Transition from Original GST to New GST: GST 1.0 vs GST 2.0
Page Contents
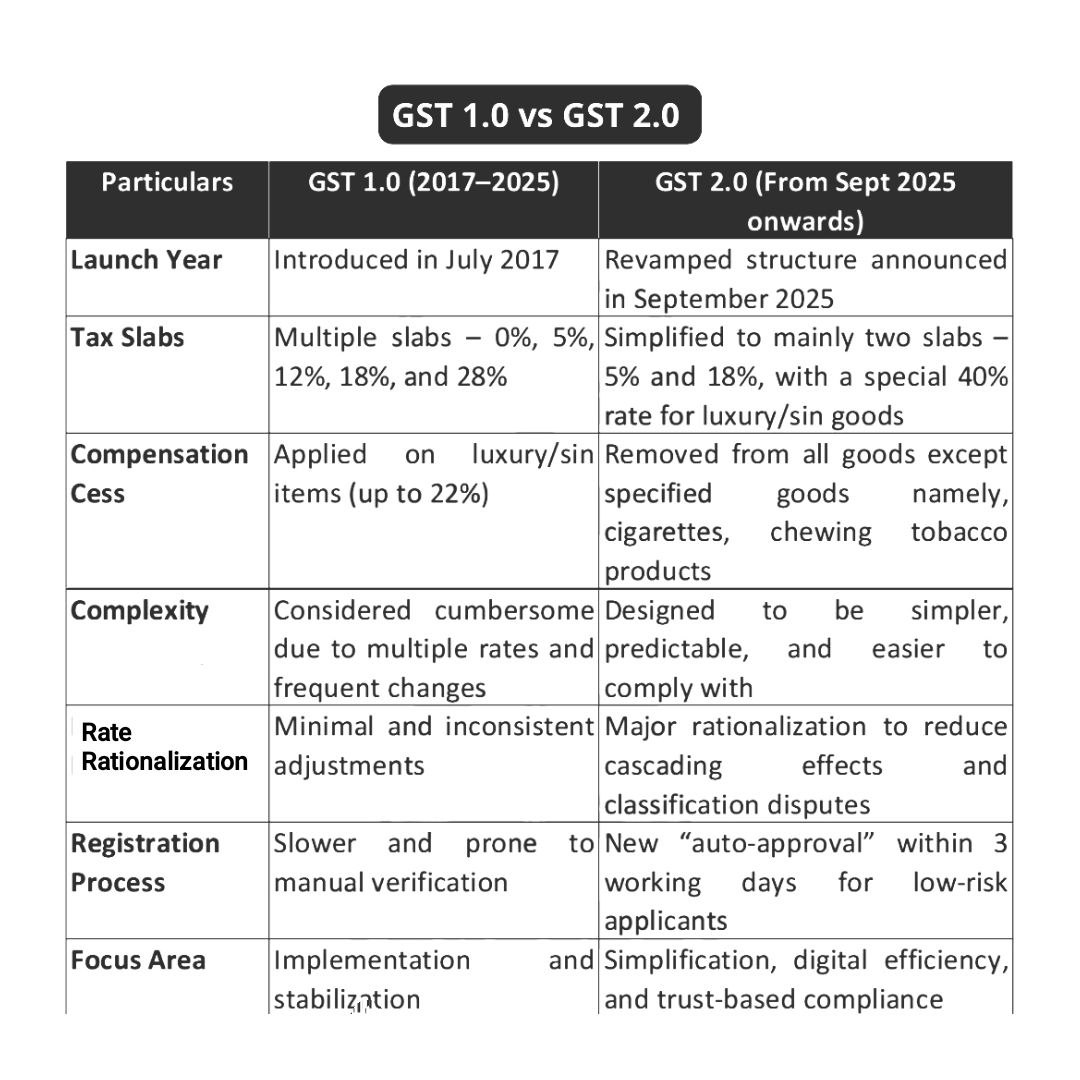
Transition from Original GST (2017) to New GST 2.0 Framework (2024–26): GST 1.0 vs GST 2.0
What is GST 1.0? :
GST 1.0 refers to the original GST framework launched on 1 July 2017, which focused on multiple return forms, self-declaration-based credits, the invoice matching concept (never fully implemented), frequent disputes due to mismatches, transitional systems, and evolving rules. It was a compliance-heavy system with several gaps, leading to litigation and fraud risks. GST 1.0 = Manual, mismatch-prone, compliance-heavy system. Practical Impact on Businesses of GST 1.0.
- More manual compliance
- Higher chances of mismatch & notices
- Credit disputes common
- Frequent portal issues
- More human interaction with department
What is GST 2.0? :
GST 2.0 refers to the new, simplified, technology-driven GST system being rolled out between 2023 and 2026, focusing on risk-based registration, automated compliance, invoice network expansion (e-invoicing & OCEN integration), AI-driven input tax credit (ITC) validation, simplified returns and rule frameworks, and stronger anti-evasion and analytics. It aims to make GST more trust-based and data-driven, improve GST portal for better uptime, provide Real-time analytics, predictive system responses, reduce fraud, and easing compliance. GST 2.0 was needed because GST 1.0 faced issues with fake invoicing ecosystems, ITC fraud risk, frequent mismatches, litigation on reconciliation, complex return formats, delayed registrations, & limitations in GSTN technology infrastructure. GST 2.0 is meant to address these structural issues. Practical Impact on Businesses Under GST 2.0.
- Reduced paperwork
- Auto-calculated credits
- Seamless data flow (e-invoice → 2B → 3B)
- Faster refunds & fewer disputes
- Lesser departmental interface
The debate on Old GST vs New GST 2.0 is one of the biggest policy discussions in India’s tax reform journey. When GST 1.0 was launched in 2017, it replaced a mix of indirect taxes such as VAT, Service Tax, and Excise Duty with a unified system. This was a landmark move that aimed to remove the cascading effect of taxes and create “One Nation, One Tax.” However, despite its benefits, GST 1.0 was complex, especially for MSMEs, traders, and service providers. Frequent slab changes, classification issues, and high compliance requirements created challenges. To resolve this, the Government has rolled out GST 2.0, an upgraded, simplified, and more business-friendly version of the earlier system.
How GST 2.0 Is Different from GST 1.0
GST 1.0 vs GST 2.0 : GST 2.0 attempts to eliminate the pain points of the earlier regime by rationalizing tax rates, simplifying processes, and introducing technology-driven compliance. One of the biggest changes is the introduction of a new 40% slab for luxury and sin goods, while retaining the 0%, 5%, 18%, and 28% slabs. GST 2.0 also focuses heavily on automation, AI-based credit matching, simplified e-invoicing, and faster refunds—reducing the dependence on consultants and minimizing manual errors. The biggest difference lies in slab rationalization and simplification.
GST 1.0 had five major slabs: 0%, 5%, 12%, 18%, and 28%, along with a Compensation Cess.
GST 2.0 removes the 12% slab, expands the 0% and 5% categories, and introduces a new 40% slab for luxury and sin goods.
This makes the structure clearer, fairer, and easier to comply with.
Under the VAT regime, tax was levied at every stage of manufacturing and distribution, often leading to a cascading effect. GST, however, is a destination-based tax levied only on the supply of goods and services. It eliminates tax-on-tax, creates uniformity, and simplifies compliance across states.
| GST 1.0 (2017–2023) | GST 2.0 (2023–2026) | |
| Registration | Manual, heavy verification; delays | Rule 14A: simplified, Aadhaar-based, risk scoring |
| Returns | Multiple returns (GSTR-1, 2, 3 → later 1 & 3B) | Likely simplified single return architecture (under discussion) |
| ITC System | Self-declared in GSTR-3B; prone to fake invoices | Real-time ITC validation from e-invoice & supplier data |
| Matching Concept | Never successfully implemented | Automated system matching through e-invoice + 2A/2B |
| E-Invoice | Introduced later (limited) | Mandatory for almost all B2B and expanding to all |
| Analytics | Limited | AI/ML-based fraud detection; risk scoring of taxpayers |
| GSTN Technology | Capacity issues, glitches | Fully revamped infra with real-time data pipelines |
| Assessments | Mostly manual | Automated scrutiny + risk reports |
| Compliance Burden | High | Significantly reduced due to automation |
| Timelines | Monthly/quarterly returns | Move towards event-based and quarterly filings |
| Refunds | Manual checks, delays | AI verification + faster automated refunds |
| Verification | Physical verification common | Tech-based, physical only if high-risk |
- GST 1.0 Drawbacks and How GST 2.0 Fixes Them
- GST 2.0 introduces a single unified return for simplified filing, pre-filled GST returns based on e-invoicing, Digital ITC matching to curb fraud, and fast-track refunds for exporters and small firms. This creates a seamless, tech-driven compliance environment.
- By reducing slab complexity, eliminating cess overlaps, and digitizing compliance, GST 2.0 enhances transparency. This increases investor confidence, reduces litigation, and aligns India’s tax system with global practices directly improving business ease.
| GST 1.0 Issue | GST 2.0 Solution |
| Too many slabs | Rationalized slabs |
| Cess confusion | Direct 40% slab |
| Mismatched invoices | Automated credit matching |
| Delayed refunds | Faster processing |
| High MSME burden | Simplified returns |
GST 2.0 is progressive because it Makes essential items cheaper, Taxed luxury goods higher, Reduces compliance burden, Encourages consumption in core sectors, Enhances transparency and efficiency/
Timeline of GST 2.0 Implementation
| Year | Key Milestone |
| 2023 | e-invoice expansion; automated scrutiny notices |
| 2024 | AI-backed risk-based registration (Rule 14A) |
| 2025 | Simplified amendments & ITC overhaul (ITC 2.0) |
| 2026 | Introduction of new return system (expected) |
Major Reforms Under GST 2.0:
- Rule 14A – Simplified Registration Risk-based, Aadhaar authenticated & 3-day deemed approval
- ITC 2.0 : Automated Credit System Based on supplier e-invoice + return filing + payment track & Reduction of fake ITC claims
- E-Invoice Expansion Soon to cover almost all businesses, creating a real-time national invoice grid.
- GST Return Simplification: Government’s stated intent: A single return form integrating outward supply and tax payment.
- AI-driven GSTN : Automated scrutiny notices, risk flags for transactions, early warnings for mismatches.
In summary, GST 2.0 is an automated, AI-driven, real-time data GST ecosystem. Benefits of GST 2.0 are improved faster registration & refunds, real-time ITC validation, e-invoice integration, less paperwork, fewer notices, and risk-based compliance.
Impact on Middle Class and MSMEs
- Middle Class Benefits includes Cheaper essentials and healthcare, Lower cost of services, Affordable appliances and travel.
- MSME Benefits includes Fewer returns, reduced compliance cost, Faster refunds, Better cash-flow management. GST 2.0 is clearly more inclusive and business-friendly.
Now as above, the complete comparison of OLD GST vs NEW GST 2.0, i.e., the transition from GST 1.0 to GST 2.0 marks a major milestone in India’s tax reform journey. While GST 1.0 brought uniformity, it also introduced complexity. GST 2.0 addresses these gaps through Simplified slab structure, Higher taxes on luxury/sin goods, Lower taxes on essentials, Technology-driven compliance, Reduced costs for MSMEs and consumers. Overall, GST 2.0 is not just an update it is a modern, transparent, and growth-oriented tax system that strengthens India’s economy, supports businesses, and benefits consumers.