Overview on Step to reading an Annual Report
Page Contents
Overview of Steps to reading an Annual Report
Step to reading an Annual Report Reading an Annual Report becomes easy when you follow a systematic approach. Below is a step-by-step guide:
- Start with the company overview; look for Company history, Business model, Core products/services, Geographic presence & Industry positioning. Which gives a quick understanding of what the company actually does.
- Read the Chairman’s / MD’s Statement contains Leadership vision, Market conditions, Key achievements & Future outlook. Which Shows management confidence, strategy, and risks foreseen.
- Analyse the Management Discussion & Analysis (MD&A) Focus on Industry trends, Opportunities & threats, Segment-wise performance & Key risks & mitigation. Which Gives deep insight into business performance and future direction.
- Review Corporate Governance Report Check for Composition of Board & Committees, Attendance of directors, Related-party transactions & independence of Directors. Which Shows transparency, accountability, and governance quality.
- Study Financial Statements Contains three major sections
- Balance Sheet Look for assets, liabilities, Net worth & Short-term vs long-term position.
- Profit & Loss Statement Check Revenue growth, Operating margins & Profitability trends.
- Cash Flow Statement Important points Cash from operations, investment activities, financing activities & free cash flow. Provides the real picture of performance and liquidity.
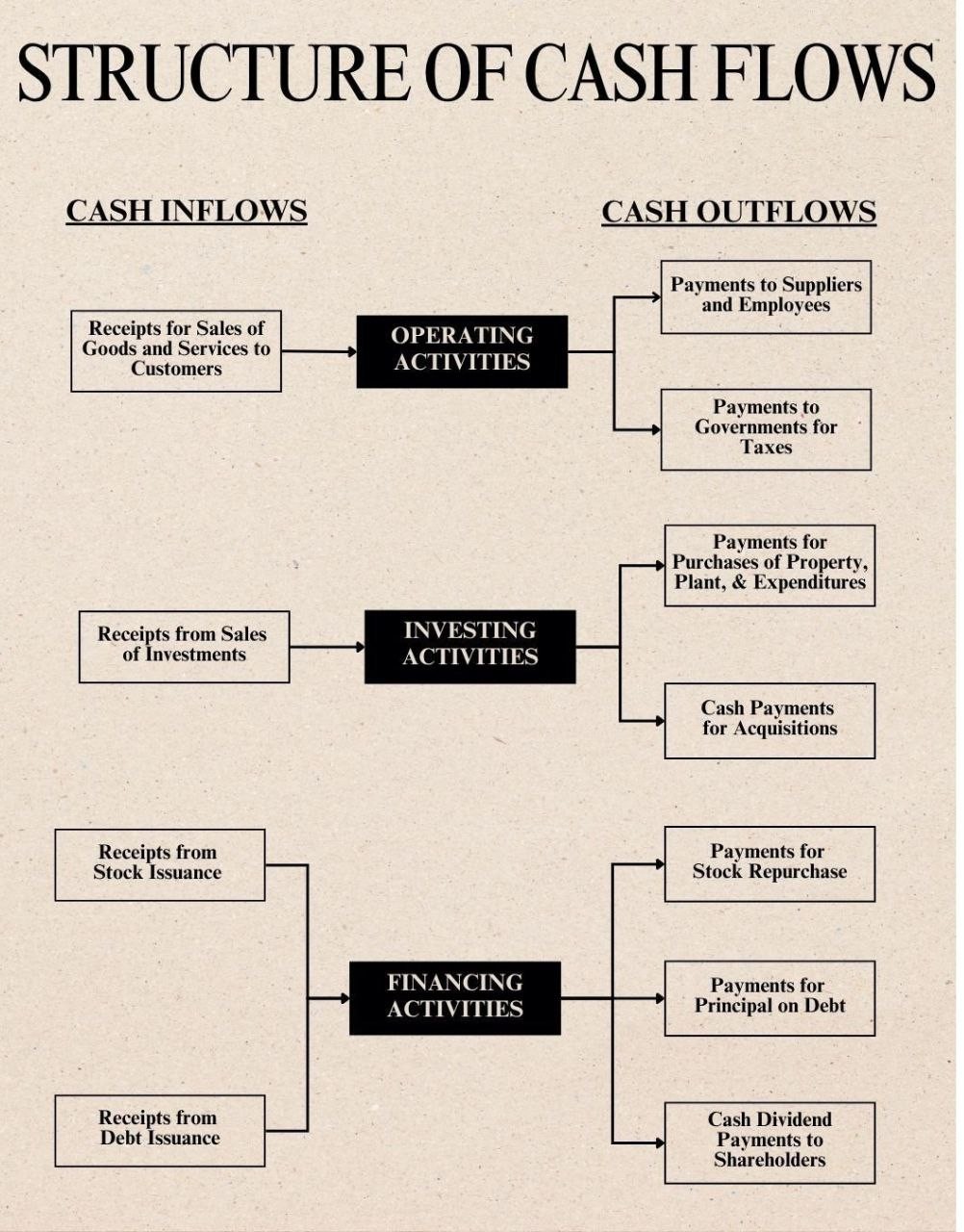
Operating Activities
-
-
- Cash Inflows:
- Receipts from sales of goods and services to customers.
- Cash Outflows:
- Payments to suppliers and employees.
- Payments to governments for taxes.
- Cash Inflows:
-
Investing Activities
-
-
- Cash Inflows:
- Receipts from sales of investments.
- Cash Outflows:
- Payments for purchases of property, plant, and expenditures.
- Cash payments for acquisitions.
- Cash Inflows:
-
Financing Activities
-
-
- Cash Inflows:
- Receipts from stock issuance.
- Receipts from debt issuance.
- Cash Outflows:
- Payments for stock repurchase.
- Payments for principal on debt.
- Cash dividend payments to shareholders.
- Cash Inflows:
-
- Read the Notes to Financial Statements Focus on Accounting policies, Contingent liabilities, Segment reporting & Auditor qualifications. Which
Critical details are often hidden in the notes. - Examine the Auditor’s Report Look for Unqualified (clean), qualified, adverse, or disclaimer opinion, Key audit matters (KAM) & Internal financial control comments which Shows reliability of financial statements and major audit concerns.
- Check Shareholding Pattern Check for Promoter shareholding changes, FPI/DII participation & public shareholding. Which Reflects confidence of promoters and institutional investors.
- Evaluate Ratios & Key Performance Indicators Some important ratios EBITDA margin, ROE, ROCE, Debt-to-equity, Current ratio & Inventory & receivable turnover which Helps compare performance year-on-year or with competitors.
- Review CSR (Corporate Social Responsibility) Report Check CSR spending, projects undertaken, & compliance with Section 135, which indicates the company’s social ethics and statutory compliance.
- Understand Risks & Internal Controls Look for operational risks, regulatory risks, market risks, and internal control framework. which shows resilience and preparedness for future challenges.
- Look at Future Strategy & Outlook Focus on Growth plans, Capex plans, Expansion or diversification, & cost optimization strategies. Helps assess long-term sustainability.
In summary, steps to reading an Annual Report
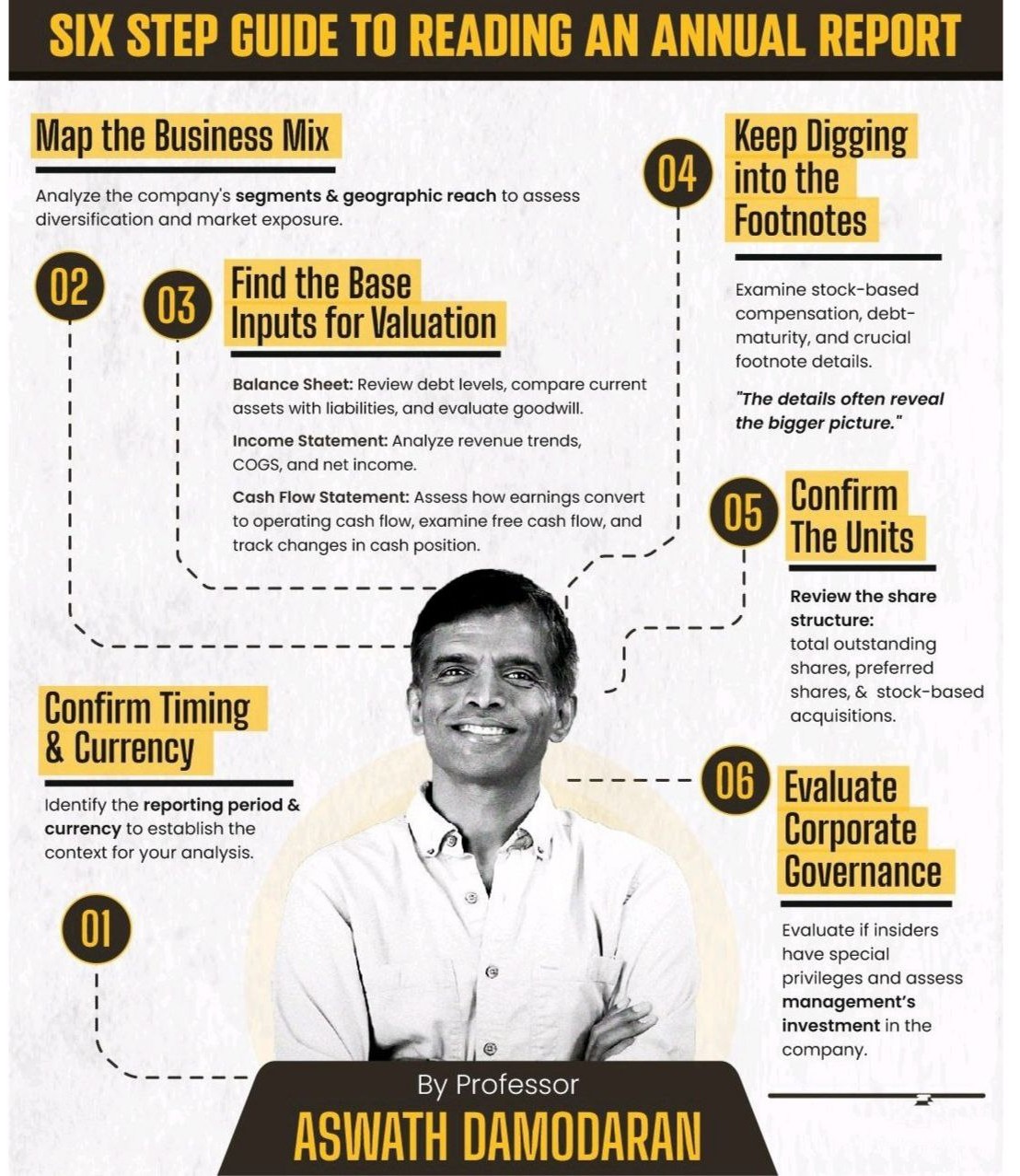
The Six-Step Guide to Reading an Annual Report mentions the Annual Report Quick Scan, like Business Overview, MD&A, Financials (P&L + Cash Flow + Balance Sheet), Auditor Report, Notes to Accounts, Risks & Strategy, Ratios, and Governance.
- Confirm Timing & Currency: Identify the reporting period and currency to establish the context for your analysis.
- Map the Business Mix : Analyze the company’s segments and geographic reach to assess diversification and market exposure.
- Find the Base Inputs for Valuation
- Balance Sheet: Review debt levels, compare current assets with liabilities, and evaluate goodwill.
- Income Statement: Analyze revenue trends, cost of goods sold (COGS), and net income.
- Cash Flow Statement: Assess how earnings convert to operating cash flow, examine free cash flow, and track changes in cash position.
- Keep Digging into the Footnotes: Examine details like stock-based compensation, debt maturity, and other crucial disclosures. Footnotes often reveal the bigger picture.
- Confirm the Units: Review the share structure, including total outstanding shares, preferred shares, and stock-based acquisitions.
- Evaluate Corporate Governance: Assess if insiders have special privileges and evaluate management’s incentives and independence.