Auditor Responsibility/Form 3CD Report Compliance u/s 43B(h)
Page Contents
Auditor’s Responsibility / Form 3CD Reporting & Compliance Requirements u/s 43B(h)
Tax Auditors (u/s 44AB) or Statutory Auditors (Companies Act) have increased responsibilities due to this provision. Tax auditor must Verification & Documentation along with Identify MSME Suppliers Obtain a list of suppliers with Udyam Registration Certificates. Auditor Verify whether they qualify as Micro or Small enterprises. Morover that auditor must examine Payment Terms & Tax auditor Check purchase orders, invoices, and agreements for credit period. & also Ensure the agreed period does not exceed 45 days as per MSMED Act. Tax auditor verify Payment Dates Match invoice date, acceptance date, and payment date also Identify delayed payments beyond the permissible period.
Tax Audit Reporting : Clause 26 of Form 3CD :
CBDT Notification No. 27/2024 (dated 5th March 2024) amended Form 3CD to include specific reporting on Section 43B(h). Clause 26 now requires: “Amounts debited to the profit and loss account, being sums payable to micro or small enterprises beyond the time limit specified in section 15 of the MSMED Act, 2006.” Auditor must report Amounts outstanding beyond 45 days as at year-end. Tax auditor Whether deduction has been disallowed as per Section 43B(h). Tax audit Clause 22 now includes reporting of Interest disallowed under Section 23 of MSMED Act. & Amounts disallowed under Section 43B(h). & Tax audit Clause 26 is no longer applicable for this purpose.
Disclosure in Financial Statements
Under the Companies Act, 2013 (Schedule III): Disclosure of Principal and interest due to MSEs, Interest paid / payable under MSMED Act & Delayed payments to such suppliers. In the Financial Statement Disclosures; As per Section 22 of MSMED Act, buyers must disclose:
- Principal and interest unpaid.
- Interest paid and payable.
- Interest accrued and unpaid.
- Future interest due until actual payment
Internal Control & Advisory Role
Auditor should Recommend maintenance of a vendor master database with Udyam details. tax audit Ensure the ERP/accounting system flags delayed payments. Tax audit Advise clients to Regularly obtain Udyam registrations from suppliers or Align payment terms to avoid disallowance
Audit Trail -Legal Mandate
Audit Trail is Applicable to companies from 1st April 2023 & As per Rule 3(1) and Rule 11(g) of Companies (Accounts) Rules. Audit Approach with Audit Trail is to Identify relevant records and software. Auditors must ensure audit trail is Enabled and protected, retained for 8 years, Monitored for tampering or gaps. Software Requirements of Audit Trail Accounting software must Record audit trail of every transaction, Maintain edit logs with timestamps, & Ensure audit trail cannot be disabled. Audit Trail Audit Reporting Scenarios must be taken care modified reporting required if:
- Audit trail is not enabled for some modules.
- Software is maintained by third party.
- Migration to new software during the year.
- Audit trail is not operating effectively.
Compliance Checklist for Section 43B(h)
Section 43B(h) applies only to Micro and Small enterprises, not Medium. Where a supplier (registered as a Micro or Small Enterprise) supplies goods or services, the buyer must make payment on or before the agreed date, or within 45 days from the date of acceptance or deemed acceptance; whichever is earlier. Compliance checklist for Section 43B(h) to help ensure timely payments to MSMEs and avoid disallowance of expenses:
- Identify MSME Suppliers
- Verify if the supplier is a Micro or Small Enterprise.
- Confirm UDYAM Registration (mandatory for applicability).
- Check if the supplier has intimated MSME status (e.g., via invoice or letterhead).
- Nature of Supplier’s Business
- Ensure supplier is engaged in manufacturing or services.
- If supplier is a trader, confirm that 43B(h) does not apply.
- Payment Terms
- Check for a written agreement specifying payment terms (max 45 days).
- If no agreement, ensure payment is made within 15 days of delivery.
- Timing of Payment
- Ensure payment is made within 15/45 days to claim deduction in the same year.
- If payment is delayed beyond MSMED timelines, deduction allowed only in year of actual payment.
- Year-End Provisions
- For provisions made after March 15, verify if 15-day period expires post year-end.
- If goods/services not delivered by year-end, no disallowance under 43B(h).
- Capital Expenditure
- Confirm that outstanding dues relate to revenue expenditure.
- Capital expenditure is not covered under 43B(h).
-
Presumptive Taxation
- If assessee opts for 44AD/44ADA/44AE, 43B(h) does not apply.
- Disputed Payments
- If buyer raises objections within 15 days, payment timeline starts from date of acceptance.
- Cheque Payments
- If cheque issued but not encashed, retain:
- Copy of cheque with date.
- Proof of delivery to supplier within time limit.
- Documentation & Audit Trail
- Maintain records of:
- UDYAM registration verification.
- Payment dates and modes.
- Agreements and invoices.
- Communication of MSME status.
ICAI’s Implementation Guide: Section 43B(h) Compliance Rule:
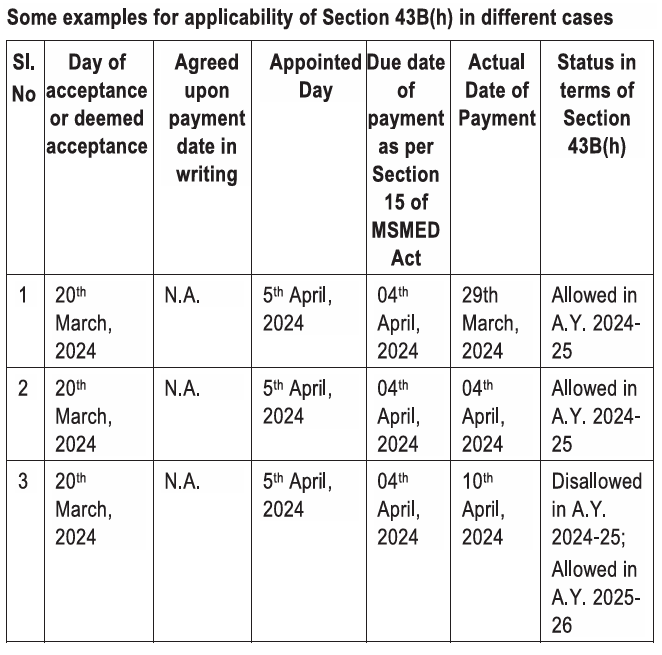
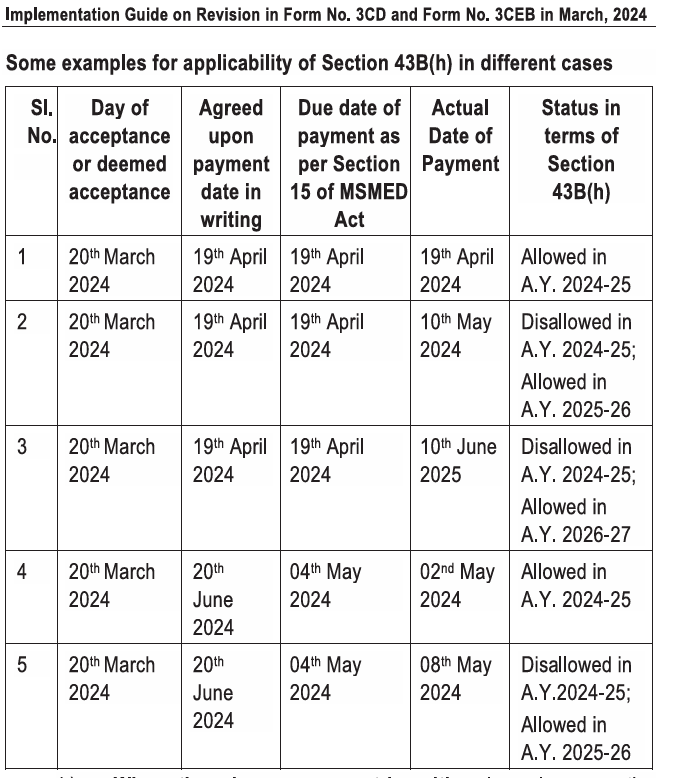
If written agreement exists, use agreed date (max 45 days). If there is no agreement, use 15 days from acceptance. Section 43B(h) deduction is allowed only if payment is within MSMED timeline; otherwise, allowed in year of actual payment. Practical Issues & Case Studies ICAI Clarifies treatment of Payments made within or beyond MSMED limits, Supplier registration status, Capital assets, retention money, audit fees., TDS implications and unbilled expenses. ICAI’s Implementation Guide illustrates how Section 43B(h) applies based on:
- Day of acceptance or deemed acceptance (e.g., 20th March 2025).
- Agreed payment date in writing (cannot exceed 45 days).
- Due date as per Section 15 of MSMED Act:
- If agreement exists : agreed date (max 45 days).
- If no agreement: 15 days from acceptance.
- Actual payment date. : Status under Section 43B(h): Allowed in the same A.Y. if paid within MSMED timeline. Or disallowed if paid beyond MSMED timeline → allowed only in year of actual payment. Following are few example :
- Practical Example 1
- Acceptance: 20 Mar 2024
- Agreed date: 19 Apr 2024
- Payment: 19 Apr 2024
- Within MSMED timeline: Allowed in AY 2024-25.
- Practical Example 2
- Payment: 10 May 2024 (after 19 Apr)
- Beyond MSMED timeline : Disallowed in AY 2024-25; allowed in AY 2025-26.
- Practical Example 3
- Payment: 10 Jun 2025
- Disallowed in AY 2024-25; allowed in AY 2026-27.
- Practical Example 4
- Agreement: 20 Jun 2024 (within 45 days)
- Payment: 02 May 2024
- Before agreed date : Allowed in AY 2024-25.
- Practical Example 5
- Payment: 08 May 2024 (after 04 May agreed date)
- Disallowed in AY 2024-25; allowed in AY 2025-26.
Practical Example 6
| Particulars | Date | Amount (₹) | Due Date (per MSMED Act) | Payment Date | Tax Treatment |
| Invoice from Small Enterprise | 01-02-2025 | 1,00,000 | 18-03-2025 (45 days) | 25-04-2025 | Not allowed in FY 2024-25; allowed in FY 2025-26 |
| Invoice from Non-MSME | 01-02-2025 | 1,00,000 | NA | 25-04-2025 | Allowed on accrual basis |