unable to discharge his debts and does not have adequate resources such as available funds, then the corporate debtor will voluntarily file the insolvency petition for the Corporate Insolvency Resolution Process and NCLT must accept it if the petition has not been submitted to defraud the creditors.
| Forms | Description | Go to |
| Form A | Public Announcements | Click here |
| Form B | Proof of claim | Click here |
| Form C | Submission of a claim by the financial creditor | Click here |
| Form D | Proof of claim by workman or employee | Click here |
| Form E | Proof of claim by workman or employee by an authorized representative | Click here |
| Form F | Submission of a claim by creditors | Click here |
| Schedule 11 | Form for cashbook, general ledger, bank ledger, register of assets, securities, and investment registers, tenants ledger, etc. | Click here |
- Connect to us for expert legal consultation for more effective legal aid or knowledge about the value of claim notice under the insolvency and bankruptcy code.
- The insolvency law requires a financial creditor and operational creditor to file insolvency proceedings against a defaulting corporation after determining that there is a dispute between the parties.
- The first move is to give the corporate defaulter a claim notice (Form 3 of IBC) to recover operating debt under insolvency law.
- To creditors that are not financial creditors and operational creditors, to example: homebuyers, submission of a “Form F” is necessary to file a claim.
- Depending on the facts and details of the operating debt to be recovered, a good corporate lawyer will draft a notice of claim on your behalf.
IBBI issue Discussion paper on Reducing Compliance by Review of CIRP Forms submitted by IPs to IBBI
Popular blog:-